Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T94692
(Former ID: TTDR00225)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDL-R)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
LDL receptor
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
LDLR
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||||
| Function |
In order to be internalized, the receptor-ligand complexes must first cluster into clathrin-coated pits. Binds LDL, the major cholesterol-carrying lipoprotein of plasma, and transports it into cells by endocytosis.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Low density lipoprotein receptor
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MGPWGWKLRWTVALLLAAAGTAVGDRCERNEFQCQDGKCISYKWVCDGSAECQDGSDESQ
ETCLSVTCKSGDFSCGGRVNRCIPQFWRCDGQVDCDNGSDEQGCPPKTCSQDEFRCHDGK CISRQFVCDSDRDCLDGSDEASCPVLTCGPASFQCNSSTCIPQLWACDNDPDCEDGSDEW PQRCRGLYVFQGDSSPCSAFEFHCLSGECIHSSWRCDGGPDCKDKSDEENCAVATCRPDE FQCSDGNCIHGSRQCDREYDCKDMSDEVGCVNVTLCEGPNKFKCHSGECITLDKVCNMAR DCRDWSDEPIKECGTNECLDNNGGCSHVCNDLKIGYECLCPDGFQLVAQRRCEDIDECQD PDTCSQLCVNLEGGYKCQCEEGFQLDPHTKACKAVGSIAYLFFTNRHEVRKMTLDRSEYT SLIPNLRNVVALDTEVASNRIYWSDLSQRMICSTQLDRAHGVSSYDTVISRDIQAPDGLA VDWIHSNIYWTDSVLGTVSVADTKGVKRKTLFRENGSKPRAIVVDPVHGFMYWTDWGTPA KIKKGGLNGVDIYSLVTENIQWPNGITLDLLSGRLYWVDSKLHSISSIDVNGGNRKTILE DEKRLAHPFSLAVFEDKVFWTDIINEAIFSANRLTGSDVNLLAENLLSPEDMVLFHNLTQ PRGVNWCERTTLSNGGCQYLCLPAPQINPHSPKFTCACPDGMLLARDMRSCLTEAEAAVA TQETSTVRLKVSSTAVRTQHTTTRPVPDTSRLPGATPGLTTVEIVTMSHQALGDVAGRGN EKKPSSVRALSIVLPIVLLVFLCLGVFLLWKNWRLKNINSINFDNPVYQKTTEDEVHICH NQDGYSYPSRQMVSLEDDVA Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T49PL1 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 1 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Porfimer Sodium | Drug Info | Approved | Non-small-cell lung cancer | [2] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Modulator | [+] 1 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Porfimer Sodium | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| Inhibitor | [+] 1 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Alpha-D-Mannose | Drug Info | [3] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: 12-TUNGSTOPHOSPHATE | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Extracellular domain of the LDL receptor | PDB:1N7D | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 3.70 Å | Mutation | Yes | [4] |
| PDB Sequence |
SVTCKSGDFS
53 CGGNRCIPQF65 WRCDGQVDCN76 GSDEQGCPPK86 TCSQDEFRCH96 DGRQFVCDSD 110 RDCLDGSDEA120 SCPVLTCGPA130 SFQCNSSTCI140 PQLWACDNDP150 DCEDGSDEWP 160 QRCRGLYVFQ170 GDSSPCSAFE180 FHCLSGECIH190 SSWRCDGGPD200 CKDKSDEENC 210 AVATCRPDEF220 QCSDGNCIHG230 SRQCDREYDC240 KDMSDEVGCV250 NVTLCEGPNK 260 FKCHSGECIT270 LDKVCNMARD280 CRDWSDEPIK290 ECGTNECLDN300 NGGCSHVCND 310 LKIGYECLCP320 DGFQLVAQRR330 CEDIDECQDP340 DTCSQLCVNL350 EGGYKCQCEE 360 GFQLDPHTKA370 CKAVGSIAYL380 FFTNRHERKM391 TLDRSEYTSL401 IPNLRNVVAL 411 DTEVASNRIY421 WSDLSQRMIC431 STQLDRAHGS442 SYDTVISRDI452 PDGLAVDWIH 464 SNIYWTDSVL474 GTVSVADTKG484 VKRKTLFREQ494 GSKPRAIVVD504 PVHGFMYWTD 514 WGTPAKIKKG524 GLNGVDIYSL534 VTENIQWPNG544 ITLDLLSGRL554 YWVDSKLHSI 564 SSIDVNGGNR574 KTILEDEKRL584 AHPFSLAVFE594 DKVFWTDIIN604 EAIFSANRLT 614 GSDVNLLAEN624 LLSPEDMVLF634 HQLTQPRGVN644 WCERTTLSNG654 GCQYLCLPAP 664 QINPHSPKFT674 CACPDGMLLA684 RDMRSCLTE
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
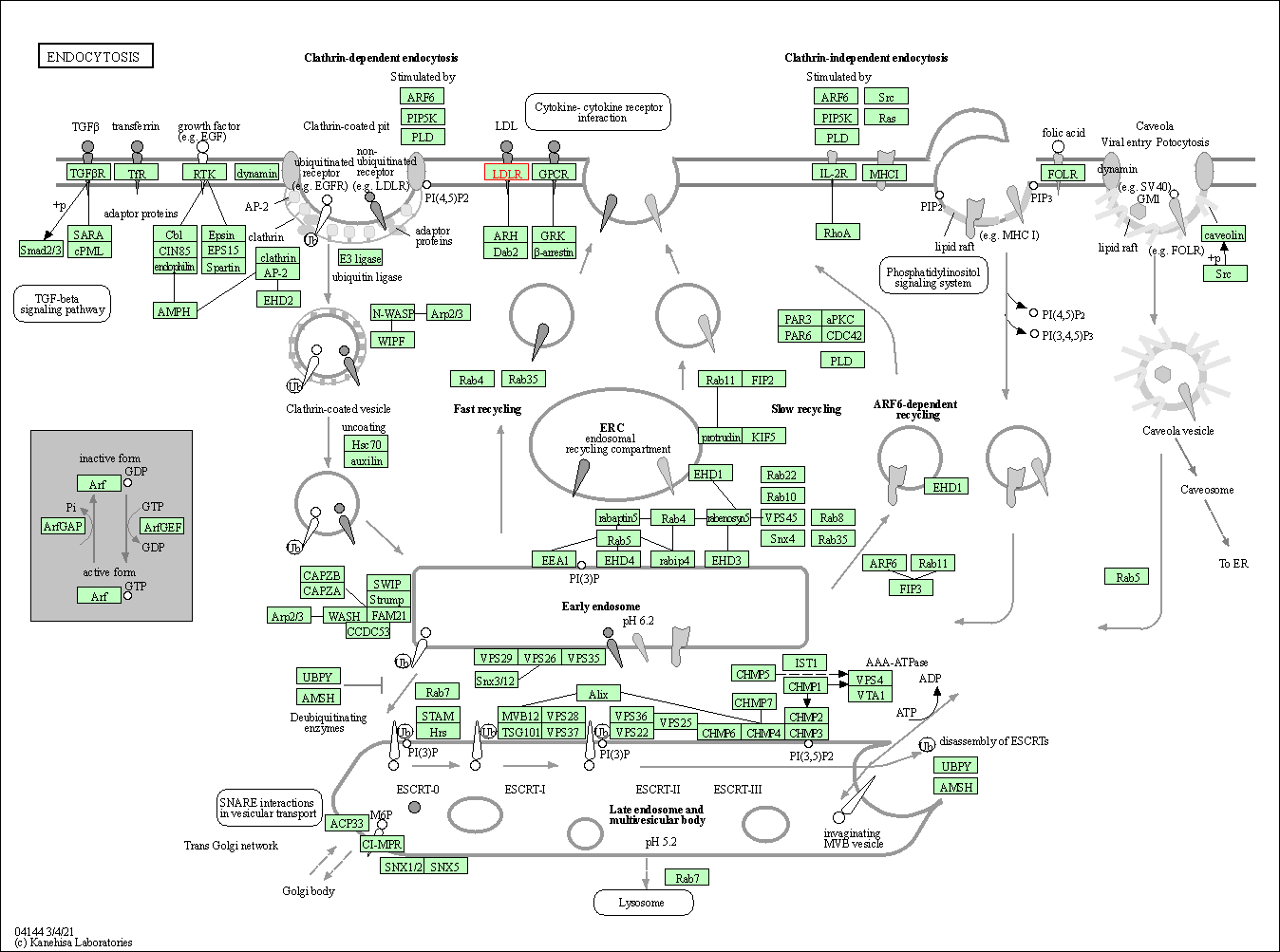
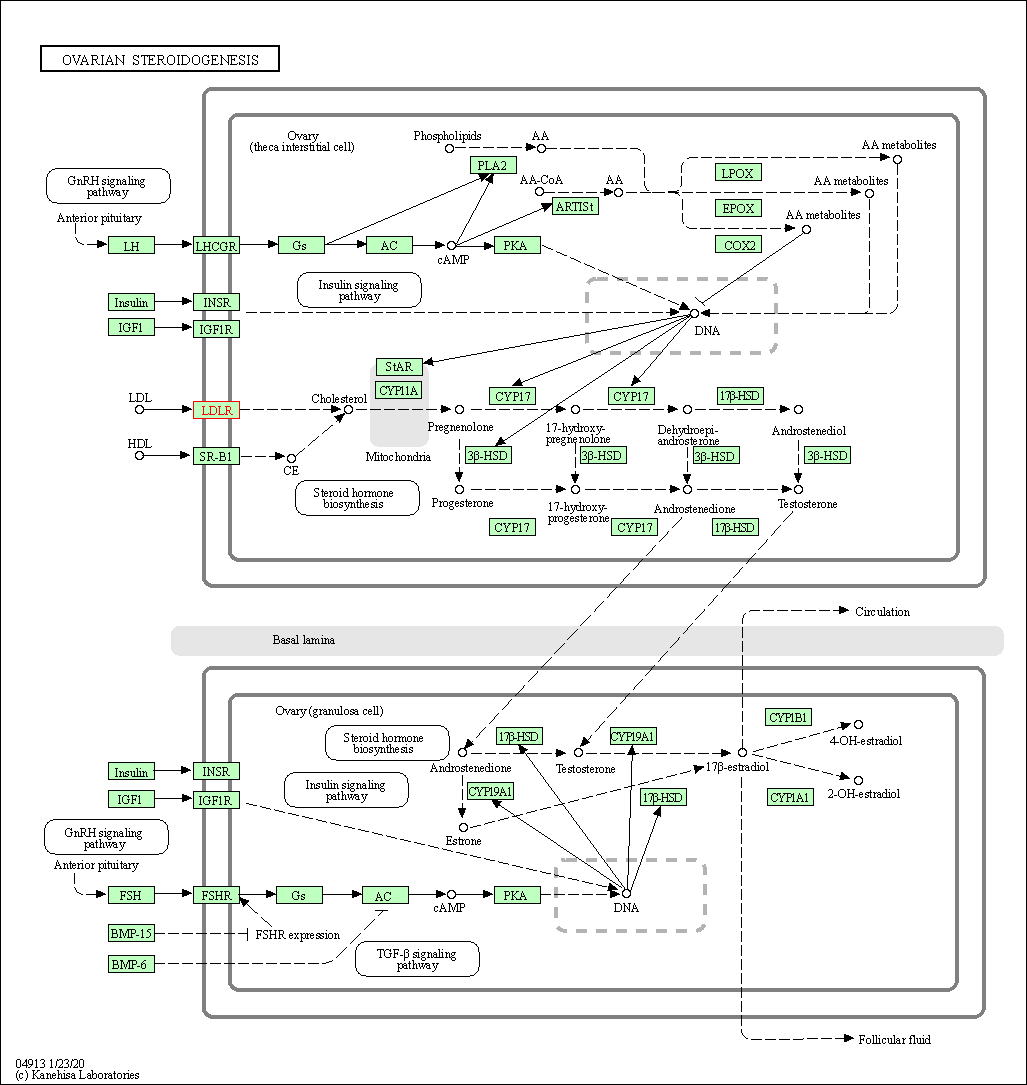
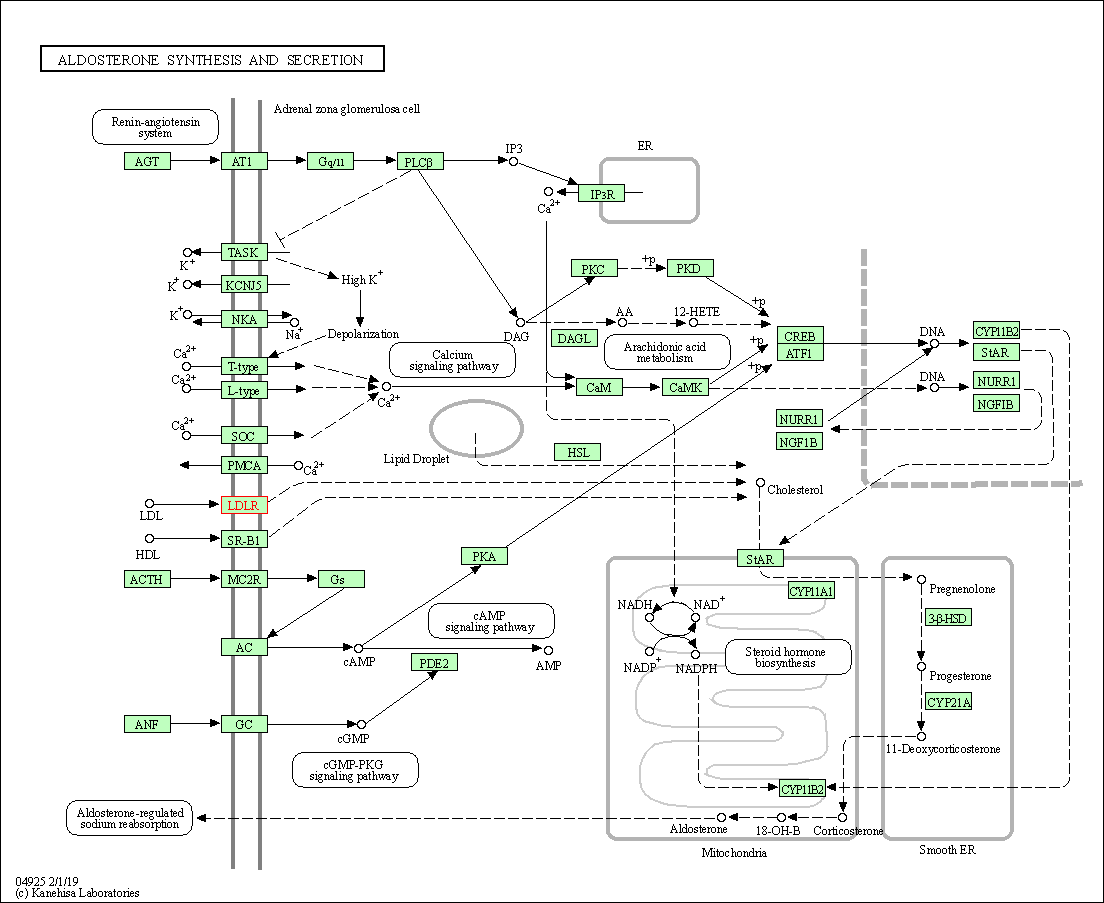
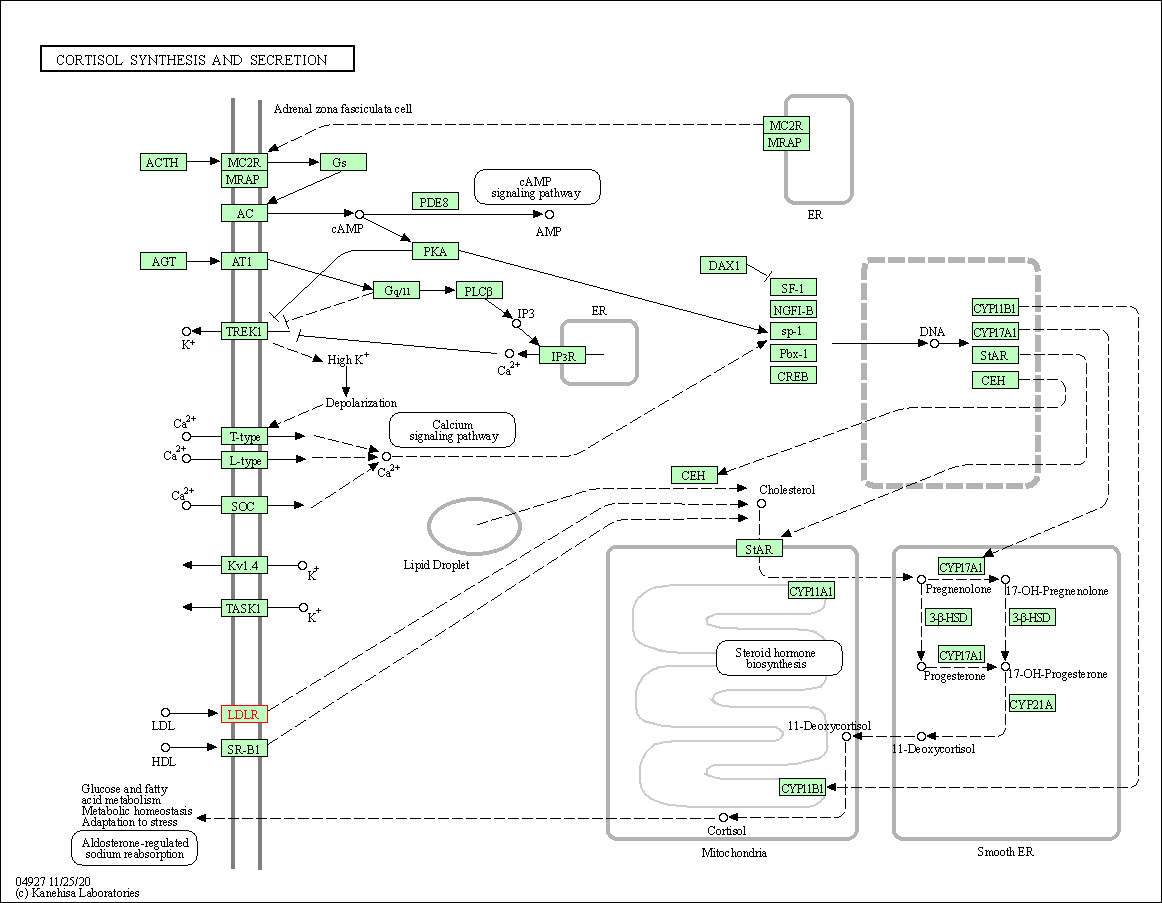
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Endocytosis | hsa04144 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Ovarian steroidogenesis | hsa04913 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Aldosterone synthesis and secretion | hsa04925 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cortisol synthesis and secretion | hsa04927 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
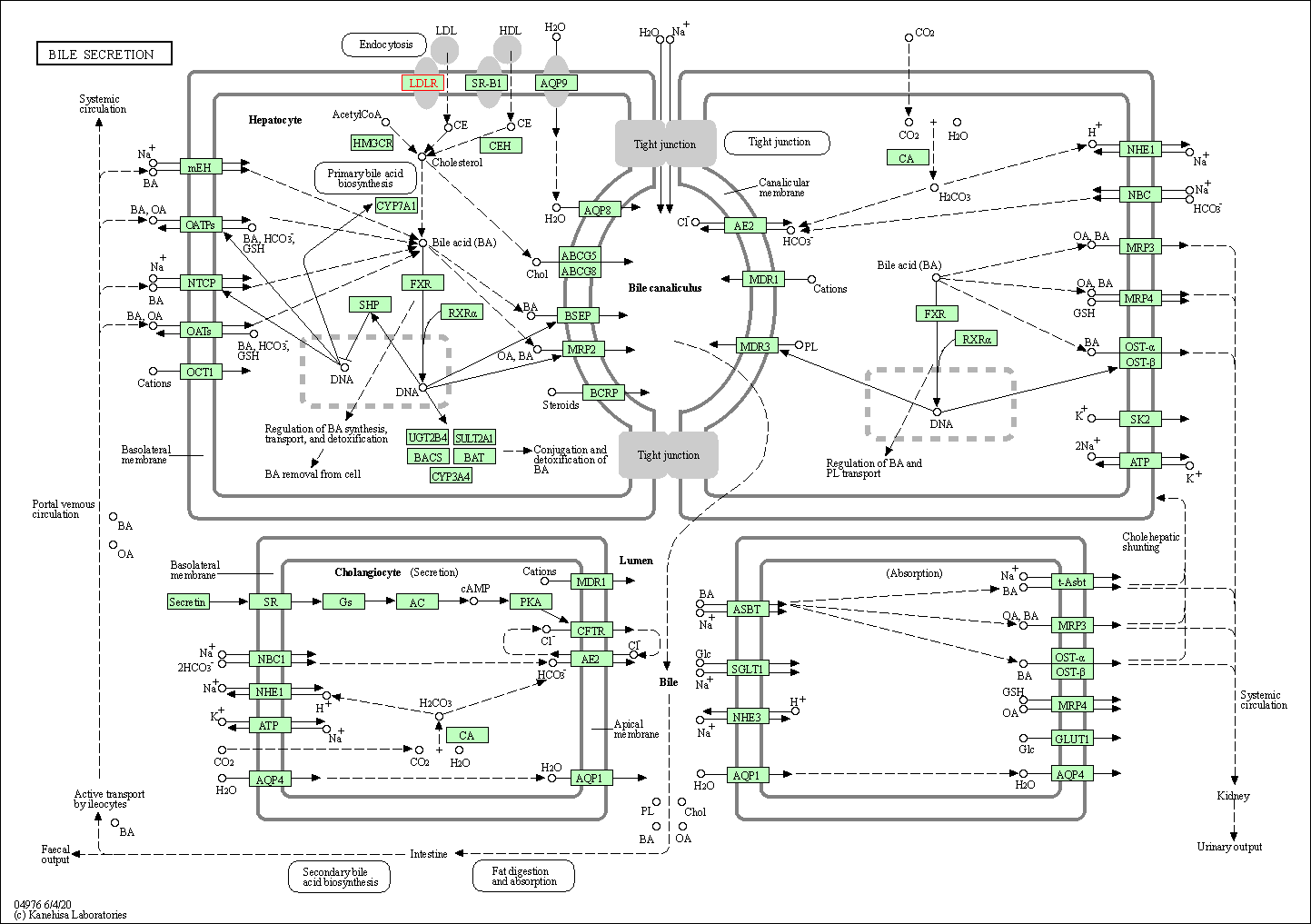
| Bile secretion | hsa04976 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
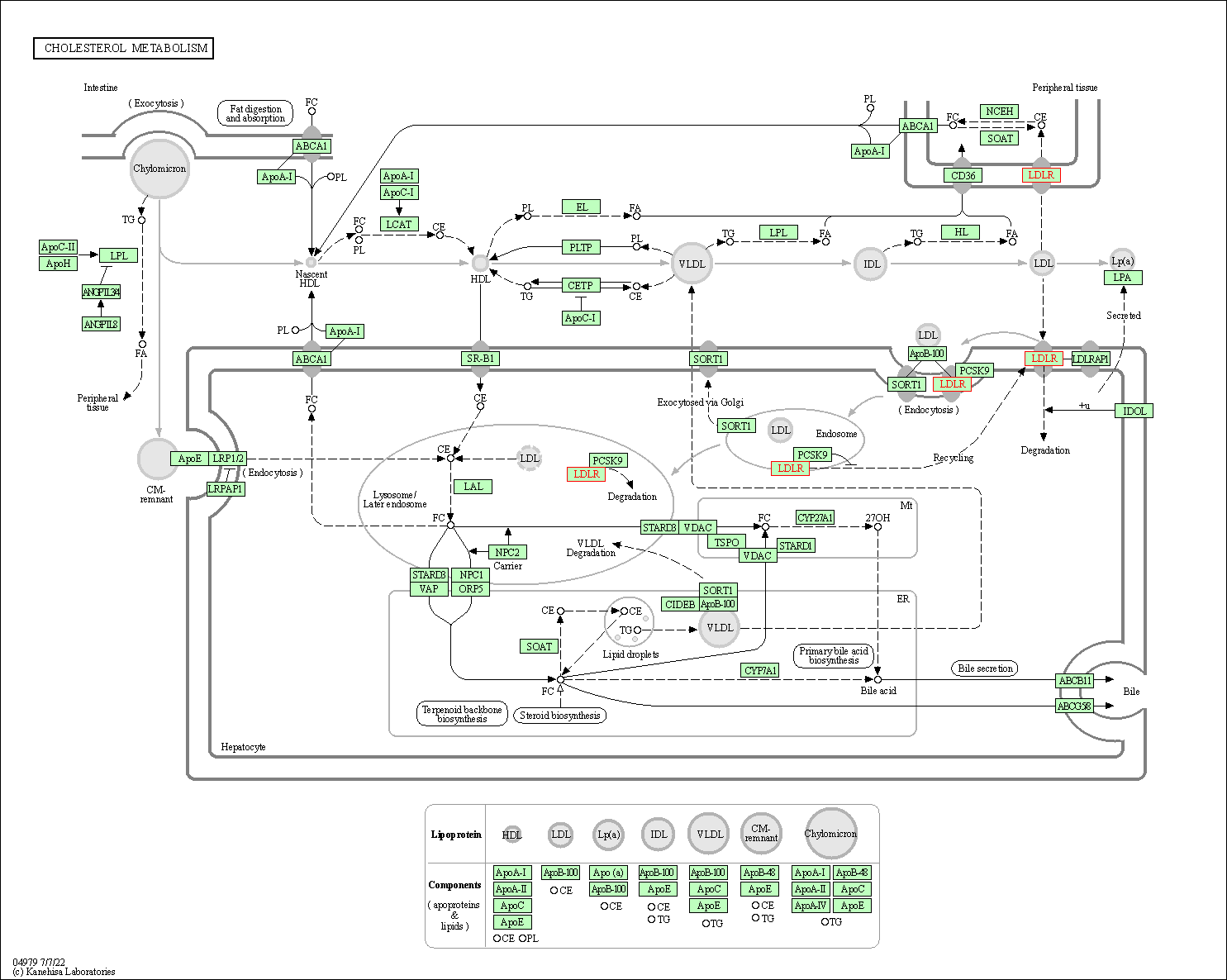
| Cholesterol metabolism | hsa04979 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 12 | Degree centrality | 1.29E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 3.97E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.11E-01 | Radiality | 1.37E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.36E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 1.52E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.40E-01 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-regulating Transcription Factors | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 5 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Endocytosis | |||||
| 2 | Ovarian steroidogenesis | |||||
| 3 | Bile secretion | |||||
| 4 | Toxoplasmosis | |||||
| 5 | Hepatitis C | |||||
| NetPath Pathway | [+] 2 NetPath Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | FSH Signaling Pathway | |||||
| 2 | IL2 Signaling Pathway | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 3 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | LDL-mediated lipid transport | |||||
| 2 | Chylomicron-mediated lipid transport | |||||
| 3 | Retinoid metabolism and transport | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 12 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | DNA Damage Response (only ATM dependent) | |||||
| 2 | Statin Pathway | |||||
| 3 | Wnt Signaling Pathway | |||||
| 4 | Wnt Signaling Pathway and Pluripotency | |||||
| 5 | Visual phototransduction | |||||
| 6 | Lipid digestion, mobilization, and transport | |||||
| 7 | Oncostatin M Signaling Pathway | |||||
| 8 | SREBF and miR33 in cholesterol and lipid homeostasis | |||||
| 9 | SREBP signalling | |||||
| 10 | Folate Metabolism | |||||
| 11 | Vitamin B12 Metabolism | |||||
| 12 | Selenium Micronutrient Network | |||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | |||||
| REF 2 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 3 | How many drug targets are there Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. | |||||
| REF 4 | Structure of the LDL receptor extracellular domain at endosomal pH. Science. 2002 Dec 20;298(5602):2353-8. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

