Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T97589
(Former ID: TTDR00968)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (MAP3K5)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 5; MEKK5; MEKK 5; MEK kinase 5; MAPKKK5; MAPK/ERK kinase kinase 5; ASK1; ASK-1
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
MAP3K5
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Chronic kidney disease [ICD-11: GB61] | |||||
| 2 | Pulmonary hypertension [ICD-11: BB01] | |||||
| Function |
Plays an important role in the cascades of cellular responses evoked by changes in the environment. Mediates signaling for determination of cell fate such as differentiation and survival. Plays a crucial role in the apoptosis signal transduction pathway through mitochondria-dependent caspase activation. MAP3K5/ASK1 is required for the innate immune response, which is essential for host defense against a wide range of pathogens. Mediates signal transduction of various stressors like oxidative stress as well as by receptor-mediated inflammatory signals, such as the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) or lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Once activated, acts as an upstream activator of the MKK/JNK signal transduction cascade and the p38 MAPK signal transduction cascade through the phosphorylation and activation of several MAP kinase kinases like MAP2K4/SEK1, MAP2K3/MKK3, MAP2K6/MKK6 and MAP2K7/MKK7. These MAP2Ks in turn activate p38 MAPKs and c-jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs). Both p38 MAPK and JNKs control the transcription factors activator protein-1 (AP-1). Serine/threonine kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.25
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MSTEADEGITFSVPPFAPSGFCTIPEGGICRRGGAAAVGEGEEHQLPPPPPGSFWNVESA
AAPGIGCPAATSSSSATRGRGSSVGGGSRRTTVAYVINEASQGQLVVAESEALQSLREAC ETVGATLETLHFGKLDFGETTVLDRFYNADIAVVEMSDAFRQPSLFYHLGVRESFSMANN IILYCDTNSDSLQSLKEIICQKNTMCTGNYTFVPYMITPHNKVYCCDSSFMKGLTELMQP NFELLLGPICLPLVDRFIQLLKVAQASSSQYFRESILNDIRKARNLYTGKELAAELARIR QRVDNIEVLTADIVINLLLSYRDIQDYDSIVKLVETLEKLPTFDLASHHHVKFHYAFALN RRNLPGDRAKALDIMIPMVQSEGQVASDMYCLVGRIYKDMFLDSNFTDTESRDHGASWFK KAFESEPTLQSGINYAVLLLAAGHQFESSFELRKVGVKLSSLLGKKGNLEKLQSYWEVGF FLGASVLANDHMRVIQASEKLFKLKTPAWYLKSIVETILIYKHFVKLTTEQPVAKQELVD FWMDFLVEATKTDVTVVRFPVLILEPTKIYQPSYLSINNEVEEKTISIWHVLPDDKKGIH EWNFSASSVRGVSISKFEERCCFLYVLHNSDDFQIYFCTELHCKKFFEMVNTITEEKGRS TEEGDCESDLLEYDYEYDENGDRVVLGKGTYGIVYAGRDLSNQVRIAIKEIPERDSRYSQ PLHEEIALHKHLKHKNIVQYLGSFSENGFIKIFMEQVPGGSLSALLRSKWGPLKDNEQTI GFYTKQILEGLKYLHDNQIVHRDIKGDNVLINTYSGVLKISDFGTSKRLAGINPCTETFT GTLQYMAPEIIDKGPRGYGKAADIWSLGCTIIEMATGKPPFYELGEPQAAMFKVGMFKVH PEIPESMSAEAKAFILKCFEPDPDKRACANDLLVDEFLKVSSKKKKTQPKLSALSAGSNE YLRSISLPVPVLVEDTSSSSEYGSVSPDTELKVDPFSFKTRAKSCGERDVKGIRTLFLGI PDENFEDHSAPPSPEEKDSGFFMLRKDSERRATLHRILTEDQDKIVRNLMESLAQGAEEP KLKWEHITTLIASLREFVRSTDRKIIATTLSKLKLELDFDSHGISQVQVVLFGFQDAVNK VLRNHNIKPHWMFALDSIIRKAVQTAITILVPELRPHFSLASESDTADQEDLDVEDDHEE QPSNQTVRRPQAVIEDAVATSGVSTLSSTVSHDSQSAHRSLNVQLGRMKIETNRLLEELV RKEKELQALLHRAIEEKDQEIKHLKLKSQPIEIPELPVFHLNSSGTNTEDSELTDWLRVN GADEDTISRFLAEDYTLLDVLYYVTRDDLKCLRLRGGMLCTLWKAIIDFRNKQT Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T03YAI | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 2 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | GS-4977 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Diabetic nephropathy | [2] | |
| 2 | GS-4997 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Diabetic nephropathy | [3] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 4 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | GS-4977 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | GS-4997 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 3 | MSC2032964A | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 4 | PMID23147077C10 | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: GS-4997 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | ASK1 kinase domain in complex with GS-4997 | PDB:6OYT | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.82 Å | Mutation | No | [6] |
| PDB Sequence |
MESDLLEYDY
675 EYDENGDRVV685 LGKGTYGIVY695 AGRDLSNQVR705 IAIKEIPERQ720 PLHEEIALHK 730 HLKHKNIVQY740 LGSFSENGFI750 KIFMEQVPGG760 SLSALLRSKW770 GPLKDNEQTI 780 GFYTKQILEG790 LKYLHDNQIV800 HRDIKGDNVL810 INTYSGVLKI820 SDFGTSKRLG 859 KAADIWSLGC869 TIIEMATGKP879 PVHPEIPESM907 SAEAKAFILK917 CFEPDPDKRA 927 CANDLLVDEF937 LK
|
|||||
|
|
LEU686
2.977
GLY687
3.570
LYS688
3.665
GLY689
3.660
VAL694
3.496
ALA707
3.564
LYS709
3.335
GLU725
4.958
VAL738
4.080
MET754
3.819
GLU755
3.311
GLN756
3.371
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: Staurosporine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal Structures of Ask1-inhibitor Complexes | PDB:4BF2 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.11 Å | Mutation | Yes | [7] |
| PDB Sequence |
LEYDYEYDEN
680 GDRVVLGKGT690 YGIVYAGRDL700 SNQVRIAIKE710 IPEEEIALHK730 HLKHKNIVQY 740 LGSFSENGFI750 KIFMEQVPGG760 SLSALLRSKW770 GPLKDNEQTI780 GFYTKQILEG 790 LKYLHDNQIV800 HRDIKGDNVL810 INTYSGVLKI820 SDFGTSKRLA830 EEFTGTLQYM 846 APEIIDKGPR856 GYGKAADIWS866 LGCTIIEMAT876 GKPPFYELGE886 PQAAMFKVGM 896 FKVHPEIPES906 MSAEAKAFIL916 KCFEPDPDKR926 ACANDLLVDE936 FLK |
|||||
|
|
LEU686
3.347
GLY687
3.246
LYS688
3.405
GLY689
3.742
VAL694
3.635
ALA707
3.370
LYS709
4.210
VAL738
3.859
MET754
3.746
GLU755
2.773
GLN756
3.371
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
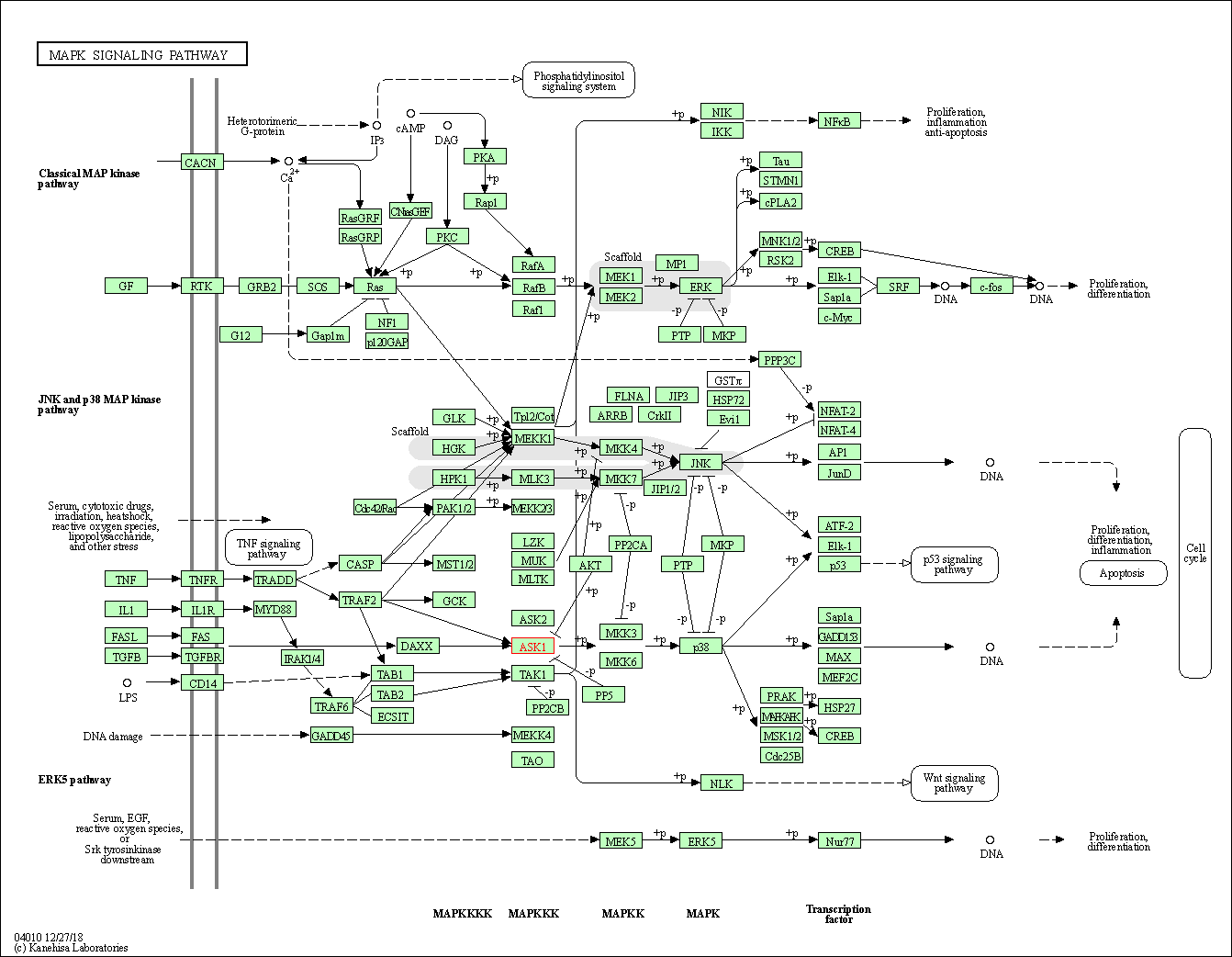
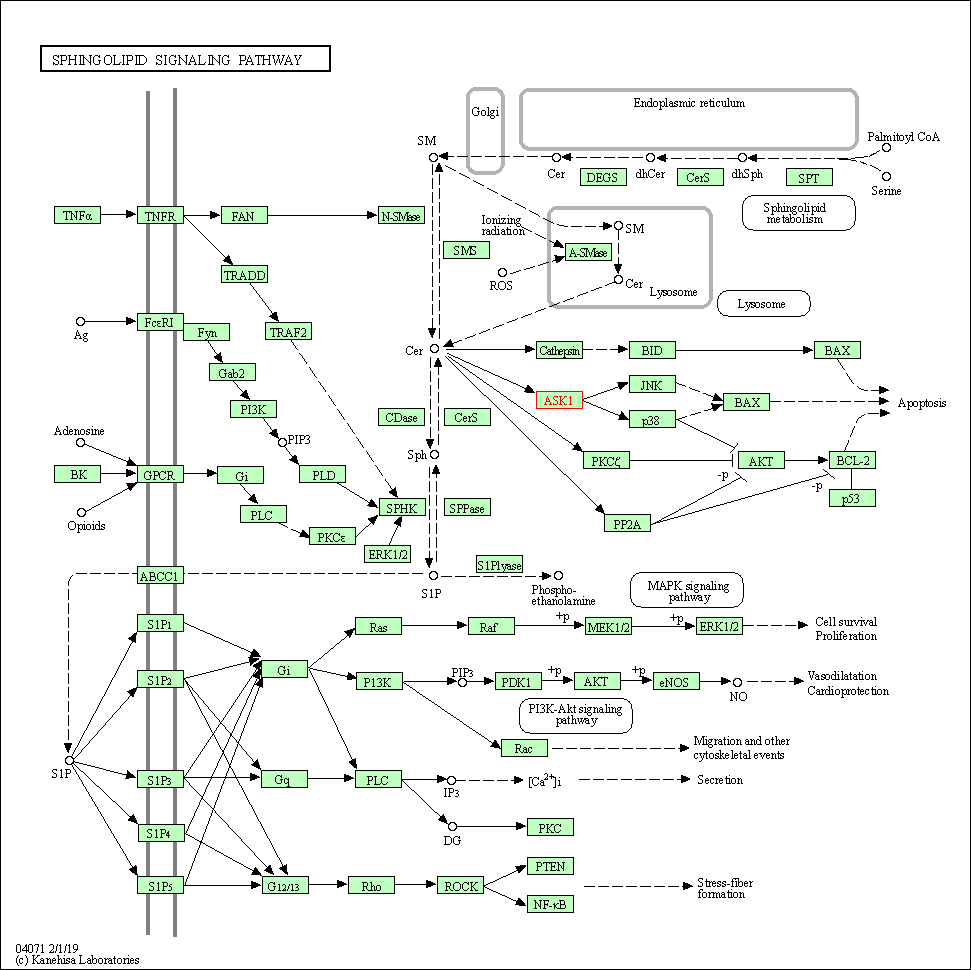
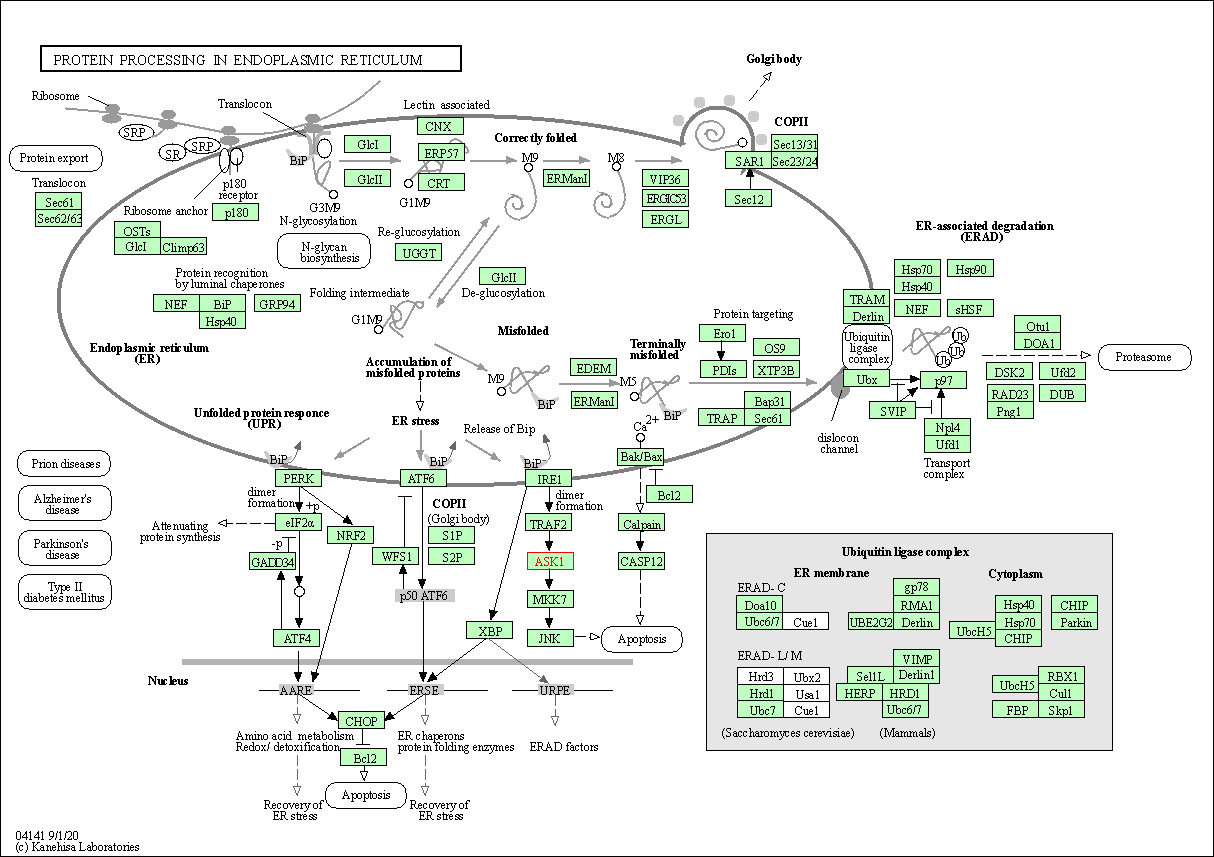
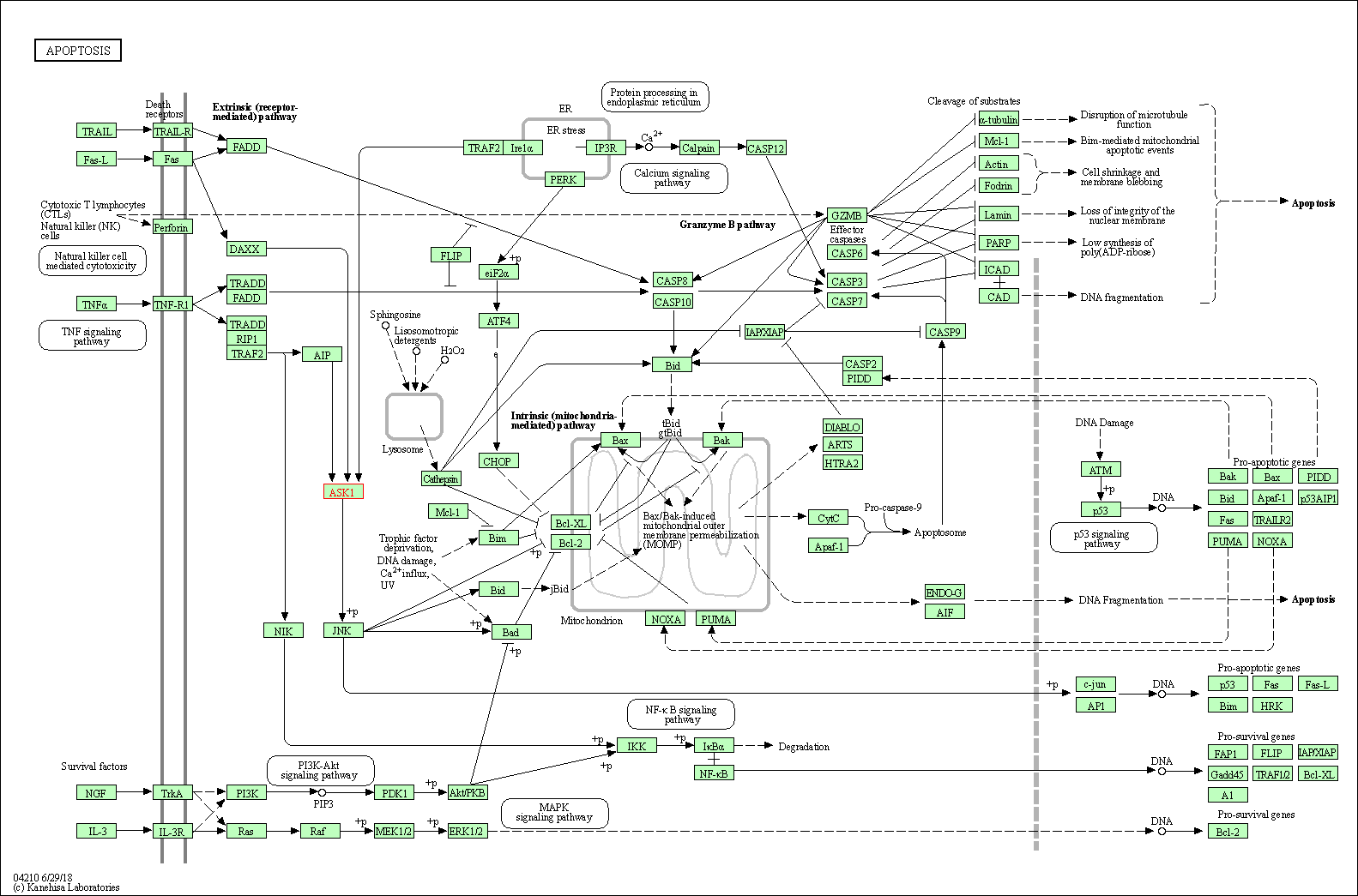
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Sphingolipid signaling pathway | hsa04071 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum | hsa04141 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Genetic Information Processing => Folding, sorting and degradation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
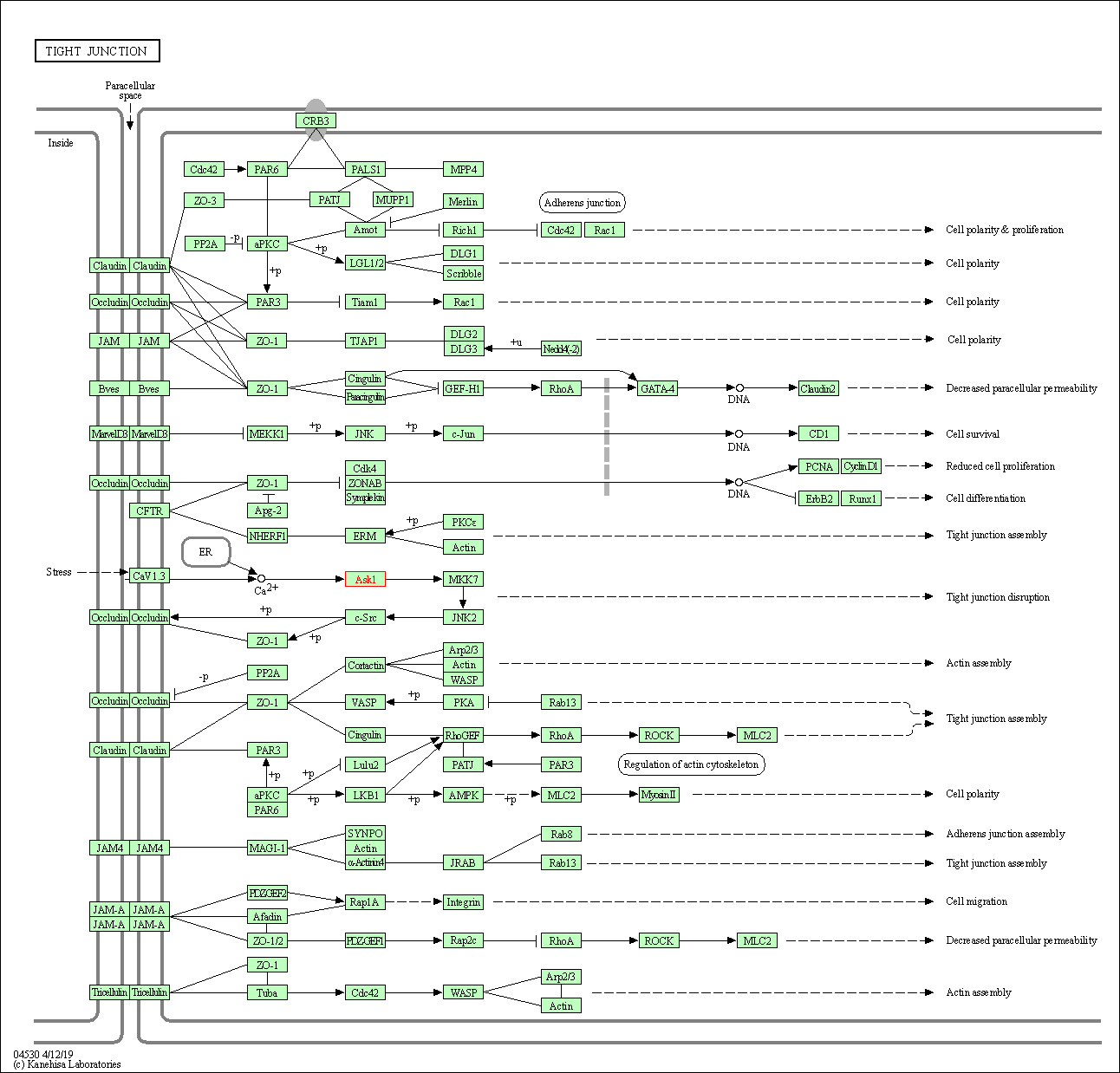
| Tight junction | hsa04530 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
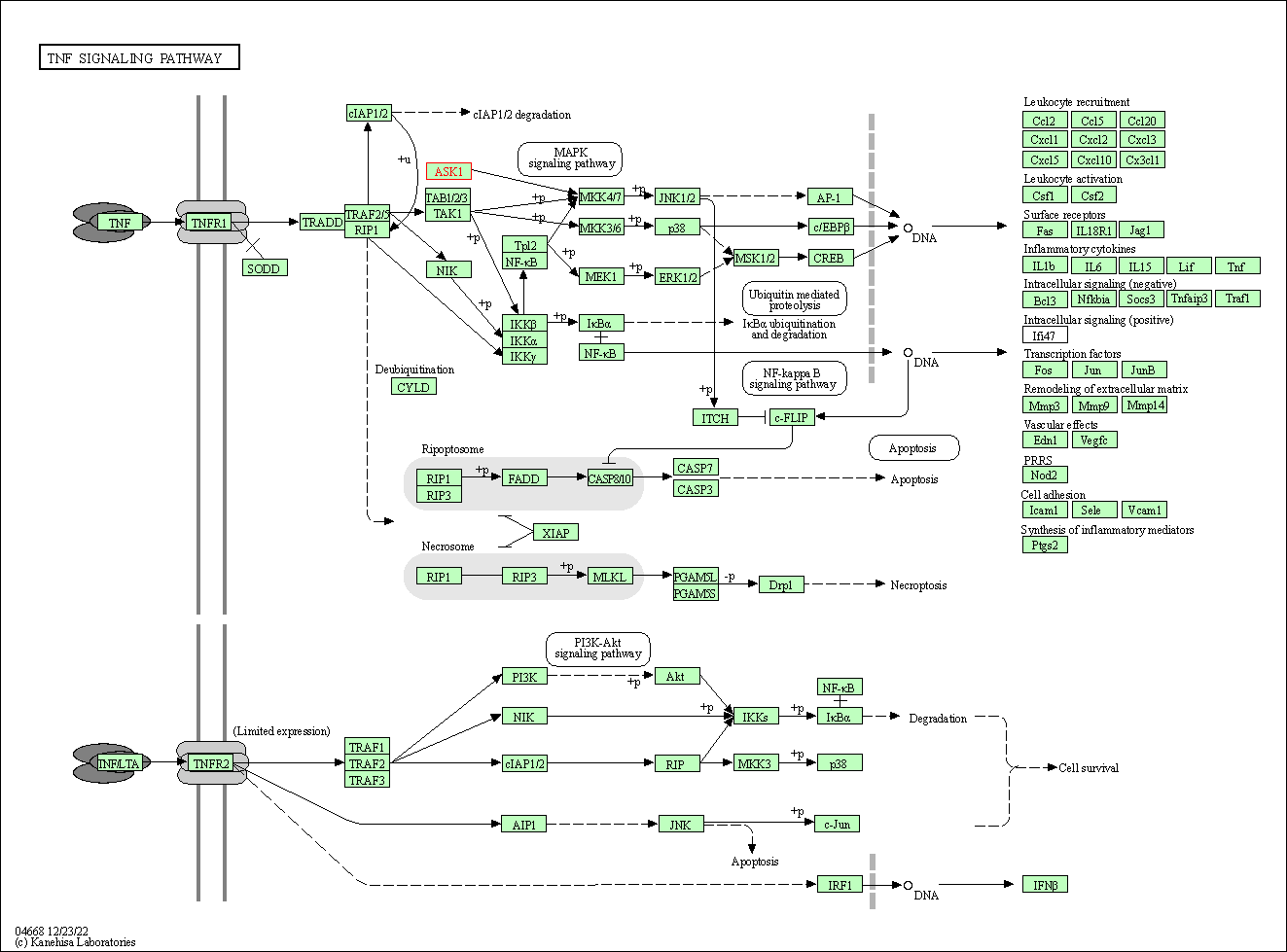
| TNF signaling pathway | hsa04668 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
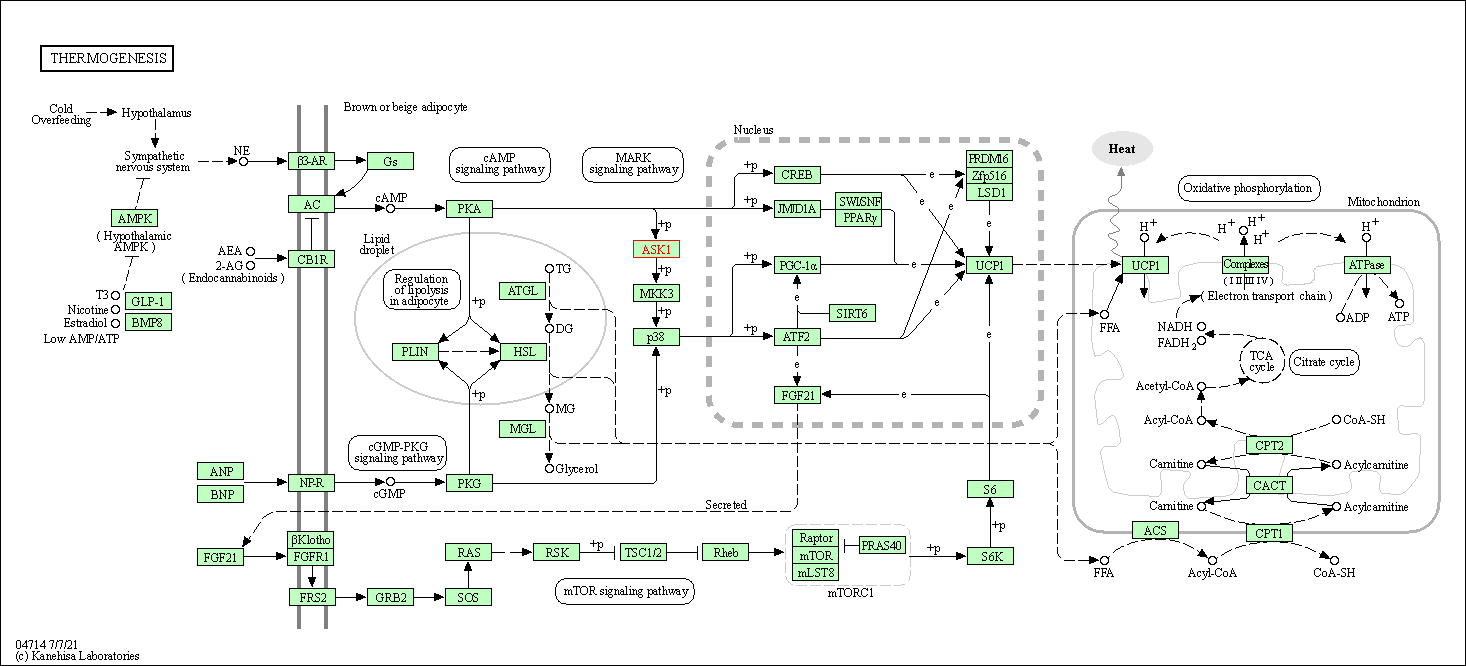
| Thermogenesis | hsa04714 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Environmental adaptation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
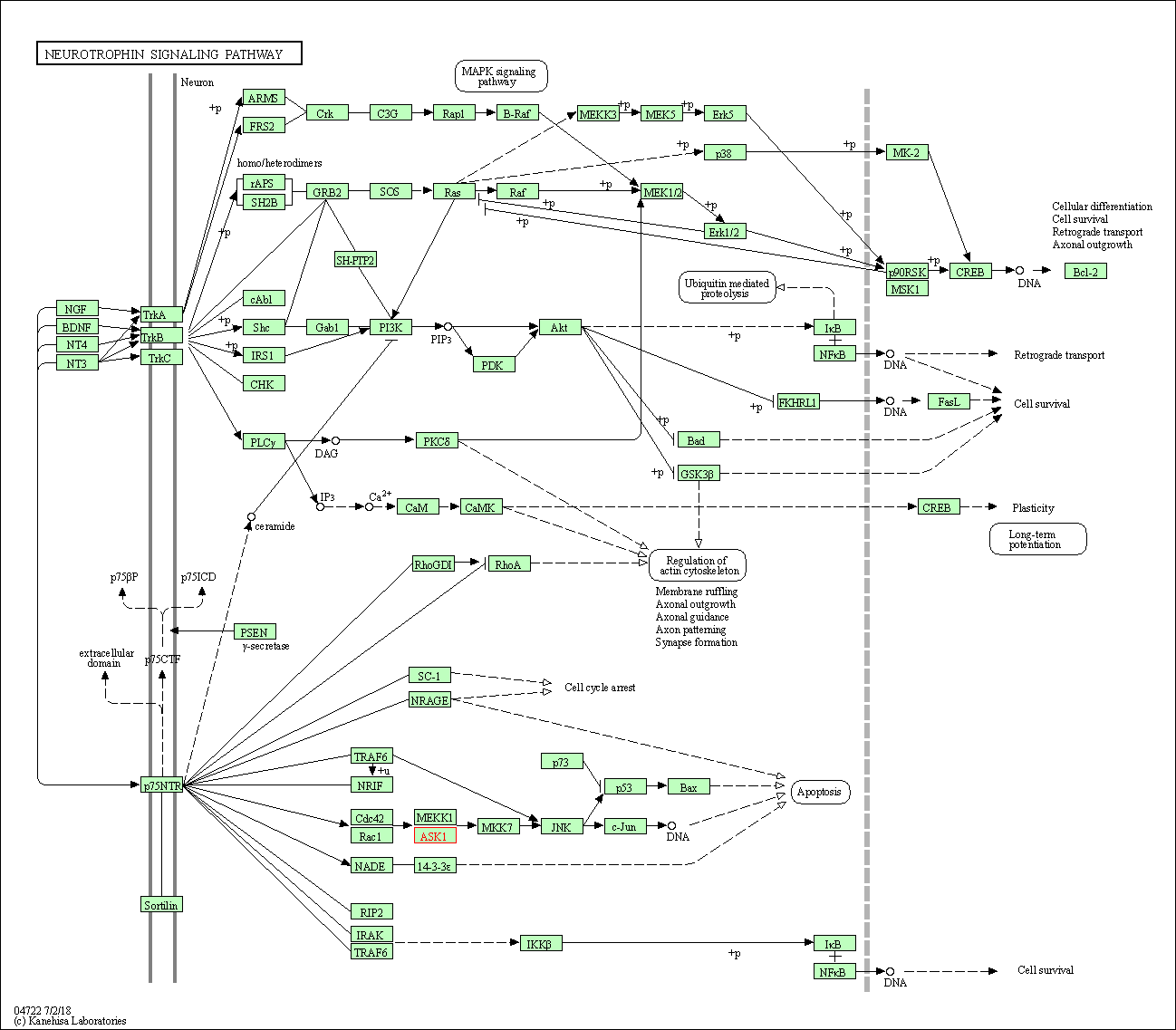
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | hsa04722 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 30 | Degree centrality | 3.22E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 2.24E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.46E-01 | Radiality | 1.43E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.29E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.24E+01 | Topological coefficient | 6.29E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Design of a phase 2 clinical trial of an ASK1 inhibitor, GS-4997, in patients with diabetic kidney disease. Nephron. 2015;129(1):29-33. | |||||
| REF 2 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800040265) | |||||
| REF 3 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02234141) GS-4997 in Adults With Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 4 | Regulation of the severity of neuroinflammation and demyelination by TLR-ASK1-p38 pathway. EMBO Mol Med. 2010 Dec;2(12):504-15. | |||||
| REF 5 | Design and biological evaluation of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines as novel and potent ASK1 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 Dec 15;22(24):7326-9. | |||||
| REF 6 | Rational Design and Optimization of a Novel Class of Macrocyclic Apoptosis Signal-Regulating Kinase 1 Inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2019 Dec 12;62(23):10740-10756. | |||||
| REF 7 | Crystal structures of ASK1-inhibtor complexes provide a platform for structure-based drug design. Protein Sci. 2013 Aug;22(8):1071-7. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

