Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T98062
(Former ID: TTDC00099)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Glycogen phosphorylase muscle form (GP)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Muscle glycogen phosphorylase; Glycogen phosphorylase, muscle form; Glycogen phosphorylase b
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
PYGM
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Patented-recorded target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Metabolic disorder [ICD-11: 5C50-5D2Z] | |||||
| Function |
Enzymes from different sources differ in their regulatory mechanisms and in their natural substrates. However, all known phosphorylases share catalytic and structural properties. Phosphorylase is an important allosteric enzyme in carbohydrate metabolism.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Glycosyltransferases
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.4.1.1
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MSRPLSDQEKRKQISVRGLAGVENVTELKKNFNRHLHFTLVKDRNVATPRDYYFALAHTV
RDHLVGRWIRTQQHYYEKDPKRIYYLSLEFYMGRTLQNTMVNLALENACDEATYQLGLDM EELEEIEEDAGLGNGGLGRLAACFLDSMATLGLAAYGYGIRYEFGIFNQKISGGWQMEEA DDWLRYGNPWEKARPEFTLPVHFYGHVEHTSQGAKWVDTQVVLAMPYDTPVPGYRNNVVN TMRLWSAKAPNDFNLKDFNVGGYIQAVLDRNLAENISRVLYPNDNFFEGKELRLKQEYFV VAATLQDIIRRFKSSKFGCRDPVRTNFDAFPDKVAIQLNDTHPSLAIPELMRILVDLERM DWDKAWDVTVRTCAYTNHTVLPEALERWPVHLLETLLPRHLQIIYEINQRFLNRVAAAFP GDVDRLRRMSLVEEGAVKRINMAHLCIAGSHAVNGVARIHSEILKKTIFKDFYELEPHKF QNKTNGITPRRWLVLCNPGLAEVIAERIGEDFISDLDQLRKLLSFVDDEAFIRDVAKVKQ ENKLKFAAYLEREYKVHINPNSLFDIQVKRIHEYKRQLLNCLHVITLYNRIKREPNKFFV PRTVMIGGKAAPGYHMAKMIIRLVTAIGDVVNHDPAVGDRLRVIFLENYRVSLAEKVIPA ADLSEQISTAGTEASGTGNMKFMLNGALTIGTMDGANVEMAEEAGEENFFIFGMRVEDVD KLDQRGYNAQEYYDRIPELRQVIEQLSSGFFSPKQPDLFKDIVNMLMHHDRFKVFADYED YIKCQEKVSALYKNPREWTRMVIRNIATSGKFSSDRTIAQYAREIWGVEPSRQRLPAPDE AI Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | URSOLIC ACID | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Metabolic syndrome x | [2] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 1 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | JTT-651 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 1 | Type-2 diabetes | [3] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 43 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | URSOLIC ACID | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 2 | JTT-651 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 3 | 1-D-glucopyranosyl cytosine | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 4 | 1-D-glucopyranosyl uracil | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 5 | 1-Deoxy-1-Methoxycarbamido-Beta-D-Glucopyranose | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 6 | 1-N-Acetyl-Beta-D-Glucosamine | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 7 | 2-Deoxy-Glucose-6-Phosphate | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 8 | 2-Hydroxyiminoolean-12-en-28-oic acid | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 9 | 2-Hydroxyiminours-12-en-28-oic acid | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 10 | 2-isooleanolic acid | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 11 | 2-isoursolic acid | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 12 | 2-Oxoolean-12-en-28-oic acid | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 13 | 23-hydroxybetulinic acid | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 14 | 2alpha-Hydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 15 | 2alpha-Hydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 16 | 2beta,3alpha-dihydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 17 | 2beta,3alpha-dihydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 18 | 3alpha-Hydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic Acid | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 19 | 4-{2-[(3-Nitrobenzoyl)Amino]Phenoxy}Phthalic Acid | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 20 | Acurea | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 21 | Alpha-D-Glucopyranosyl-2-Carboxylic Acid Amide | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 22 | Alpha-D-Glucose-1-Phosphate | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 23 | Alpha-D-Glucose-6-Phosphate | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 24 | ASIATIC ACID | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 25 | Benzyl 2-hydroxyiminoolean-12-en-28-oate | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 26 | Beta-D-Glucopyranose Spirohydantoin | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 27 | Beta-D-Glucose | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 28 | BETULIN | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 29 | C-(1-Azido-Alpha-D-Glucopyranosyl) Formamide | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 30 | C-(1-Hydrogyl-Beta-D-Glucopyranosyl) Formamide | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 31 | Ethyl 2beta-hydroxyolean-12-en-28-oate | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 32 | Fluoro-Phosphite Ion | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 33 | Heptulose-2-Phosphate | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 34 | Indirubin-5-sulfonate | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 35 | Inosinic Acid | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 36 | L-serine-O-phosphate | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 37 | N'-Pyridoxyl-Lysine-5'-Monophosphate | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 38 | N-Acetyl-N'-Beta-D-Glucopyranosyl Urea | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 39 | N-Benzoyl-N'-Beta-D-Glucopyranosyl Urea | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 40 | N-Butyl 2beta-hydroxyolean-12-en-28-oate | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 41 | Nojirimycine Tetrazole | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 42 | OLEANOLIC_ACID | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 43 | Oleanonic acid | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Adenine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal Structure of Human Muscle Glycogen Phosphorylase a with AMP and Glucose | PDB:1Z8D | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.30 Å | Mutation | Yes | [12] |
| PDB Sequence |
RPLSDQEKRK
11 QIVRGVENVT25 ELKKNFNRHL35 HFTLVKDRNV45 ATPRDYYFAL55 AHTVRDHLVG 65 RWIRTQQHYY75 EKDPKRIYYL85 SLEFYMGRTL95 QNTMVNLALE105 NACDEATYQL 115 GLDMEELEEI125 EEDAGLGNGG135 LGRLAACFLD145 SMATLGLAAY155 GYGIRYEFGI 165 FNQKISGGWQ175 MEEADDWLRY185 GNPWEKARPE195 FTLPVHFYGH205 VEHTSQGAKW 215 VDTQVVLAMP225 YDTPVPGYRN235 NVVNTMRLWS245 AKAPGYIQAV266 LDRNLAENIS 276 RVLYPNDNFF286 EGKELRLKQE296 YFVVAATLQD306 IIRRFKSSKF316 GCRDPVRTNF 326 DAFPDKVAIQ336 LNDTHPSLAI346 PELMRILVDL356 ERMDWDKAWD366 VTVRTCAYTN 376 HTVLPEALER386 WPVHLLETLL396 PRHLQIIYEI406 NQRFLNRVAA416 AFPGDVDRLR 426 RMSLVEEGAV436 KRINMAHLCI446 AGSHAVNGVA456 RIHSEILKKT466 IFKDFYELEP 476 HKFQNKTNGI486 TPRRWLVLCN496 PGLAEVIAER506 IGEDFISDLD516 QLRKLLSFVD 526 DEAFIRDVAK536 VKQENKLKFA546 AYLEREYKVH556 INPNSLFDIQ566 VKRIHEYKRQ 576 LLNCLHVITL586 YNRIKREPNK596 FFVPRTVMIG606 GKAAPGYHMA616 KMIIRLVTAI 626 GDVVNHDPAV636 GDRLRVIFLE646 NYRVSLAEKV656 IPAADLSEQI666 STAGTEASGT 676 GNMFMLNGAL687 TIGTMDGANV697 EMAEEAGEEN707 FFIFGMRVED717 VDKLDQRGYN 727 AQEYYDRIPE737 LRQVIEQLSS747 GFFSPKQPDL757 FKDIVNMLMH767 HDRFKVFADY 777 EDYIKCQEKV787 SALYKNPREW797 TRMVIRNIAT807 SGKFSSDRTI817 AQYAREIWGV 827 EPSRQRLPA
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: Adenosine monophosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal Structure of Human Muscle Glycogen Phosphorylase a with AMP and Glucose | PDB:1Z8D | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.30 Å | Mutation | Yes | [12] |
| PDB Sequence |
RPLSDQEKRK
11 QIVRGVENVT25 ELKKNFNRHL35 HFTLVKDRNV45 ATPRDYYFAL55 AHTVRDHLVG 65 RWIRTQQHYY75 EKDPKRIYYL85 SLEFYMGRTL95 QNTMVNLALE105 NACDEATYQL 115 GLDMEELEEI125 EEDAGLGNGG135 LGRLAACFLD145 SMATLGLAAY155 GYGIRYEFGI 165 FNQKISGGWQ175 MEEADDWLRY185 GNPWEKARPE195 FTLPVHFYGH205 VEHTSQGAKW 215 VDTQVVLAMP225 YDTPVPGYRN235 NVVNTMRLWS245 AKAPGYIQAV266 LDRNLAENIS 276 RVLYPNDNFF286 EGKELRLKQE296 YFVVAATLQD306 IIRRFKSSKF316 GCRDPVRTNF 326 DAFPDKVAIQ336 LNDTHPSLAI346 PELMRILVDL356 ERMDWDKAWD366 VTVRTCAYTN 376 HTVLPEALER386 WPVHLLETLL396 PRHLQIIYEI406 NQRFLNRVAA416 AFPGDVDRLR 426 RMSLVEEGAV436 KRINMAHLCI446 AGSHAVNGVA456 RIHSEILKKT466 IFKDFYELEP 476 HKFQNKTNGI486 TPRRWLVLCN496 PGLAEVIAER506 IGEDFISDLD516 QLRKLLSFVD 526 DEAFIRDVAK536 VKQENKLKFA546 AYLEREYKVH556 INPNSLFDIQ566 VKRIHEYKRQ 576 LLNCLHVITL586 YNRIKREPNK596 FFVPRTVMIG606 GKAAPGYHMA616 KMIIRLVTAI 626 GDVVNHDPAV636 GDRLRVIFLE646 NYRVSLAEKV656 IPAADLSEQI666 STAGTEASGT 676 GNMFMLNGAL687 TIGTMDGANV697 EMAEEAGEEN707 FFIFGMRVED717 VDKLDQRGYN 727 AQEYYDRIPE737 LRQVIEQLSS747 GFFSPKQPDL757 FKDIVNMLMH767 HDRFKVFADY 777 EDYIKCQEKV787 SALYKNPREW797 TRMVIRNIAT807 SGKFSSDRTI817 AQYAREIWGV 827 EPSRQRLPA
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|



| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Starch and sucrose metabolism | hsa00500 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Carbohydrate metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
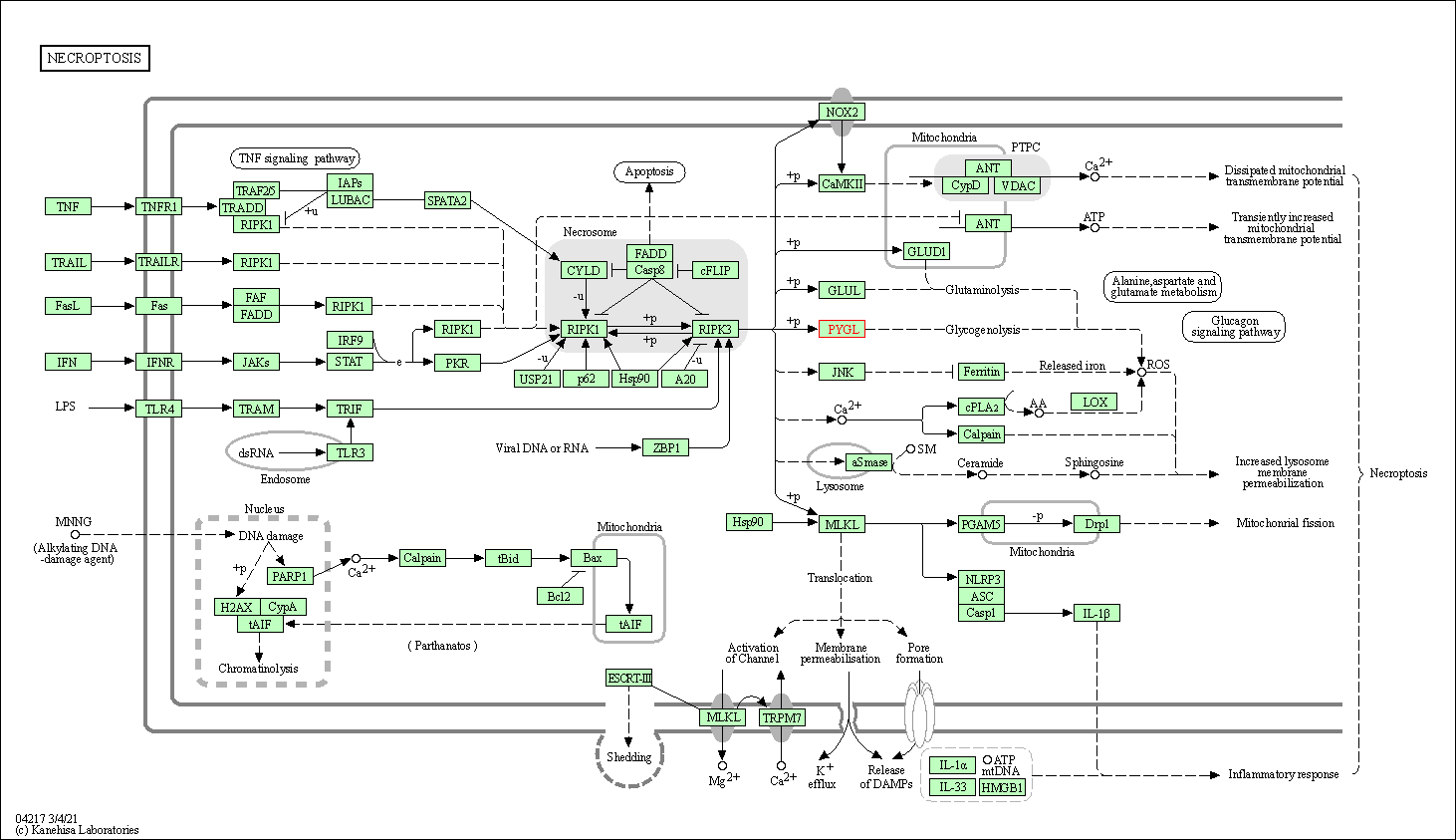
| Necroptosis | hsa04217 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Insulin signaling pathway | hsa04910 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Glucagon signaling pathway | hsa04922 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 8 | Degree centrality | 8.59E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 5.38E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.61E-01 | Radiality | 1.24E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.86E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 7.13E+00 | Topological coefficient | 2.74E-01 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BioCyc | [+] 1 BioCyc Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Glycogenolysis | |||||
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 4 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Starch and sucrose metabolism | |||||
| 2 | Metabolic pathways | |||||
| 3 | Insulin signaling pathway | |||||
| 4 | Glucagon signaling pathway | |||||
| Panther Pathway | [+] 1 Panther Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Heterotrimeric G-protein signaling pathway-Gi alpha and Gs alpha mediated pathway | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 2 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Glycogen Metabolism | |||||
| 2 | Metabolism of carbohydrates | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800026877) | |||||
| REF 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02337933) Effect of Ursolic Acid Administration on Insulin Sensitivity and Metabolic Syndrome. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 3 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800026877) | |||||
| REF 4 | Synthesis of 3-deoxypentacyclic triterpene derivatives as inhibitors of glycogen phosphorylase. J Nat Prod. 2009 Aug;72(8):1414-8. | |||||
| REF 5 | 1-(3-Deoxy-3-fluoro-beta-d-glucopyranosyl) pyrimidine derivatives as inhibitors of glycogen phosphorylase b: Kinetic, crystallographic and modellin... Bioorg Med Chem. 2010 May 15;18(10):3413-25. | |||||
| REF 6 | How many drug targets are there Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. | |||||
| REF 7 | Naturally occurring pentacyclic triterpenes as inhibitors of glycogen phosphorylase: synthesis, structure-activity relationships, and X-ray crystal... J Med Chem. 2008 Jun 26;51(12):3540-54. | |||||
| REF 8 | Practical synthesis of bredemolic acid, a natural inhibitor of glycogen phosphorylase. J Nat Prod. 2008 Nov;71(11):1877-80. | |||||
| REF 9 | The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1;28(1):235-42. | |||||
| REF 10 | Binding of N-acetyl-N '-beta-D-glucopyranosyl urea and N-benzoyl-N '-beta-D-glucopyranosyl urea to glycogen phosphorylase b: kinetic and crystallographic studies. Eur J Biochem. 2002 Mar;269(6):1684-96. | |||||
| REF 11 | DrugBank 3.0: a comprehensive resource for 'omics' research on drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Jan;39(Database issue):D1035-41. | |||||
| REF 12 | The crystal structure of human muscle glycogen phosphorylase a with bound glucose and AMP: an intermediate conformation with T-state and R-state features. Proteins. 2006 Jun 1;63(4):1123-6. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

