Drug Information
| Drug General Information | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0H7KF
|
||||
| Former ID |
DAP000001
|
||||
| Drug Name |
Quetiapine
|
||||
| Synonyms |
Norsic; Quetiapina; Quetiapinum; Seroquel; Quetiapine fumarate; Quetiapine hemifumarate; ZD5077; Co-Quetiapine; Ketipinor (TN); Norsic (TN); Quetiapine (INN); Quetiapine [INN:BAN]; Seroquel (Fumarate); Seroquel (TN); ZM 204,636; 2-(2-(4-Dibenzo(b,f)(1,4)thiazepin-11-yl-1-piperazinyl)ethoxy)ethanol; 2-[2-(4-Dibenzo[b,f][1,4]thiazepin-11-yl-1-piperazinyl)ethoxy]ethanol; 2-[2-(4-benzo[b][1,4]benzothiazepin-6-ylpiperazin-1-yl)ethoxy]ethanol; 2-[2-(4-dibenzo[b,f][1,4]thiazepin-11-ylpiperazin-1-yl)ethoxy]ethanol; 2-{[2-(4-dibenzo[b,f][1,4]thiazepin-11-ylpiperazin-1-yl)ethyl]oxy}ethanol
|
||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||
| Indication | Schizophrenia [ICD9: 295; ICD10:F20] | Approved | [1], [2] | ||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antipsychotic Agents
|
||||
| Company |
AstraZeneca
|
||||
| Structure |
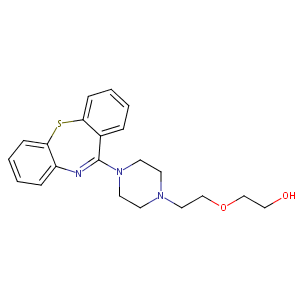
|
Download2D MOL |
|||
| Formula |
C21H25N3O2S
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C21H25N3O2S/c25-14-16-26-15-13-23-9-11-24(12-10-23)21-17-5-1-3-7-19(17)27-20-8-4-2-6-18(20)22-21/h1-8,25H,9-16H2
|
||||
| InChIKey |
URKOMYMAXPYINW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| CAS Number |
CAS 111974-69-7
|
||||
| PubChem Compound ID | |||||
| PubChem Substance ID |
9601, 631813, 5198881, 7980444, 8153080, 14756073, 26612817, 26749928, 29215183, 29215184, 29224074, 46504800, 48416505, 49666155, 49666758, 50064167, 50606342, 56312011, 56312821, 56394834, 57288825, 61127934, 85209878, 92308036, 93166437, 93619787, 96025142, 103195252, 103993497, 104307995, 108136177, 114919760, 124799953, 125337908, 126525318, 126653074, 126671681, 127275837, 127275838, 127275839, 127275840, 127275841, 127275842, 127275843, 129409886, 134337331, 134338691, 134339382, 134358152, 135017541
|
||||
| ChEBI ID |
ChEBI:8707
|
||||
| SuperDrug ATC ID |
N05AH04
|
||||
| SuperDrug CAS ID |
cas=111974697
|
||||
| Target and Pathway | |||||
| Target(s) | D(2) dopamine receptor | Target Info | Agonist | [3], [4] | |
| KEGG Pathway | Rap1 signaling pathway | ||||
| cAMP signaling pathway | |||||
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | |||||
| Gap junction | |||||
| Dopaminergic synapse | |||||
| Parkinson's disease | |||||
| Cocaine addiction | |||||
| Alcoholism | |||||
| PANTHER Pathway | Heterotrimeric G-protein signaling pathway-Gi alpha and Gs alpha mediated pathway | ||||
| Heterotrimeric G-protein signaling pathway-Gq alpha and Go alpha mediated pathway | |||||
| Dopamine receptor mediated signaling pathway | |||||
| Nicotine pharmacodynamics pathway | |||||
| Reactome | Dopamine receptors | ||||
| G alpha (i) signalling events | |||||
| WikiPathways | Hypothetical Network for Drug Addiction | ||||
| Monoamine GPCRs | |||||
| GPCRs, Class A Rhodopsin-like | |||||
| Genes and (Common) Pathways Underlying Drug Addiction | |||||
| GPCR ligand binding | |||||
| GPCR downstream signaling | |||||
| Nicotine Activity on Dopaminergic Neurons | |||||
| References | |||||
| REF 1 | (http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/) Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 50). | ||||
| REF 2 | How many modes of action should an antibiotic have? Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2008 Oct;8(5):564-73. Epub 2008 Jul 30. | ||||
| REF 3 | Atypical antipsychotics: mechanism of action. Can J Psychiatry. 2002 Feb;47(1):27-38. | ||||
| REF 4 | Receptor reserve-dependent properties of antipsychotics at human dopamine D2 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 2009 Apr 1;607(1-3):35-40. Epub 2009 Feb 13. | ||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

