Drug Information
| Drug General Information | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug ID |
D0V1SD
|
|||
| Former ID |
DCL000728
|
|||
| Drug Name |
BP4.879a
|
|||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||
| Indication | Schizophrenia [ICD-11: 6A20] | Terminated | [1] | |
| Company |
Bioprojet
|
|||
| Structure |
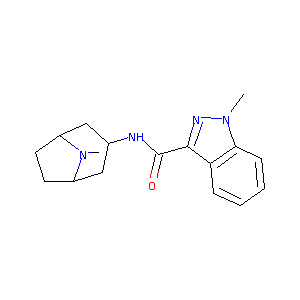 |
Download2D MOL |
||
| Formula |
C17H22N4O
|
|||
| Canonical SMILES |
CN1C2CCC1CC(C2)NC(=O)C3=NN(C4=CC=CC=C43)C
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C17H22N4O/c1-20-12-7-8-13(20)10-11(9-12)18-17(22)16-14-5-3-4-6-15(14)21(2)19-16/h3-6,11-13H,7-10H2,1-2H3,(H,18,22)/t11?,12-,13+
|
|||
| InChIKey |
DDHAJFBBJWHSBR-YHWZYXNKSA-N
|
|||
| PubChem Compound ID | ||||
| PubChem Substance ID | ||||
| Target and Pathway | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | 5-HT 3 receptor (5HT3R) | Target Info | Antagonist | [2] |
| 5-HT 3A receptor (HTR3A) | Target Info | Antagonist | [3] | |
| Dopamine D3 receptor (D3R) | Target Info | Antagonist | [1] | |
| KEGG Pathway | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | |||
| Dopaminergic synapse | ||||
| Serotonergic synapse | ||||
| NetPath Pathway | IL2 Signaling Pathway | |||
| Panther Pathway | 5HT3 type receptor mediated signaling pathway | |||
| Reactome | Dopamine receptors | |||
| G alpha (i) signalling events | ||||
| Ligand-gated ion channel transport | ||||
| WikiPathways | Monoamine GPCRs | |||
| GPCRs, Class A Rhodopsin-like | ||||
| GPCR ligand binding | ||||
| GPCR downstream signaling | ||||
| Nicotine Activity on Dopaminergic Neurons | ||||
| GPCRs, Other | ||||
| SIDS Susceptibility Pathways | ||||
| Iron uptake and transport | ||||
| References | Top | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | The pipeline and future of drug development in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry. 2007 Oct;12(10):904-22. | |||
| REF 2 | 5-HT(3A) receptor subunit is required for 5-HT3 antagonist-induced reductions in alcohol drinking. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004 Oct;29(10):1807-13. | |||
| REF 3 | Pharmacological and regional characterization of [3H]LY278584 binding sites in human brain. J Neurochem. 1993 Feb;60(2):730-7. | |||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

