Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T40111
(Former ID: TTDS00062)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Inosine-5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase 1 (IMPDH1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Superoxide-inducible protein 12; SOI12; Probable inosine-5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase IMD1; NAD-dependent inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase; Inosine dehydrogenase; IMPDH-I; IMPDH 1; IMPDH; IMPD1; IMPD 1; IMPD; IMP dehydrogenase 1; IMP dehydrogenase
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
IMPDH1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 5 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60-2C6Y] | |||||
| 2 | Hepatitis virus infection [ICD-11: 1E50-1E51] | |||||
| 3 | Mature B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85] | |||||
| 4 | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||||
| 5 | Transplant rejection [ICD-11: NE84] | |||||
| Function |
Could also have a single-stranded nucleic acid-binding activity and could play a role in RNA and/or DNA metabolism. It may also have a role in the development of malignancy and the growth progression of some tumors. Catalyzes the conversion of inosine 5'-phosphate (IMP) to xanthosine 5'-phosphate (XMP), the first committed and rate-limiting step in the de novo synthesis of guanine nucleotides, and therefore plays an important role in the regulation of cell growth.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
CH-OH donor oxidoreductase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 1.1.1.205
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MADYLISGGTGYVPEDGLTAQQLFASADGLTYNDFLILPGFIDFIADEVDLTSALTRKIT
LKTPLISSPMDTVTEADMAIAMALMGGIGFIHHNCTPEFQANEVRKVKKFEQGFITDPVV LSPSHTVGDVLEAKMRHGFSGIPITETGTMGSKLVGIVTSRDIDFLAEKDHTTLLSEVMT PRIELVVAPAGVTLKEANEILQRSKKGKLPIVNDCDELVAIIARTDLKKNRDYPLASKDS QKQLLCGAAVGTREDDKYRLDLLTQAGVDVIVLDSSQGNSVYQIAMVHYIKQKYPHLQVI GGNVVTAAQAKNLIDAGVDGLRVGMGCGSICITQEVMACGRPQGTAVYKVAEYARRFGVP IIADGGIQTVGHVVKALALGASTVMMGSLLAATTEAPGEYFFSDGVRLKKYRGMGSLDAM EKSSSSQKRYFSEGDKVKIAQGVSGSIQDKGSIQKFVPYLIAGIQHGCQDIGARSLSVLR SMMYSGELKFEKRTMSAQIEGGVHGLHSYEKRLY Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T00RT4 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 5 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Mercaptopurine | Drug Info | Approved | Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia | [2], [3] | |
| 2 | Merimepodib | Drug Info | Approved | Breast cancer | [4] | |
| 3 | Mizoribine | Drug Info | Approved | Transplant rejection | [5], [6] | |
| 4 | Ribavirin | Drug Info | Approved | Hepatitis C virus infection | [7], [8] | |
| 5 | Tiazofurin | Drug Info | Approved | Solid tumour/cancer | [9] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 2 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Viramidine | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Hepatitis C virus infection | [10] | |
| 2 | VX-944 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Solid tumour/cancer | [11] | |
| Patented Agent(s) | [+] 1 Patented Agents | + | ||||
| 1 | VX-148 | Drug Info | Patented | Psoriasis vulgaris | [12] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 1 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Phenacetin | Drug Info | Withdrawn from market | Analgesia | [13], [14] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 69 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Mercaptopurine | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | Merimepodib | Drug Info | [15], [16] | |||
| 3 | Mizoribine | Drug Info | [15], [17] | |||
| 4 | Ribavirin | Drug Info | [18], [19] | |||
| 5 | Tiazofurin | Drug Info | [20], [21], [22] | |||
| 6 | Viramidine | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 7 | VX-944 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 8 | Carbamide derivative 10 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 9 | Carbamide derivative 11 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 10 | Carbamide derivative 4 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 11 | Carbamide derivative 5 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 12 | Carbamide derivative 6 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 13 | Carbamide derivative 7 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 14 | Carbamide derivative 8 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 15 | Carbamide derivative 9 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 16 | Mycophenolic acid/nucleotide derivative 1 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 17 | Mycophenolic acid/nucleotide derivative 10 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 18 | Mycophenolic acid/nucleotide derivative 11 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 19 | Mycophenolic acid/nucleotide derivative 12 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 20 | Mycophenolic acid/nucleotide derivative 2 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 21 | Mycophenolic acid/nucleotide derivative 3 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 22 | Mycophenolic acid/nucleotide derivative 4 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 23 | Mycophenolic acid/nucleotide derivative 5 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 24 | Mycophenolic acid/nucleotide derivative 6 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 25 | Mycophenolic acid/nucleotide derivative 7 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 26 | Mycophenolic acid/nucleotide derivative 8 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 27 | Mycophenolic acid/nucleotide derivative 9 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 28 | PMID28074661-Compound-US20100022547C80 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 29 | PMID28074661-Compound-US20100022547C81 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 30 | PMID28074661-Compound-US20100022547C82 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 31 | PMID28074661-Compound-US20100022547C83 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 32 | PMID28074661-Compound-US20100022547C86 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 33 | PMID28074661-Compound-US20100022547C87 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 34 | PMID28074661-Compound-US20100022547C88 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 35 | PMID28074661-Compound-US20120264760C80 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 36 | PMID28074661-Compound-US20120264760C81 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 37 | PMID28074661-Compound-US20120264760C82 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 38 | PMID28074661-Compound-US20120264760C83 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 39 | PMID28074661-Compound-US20120264760C86 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 40 | PMID28074661-Compound-US20120264760C87 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 41 | PMID28074661-Compound-US20120264760C88 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 42 | PMID28074661-Compound-US20128202889C90 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 43 | PMID28074661-Compound-US20158969342C84 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 44 | PMID28074661-Compound-US20169447134C85 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 45 | PMID28074661-Compound-WO2009018344C78 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 46 | PMID28074661-Compound-WO2009018344C79 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 47 | Quinazolinone derivative 1 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 48 | Quinazolinone derivative 2 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 49 | Quinolone derivative 1 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 50 | Urea and carbamate bioisostere derivative 10 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 51 | Urea and carbamate bioisostere derivative 11 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 52 | Urea and carbamate bioisostere derivative 13 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 53 | Urea and carbamate bioisostere derivative 14 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 54 | Urea and carbamate bioisostere derivative 15 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 55 | Urea and carbamate bioisostere derivative 16 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 56 | Urea and carbamate bioisostere derivative 18 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 57 | Urea and carbamate bioisostere derivative 2 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 58 | Urea and carbamate bioisostere derivative 3 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 59 | Urea and carbamate bioisostere derivative 4 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 60 | Urea and carbamate bioisostere derivative 5 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 61 | Urea and carbamate bioisostere derivative 6 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 62 | Urea and carbamate bioisostere derivative 7 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 63 | Urea and carbamate bioisostere derivative 9 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 64 | VX-148 | Drug Info | [24], [16] | |||
| 65 | Phenacetin | Drug Info | [25] | |||
| 66 | 6-Cl-IMP | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 67 | Inosinic Acid | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 68 | Selenazofurin | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| 69 | TAD | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Adenosine triphosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | HUMAN IMPDH1 TREATED WITH GTP, IMP, AND NAD+; INTERFACE-CENTERED | PDB:7RFE | ||||
| Method | Electron microscopy | Resolution | 2.60 Å | Mutation | No | [29] |
| PDB Sequence |
GYVPEDGLTA
20 QQLFASADGL30 TYNDFLILPG40 FIDFIADEVD50 LTSALTRKIT60 LKTPLISSPM 70 DTVTEADMAI80 AMALMGGIGF90 IHHNCTPEFQ100 ANEVRKVKKF110 EQGFITDPVV 120 LSPSHTVGDV130 LEAKMRHGFS140 GIPITETGTM150 GSKLVGIVTS160 RDIVMTPRIE 184 LVVAPAGVTL194 KEANEILQRS204 KKGKLPIVND214 CDELVAIIAR224 TDLKKNRDYP 234 LASKDSQKQL244 LCGAAVGTRE254 DDKYRLDLLT264 QAGVDVIVLD274 SSQGNSVYQI 284 AMVHYIKQKY294 PHLQVIGGNV304 VTAAQAKNLI314 DAGVDGLRVG324 MGCGSICITQ 334 EVMACGRPQG344 TAVYKVAEYA354 RRFGVPIIAD364 GGIQTVGHVV374 KALALGASTV 384 MMGSLLAATT394 EAPGEYFFSD404 GVRLKKYRGM414 GSLDAMKVKI439 AQGVSGSIQD 449 KGSIQKFVPY459 LIAGIQHGCQ469 DIGARSLSVL479 RSMMYSGELK489 FEKRTMSAQI 499 EGGVHGLHSY509 EKRLY
|
|||||
|
|
GLY141
4.838
ILE157
2.787
VAL158
3.407
THR159
2.298
SER160
1.689
ARG161
1.804
ASP162
1.670
MET179
4.618
THR180
1.770
GLU184
3.418
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: 6-Chloropurine Riboside, 5'-Monophosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | BINARY COMPLEX OF HUMAN TYPE-I INOSINE MONOPHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE WITH 6-CL-IMP | PDB:1JCN | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.50 Å | Mutation | No | [30] |
| PDB Sequence |
TGYVPEDGLT
19 AQQLFASADD29 LTYNDFLILP39 GFIDFIADEV49 DLTSALTRKI59 TLKTPLISSP 69 MDTVTEADMA79 IAMALMGGIG89 FIHHNCTPEF99 QANEVRKVKN109 FEQGFITDPV 119 VLSPGIPITE146 VGIVTSRDID164 PRIELVVAPA190 GVTLKEANEI200 LQRSKKGKLP 210 IVNDCDELVR224 TDLKKNRDYP234 LASKDSQKQL244 LCGAAVGTRE254 DDKYRLDLLT 264 QAGVDVIVLD274 SSQGNSVYQI284 AMVHYIKQKY294 PHLQVIGGNV304 VTAAQAKNLI 314 DAGVDGLRVG324 MGCGSICITQ334 EVMACGRPQG344 TAVYKVAEYA354 RRFGVPIIAD 364 GGIQTVGHVV374 KALALGASTV384 MMGSLLAATT394 EAPGEKGSIQ454 KFVPYLIAGI 464 QHGCQDIGAR474 SLSVLRSMMY484 SGELKFEKRT494 MSAQI
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
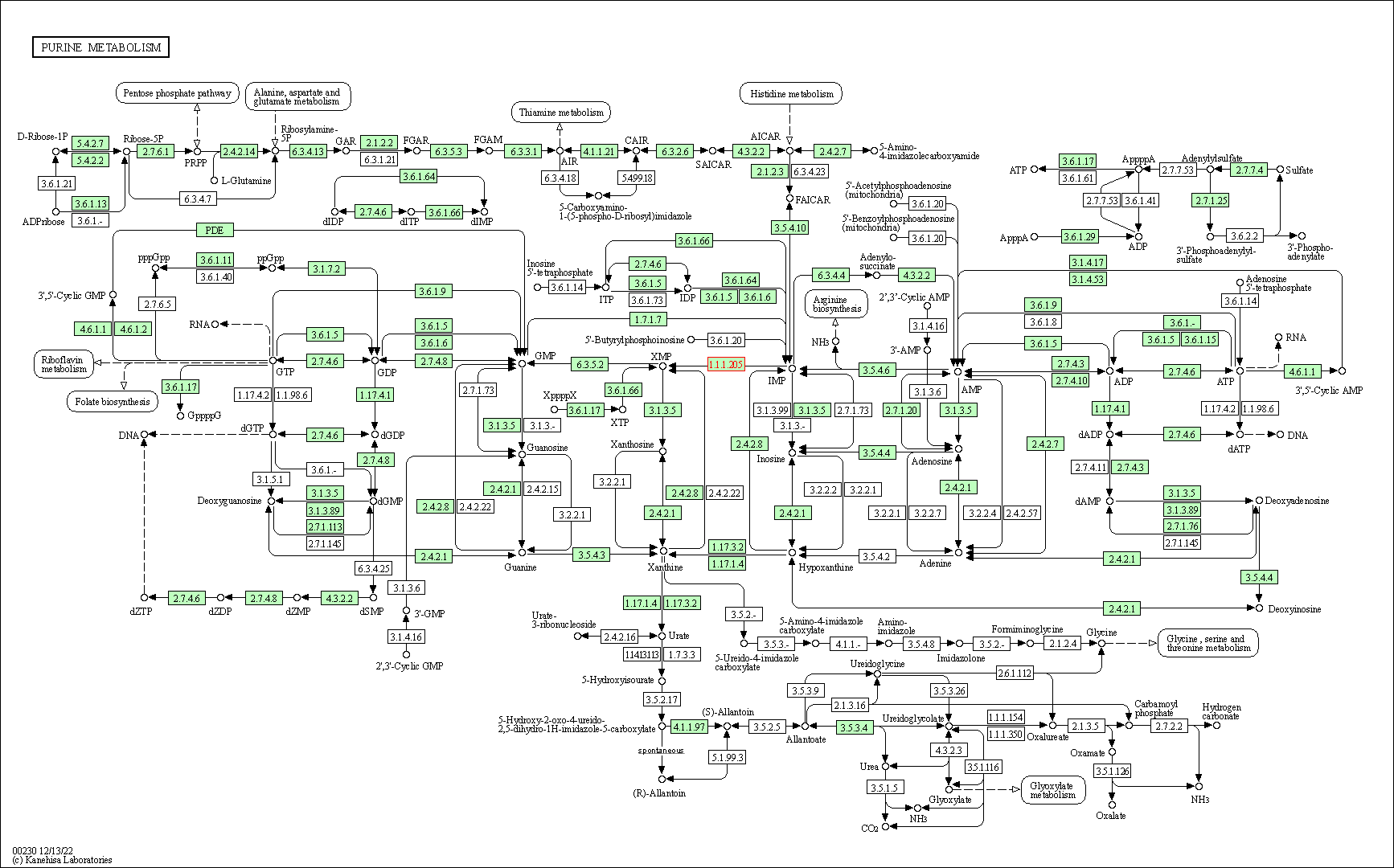
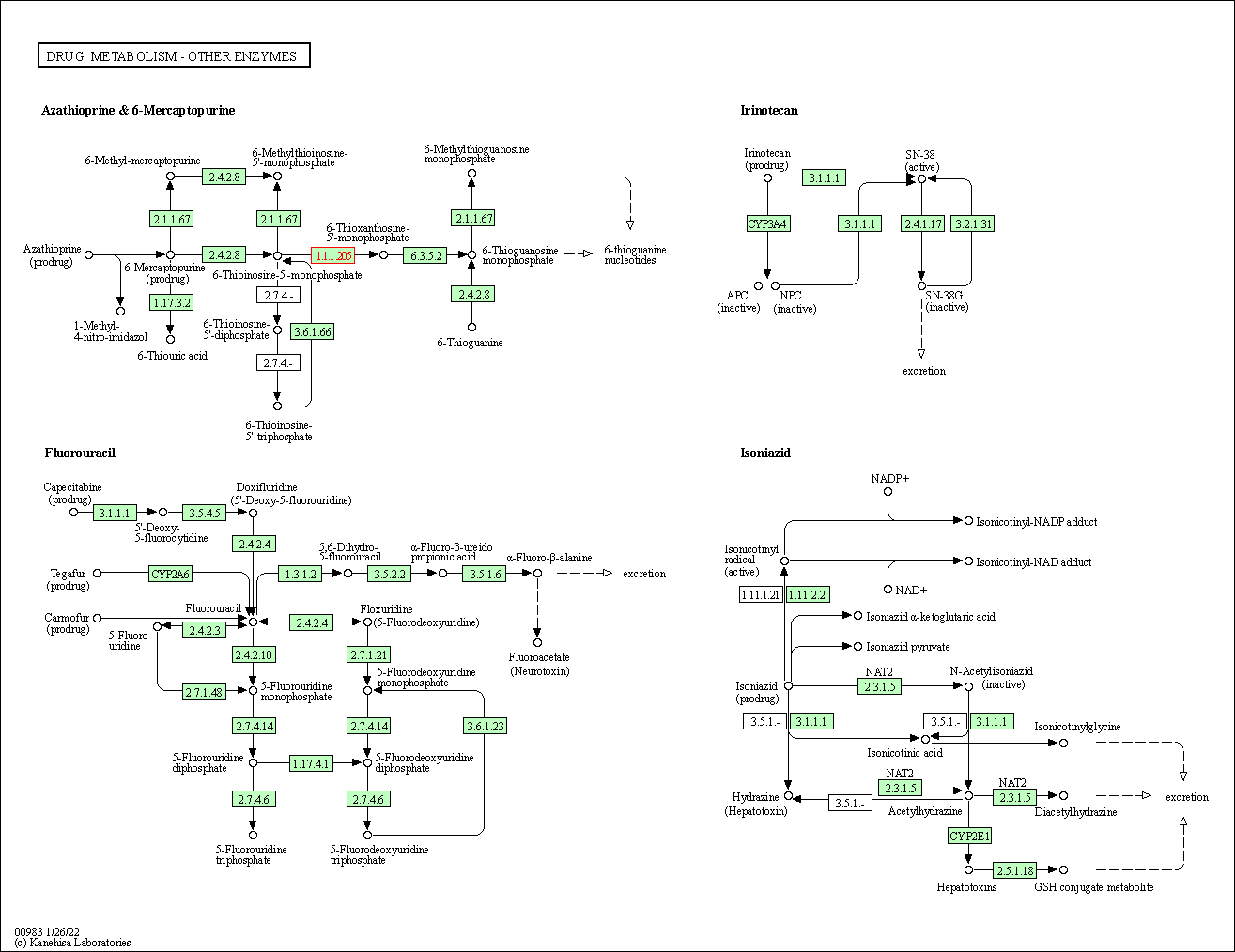
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purine metabolism | hsa00230 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Nucleotide metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Drug metabolism - other enzymes | hsa00983 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 4 | Degree centrality | 4.30E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 9.24E-06 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.69E-01 | Radiality | 1.27E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 6.67E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 1.28E+01 | Topological coefficient | 3.98E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Clinical pharmacology and pharmacogenetics of thiopurines. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2008 Aug;64(8):753-67. | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7226). | |||||
| REF 3 | S-adenosylmethionine regulates thiopurine methyltransferase activity and decreases 6-mercaptopurine cytotoxicity in MOLT lymphoblasts. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Jun 15;77(12):1845-53. | |||||
| REF 4 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (NDA) 022059. | |||||
| REF 5 | Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod. 2007 Mar;70(3):461-77. | |||||
| REF 6 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 7 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6842). | |||||
| REF 8 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (ANDA) 076192. | |||||
| REF 9 | De novo synthesis of two new cytotoxic tiazofurin analogues with modified sugar moieties. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2003 Oct 6;13(19):3167-70. | |||||
| REF 10 | A phase III study of the safety and efficacy of viramidine versus ribavirin in treatment-na ve patients with chronic hepatitis C: ViSER1 results. Hepatology. 2009 Sep;50(3):717-26. | |||||
| REF 11 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00493441) AVN944 in Combination With Gemcitabine for the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 12 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800013965) | |||||
| REF 13 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7402). | |||||
| REF 14 | An epidemiologic study of abuse of analgesic drugs. Effects of phenacetin and salicylate on mortality and cardiovascular morbidity (1968 to 1987)Dubach UC1, Rosner B, St rmer T.Author information1Department of Internal Medicine, Kantonsspital, Basel, Switzerland.AbstractBACKGROUND: Phenacetin abuse is known to produce kidney disease; salicylate use is supposed to prevent cardiovascular disease. We conducted a prospective, longitudinal epidemiologic study to examine the effects of these drugs on cause-specific mortality and on cardiovascular morbidity.METHODS: In 1968 we evaluated a study group of 623 healthy women 30 to 49 years old who had evidence of a regular intake of phenacetin, as measured by urinary excretion of its metabolites, and a matched control group of 621 women. Salicylate excretion was also measured. All subjects were examined over a period of 20 years.RESULTS: Life-table analyses of mortality during the 20 years, with adjustment for the year of birth, cigarette smoking, and length of follow-up, revealed significant differences between the groups in overall mortality (study group vs. control group, 74 vs. 27 deaths; relative risk, 2.2; 95 percent confidence interval, 1.5 to 3.3), deaths due to urologic or renal disease (relative risk, 16.1; 95 percent confidence interval, 3.9 to 66.1), deaths due to cancer (relative risk, 1.9; 95 percent confidence interval, 1.1 to 3.3), and deaths due to cardiovascular disease (relative risk, 2.9; 95 percent confidence interval, 1.5 to 5.5). The relative risk of cardiovascular disease (fatal or nonfatal myocardial infarction, heart failure, or stroke) was 1.8, and the 95 percent confidence interval 1.3 to 2.6. The odds ratio for the incidence of hypertension was 1.6, and the 95 percent confidence interval 1.2 to 2.1. The effects of phenacetin on morbidity and mortality, with adjustment for base-line salicylate excretion, were similar. In contrast, salicylate use had no effect on either mortality or morbidity.CONCLUSIONS: Regular use of analgesic drugs containing phenacetin is associated with an increased risk of hypertension and mortality and morbidity due to cardiovascular disease, as well as an increased riskof mortality due to cancer and urologic or renal disease. The use of salicylates carries no such risk.Comment inThe risks of phenacetin use. [N Engl J Med. 1991]PMID: 1984193 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] Free full textSharePublication Types, MeSH Terms, SubstancesPublication TypesResearch Support, Non-U.S. Gov'tMeSH TermsAdultAgedAspirin/adverse effects*Cardiovascular Diseases/epidemiology*Cardiovascular Diseases/mortalityDose-Response Relationship, DrugFemaleHumansHypertension/epidemiologyKidney Diseases/mortalityLongitudinal StudiesMiddle AgedMortality*Neoplasms/mortalityPhenacetin/adverse effects*Prospective StudiesRiskSubstance-Related Disorders*Urologic Diseases/mortalitySubstancesPhenacetinAspirinLinkOut - more resourcesFull Text SourcesAtypon - PDFAtyponOvid Technologies, Inc.MedicalDrug Abuse - MedlinePlus Health InformationMiscellaneousACETYLSALICYLIC ACID - Hazardous Substances Data BankPHENACETIN - Hazardous Substances Data BankPubMed Commons home N Engl J Med. 1991 Jan 17;324(3):155-60. | |||||
| REF 15 | VX-497: a novel, selective IMPDH inhibitor and immunosuppressive agent. J Pharm Sci. 2001 May;90(5):625-37. | |||||
| REF 16 | Inosine-5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) inhibitors: a patent and scientific literature review (2002-2016).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2017 Jun;27(6):677-690. | |||||
| REF 17 | Cofactor mimics as selective inhibitors of NAD-dependent inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH)--the major therapeutic target. Curr Med Chem. 2004 Apr;11(7):887-900. | |||||
| REF 18 | Treating HCV with ribavirin analogues and ribavirin-like molecules. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006 Jan;57(1):8-13. | |||||
| REF 19 | A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled dose-escalation trial of merimepodib (VX-497) and interferon-alpha in previously untreated patients with chronic hepatitis C. Antivir Ther. 2005;10(5):635-43. | |||||
| REF 20 | In vitro and in vivo antiproliferative activity of IPCAR, a new pyrazole nucleoside analog. Anticancer Res. 1998 Jul-Aug;18(4A):2623-30. | |||||
| REF 21 | Sequential impact of tiazofurin and ribavirin on the enzymic program of the bone marrow. Cancer Res. 1993 Dec 15;53(24):5982-6. | |||||
| REF 22 | Relationships between the cytotoxicity of tiazofurin and its metabolism by cultured human lung cancer cells. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):175-82. | |||||
| REF 23 | Antiviral agents active against influenza A viruses. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):1015-25. | |||||
| REF 24 | Characterization of pharmacological efficacy of VX-148, a new, potent immunosuppressive inosine 5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase inhibitor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002 Sep;302(3):1272-7. | |||||
| REF 25 | A potent "fat base" nucleotide inhibitor of IMP dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1998 Aug 25;37(34):11949-52. | |||||
| REF 26 | Identification of the IMP binding site in the IMP dehydrogenase from Tritrichomonas foetus. Biochemistry. 1995 Oct 24;34(42):13889-94. | |||||
| REF 27 | How many drug targets are there Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. | |||||
| REF 28 | Crystal structure of a ternary complex of Tritrichomonas foetus inosine 5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase: NAD+ orients the active site loop for catalysis. Biochemistry. 2002 Nov 5;41(44):13309-17. | |||||
| REF 29 | IMPDH1 retinal variants control filament architecture to tune allosteric regulation. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2022 Jan;29(1):47-58. | |||||
| REF 30 | Crystal Structure of the Human Type I Inosine Monophosphate Dehydrogenase and Implications for Isoform Specificity | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

