Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T15700
(Former ID: TTDR00433)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Caspase-8 (CASP8)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
MORT1-associated CED-3 homolog; MCH5; MACH; ICE-like apoptotic protease 5; FLICE; FADD-like ICE; FADD-homologous ICE/CED-3-like protease; CASP-8; CAP4; Apoptotic protease Mch-5; Apoptotic cysteine protease
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
CASP8
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Patented-recorded target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Diabetes mellitus [ICD-11: 5A10] | |||||
| 2 | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||||
| Function |
Binding to the adapter molecule FADD recruits it to either receptor. The resulting aggregate called death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) performs CASP8 proteolytic activation. The active dimeric enzyme is then liberated from the DISC and free to activate downstream apoptotic proteases. Proteolytic fragments of the N-terminal propeptide (termed CAP3, CAP5 and CAP6) are likely retained in the DISC. Cleaves and activates CASP3, CASP4, CASP6, CASP7, CASP9 and CASP10. May participate in the GZMB apoptotic pathways. Cleaves ADPRT. Hydrolyzes the small-molecule substrate, Ac-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-|-AMC. Likely target for the cowpox virus CRMA death inhibitory protein. Isoform 5, isoform 6, isoform 7 and isoform 8 lack the catalytic site and may interfere with the pro-apoptotic activity of the complex. Most upstream protease of the activation cascade of caspases responsible for the TNFRSF6/FAS mediated and TNFRSF1A induced cell death.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Peptidase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 3.4.22.61
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MDFSRNLYDIGEQLDSEDLASLKFLSLDYIPQRKQEPIKDALMLFQRLQEKRMLEESNLS
FLKELLFRINRLDLLITYLNTRKEEMERELQTPGRAQISAYRVMLYQISEEVSRSELRSF KFLLQEEISKCKLDDDMNLLDIFIEMEKRVILGEGKLDILKRVCAQINKSLLKIINDYEE FSKERSSSLEGSPDEFSNGEELCGVMTISDSPREQDSESQTLDKVYQMKSKPRGYCLIIN NHNFAKAREKVPKLHSIRDRNGTHLDAGALTTTFEELHFEIKPHDDCTVEQIYEILKIYQ LMDHSNMDCFICCILSHGDKGIIYGTDGQEAPIYELTSQFTGLKCPSLAGKPKVFFIQAC QGDNYQKGIPVETDSEEQPYLEMDLSSPQTRYIPDEADFLLGMATVNNCVSYRNPAEGTW YIQSLCQSLRERCPRGDDILTILTEVNYEVSNKDDKKNMGKQMPQPTFTLRKKLVFPSD Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| ADReCS ID | BADD_A05675 ; BADD_A08298 | |||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T38T1U | |||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: DTD | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Caspase-3 specific unnatural amino acid-based peptides | PDB:4JJ7 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.18 Å | Mutation | No | [4] |
| PDB Sequence |
DKVYQMKSKP
232 RGYCLIINNH242 NFAKAREKVP252 KLHSIRDRNG262 THLDAGALTT272 TFEELHFEIK 282 PHDDCTVEQI292 YEILKIYQLM302 DHSNMDCFIC312 CILSHGDKGI322 IYGTDGQEAP 332 IYELTSQFTG342 LKCPSLAGKP352 KVFFIQACQG362 DNYQKGIPVE372 TDTRYIPDEA 397 DFLLGMATVN407 NCVSYRNPAE417 GTWYIQSLCQ427 SLRERCPRGD437 DILTILTEVN 447 YEVSNKDDKK457 NMGKQMPQPT467 FTLRKKLVFP477 S
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: (3S)-3-amino-5-[(2,6-dimethylbenzoyl)oxy]-4-oxopentanoic acid | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Caspase-3 specific unnatural amino acid-based peptides | PDB:4JJ7 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.18 Å | Mutation | No | [4] |
| PDB Sequence |
DKVYQMKSKP
232 RGYCLIINNH242 NFAKAREKVP252 KLHSIRDRNG262 THLDAGALTT272 TFEELHFEIK 282 PHDDCTVEQI292 YEILKIYQLM302 DHSNMDCFIC312 CILSHGDKGI322 IYGTDGQEAP 332 IYELTSQFTG342 LKCPSLAGKP352 KVFFIQACQG362 DNYQKGIPVE372 TDTRYIPDEA 397 DFLLGMATVN407 NCVSYRNPAE417 GTWYIQSLCQ427 SLRERCPRGD437 DILTILTEVN 447 YEVSNKDDKK457 NMGKQMPQPT467 FTLRKKLVFP477 S
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| p53 signaling pathway | hsa04115 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apoptosis - multiple species | hsa04215 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Necroptosis | hsa04217 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
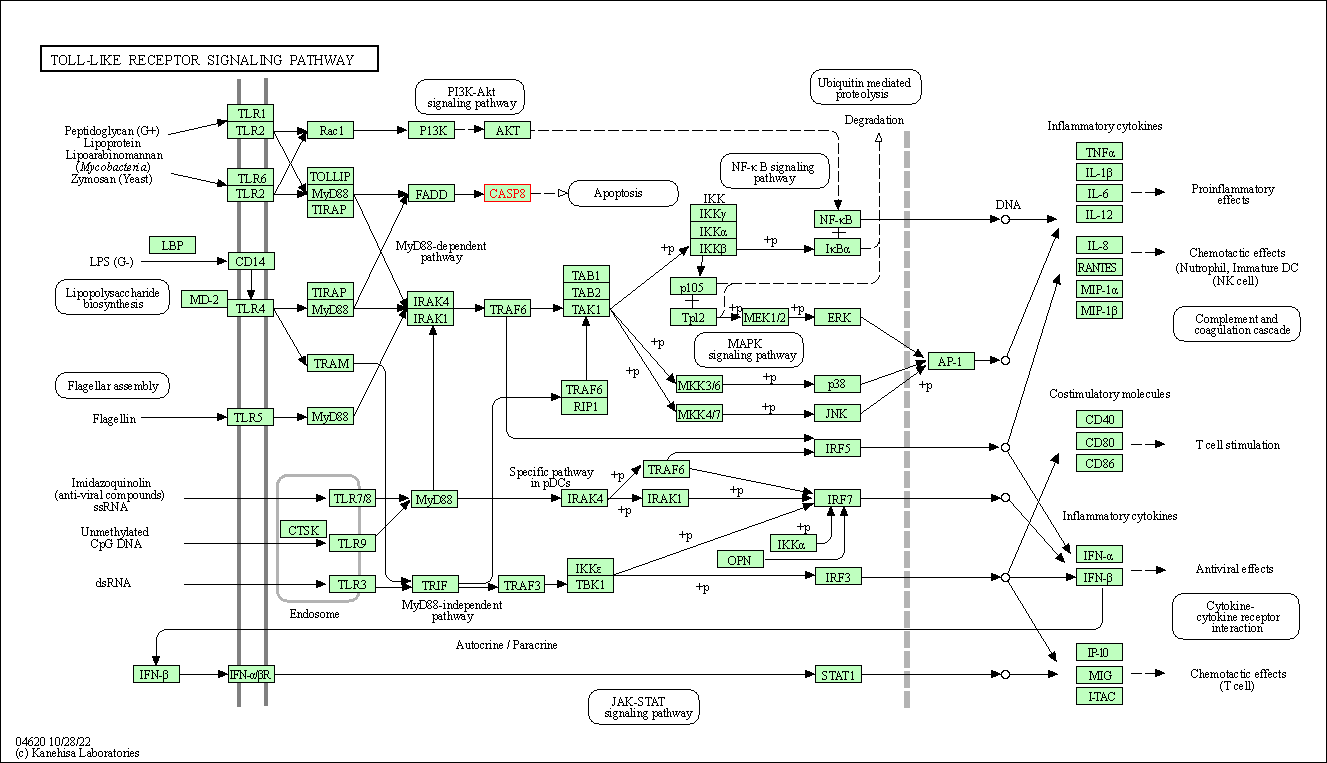
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04620 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
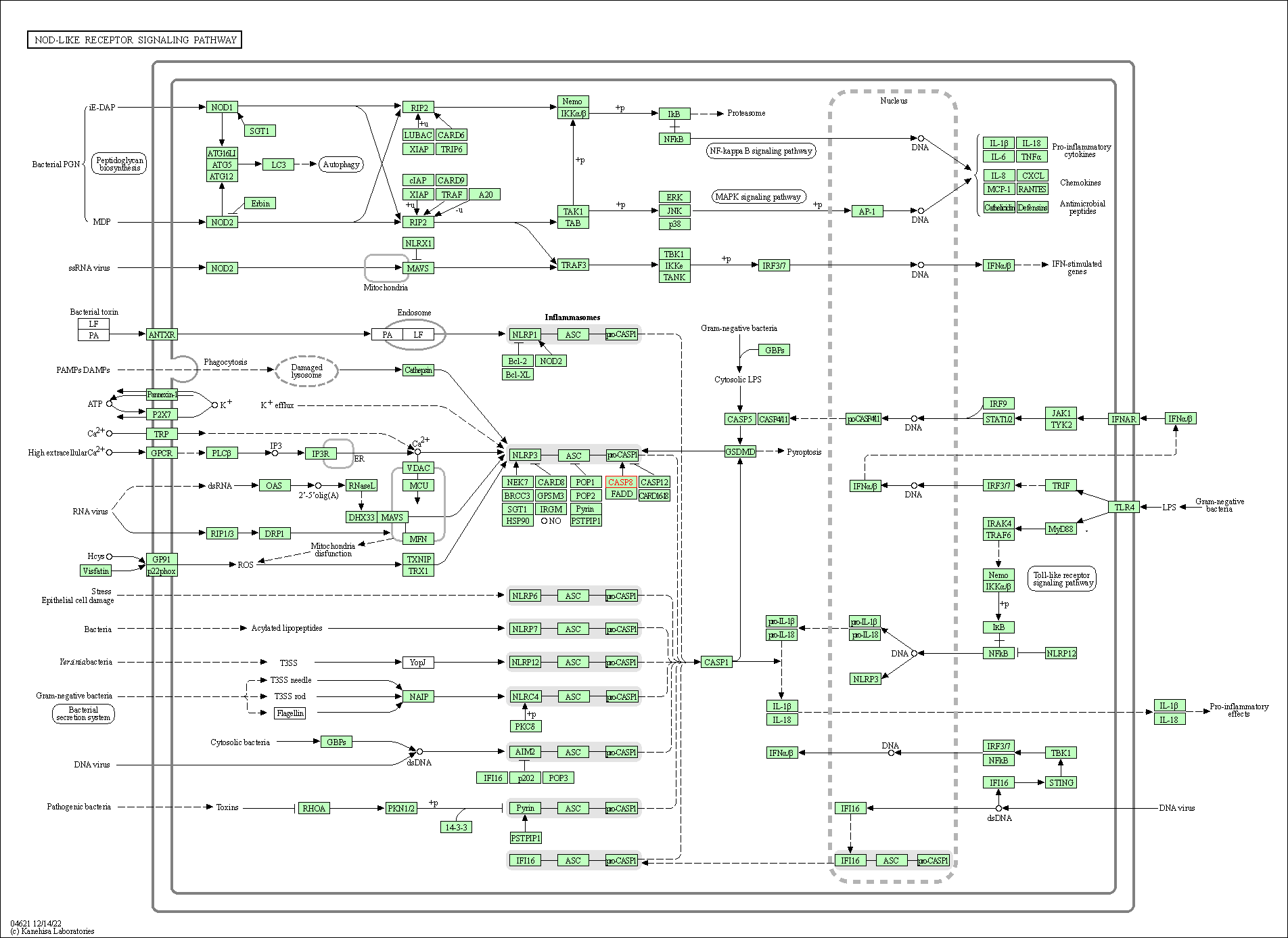
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04621 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
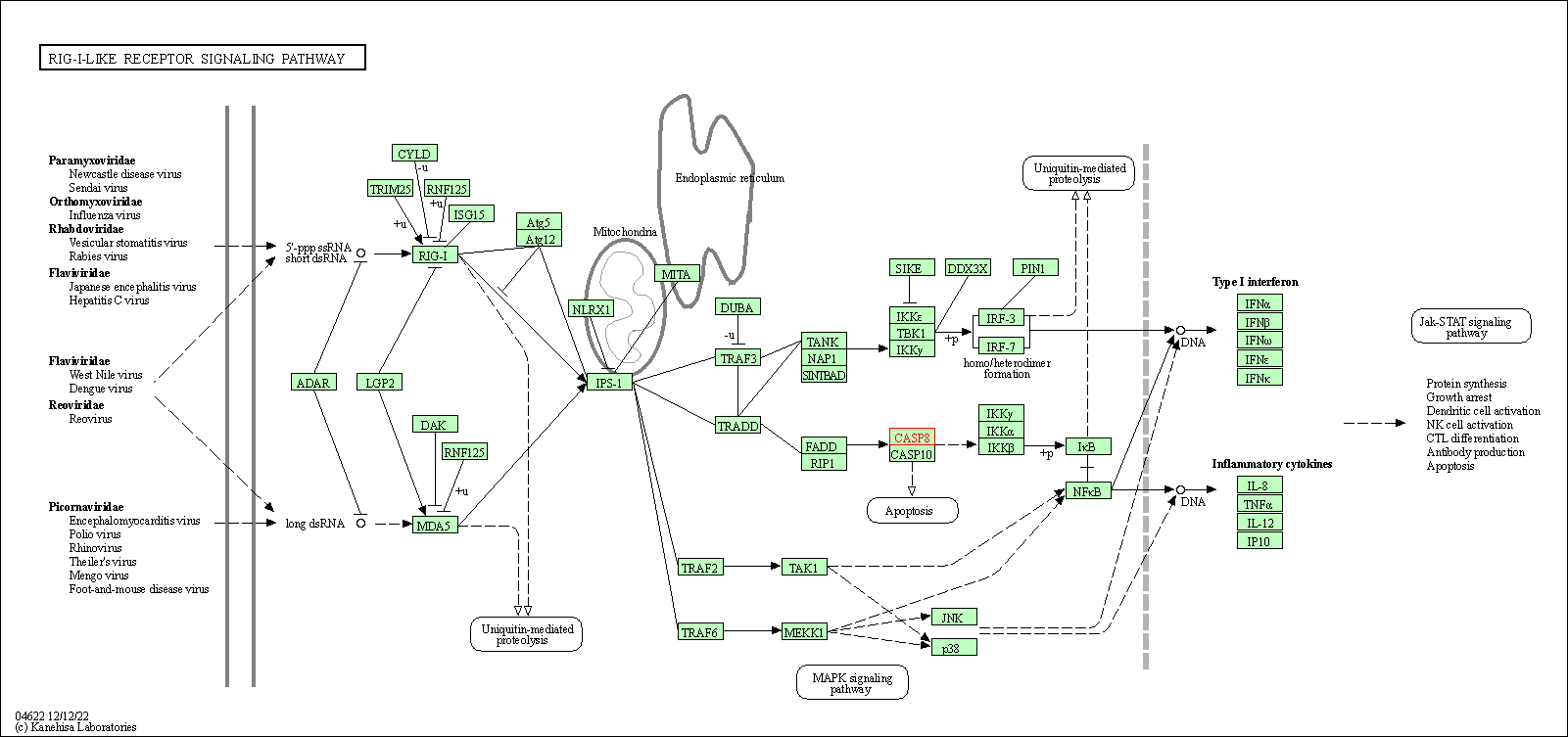
| RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04622 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
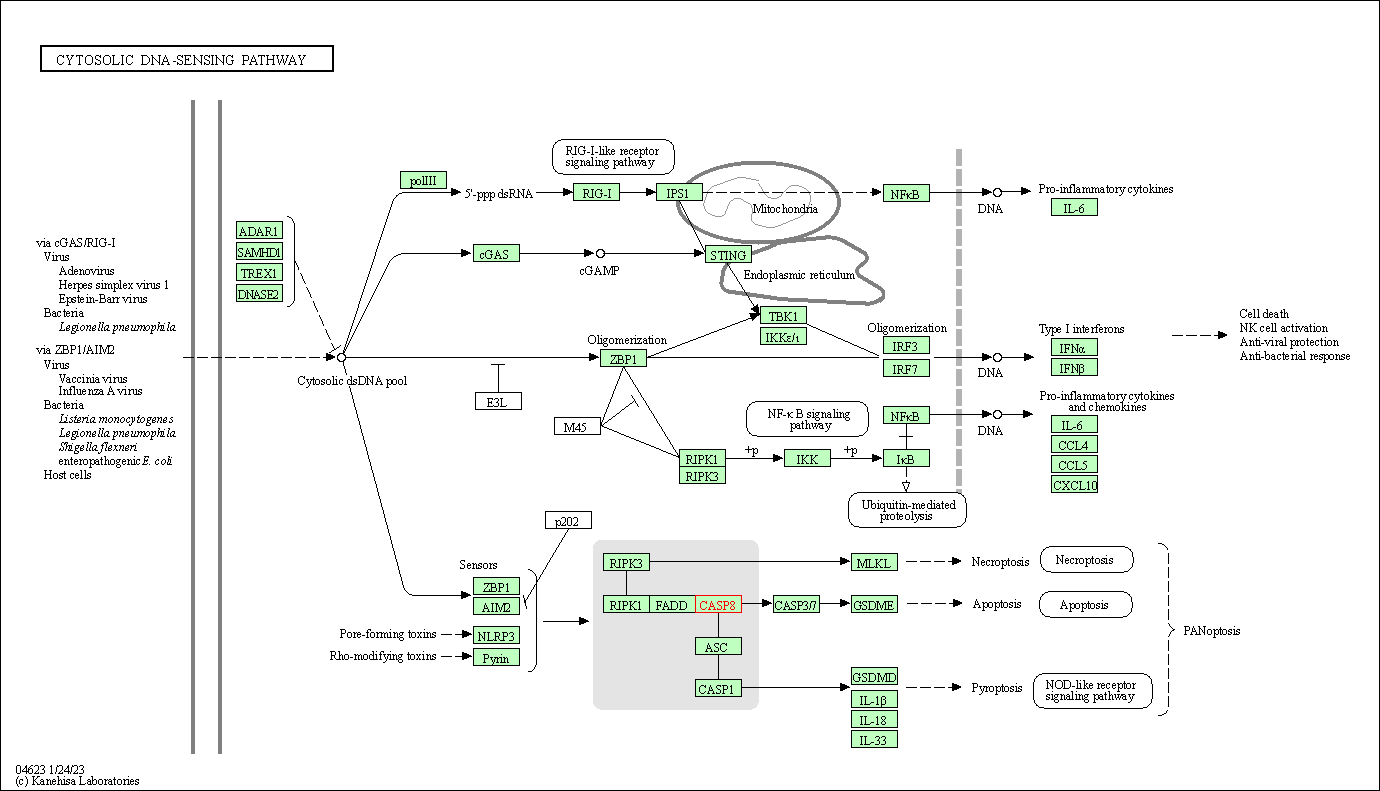
| Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway | hsa04623 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway | hsa04625 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| IL-17 signaling pathway | hsa04657 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| TNF signaling pathway | hsa04668 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 58 | Degree centrality | 6.23E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 5.81E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.62E-01 | Radiality | 1.45E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.54E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.76E+01 | Topological coefficient | 3.96E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-regulating Transcription Factors | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug Resistance Mutation (DRM) |
||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Caspase inhibitors: a review of recently patented compounds (2013-2015).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2018 Jan;28(1):47-59. | |||||
| REF 2 | The atomic-resolution structure of human caspase-8, a key activator of apoptosis. Structure. 1999 Sep 15;7(9):1135-43. | |||||
| REF 3 | Glionitrin A, a new diketopiperazine disulfide, activates ATM-ATR-Chk1/2 via 53BP1 phosphorylation in DU145 cells and shows antitumor effect in xenograft model. Biol Pharm Bull. 2014;37(3):378-86. | |||||
| REF 4 | Selective detection of caspase-3 versus caspase-7 using activity-based probes with key unnatural amino acids. ACS Chem Biol. 2013 Jul 19;8(7):1558-66. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

