Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T19160
(Former ID: TTDC00025)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Group IIA phospholipase A2 (GIIA sPLA2)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
RASF-A; Phospholipase A2, membrane associated; Phosphatidylcholine 2-acylhydrolase 2A; PLA2L; PLA2B; Non-pancreatic secretory phospholipase A2; NPS-PLA2; GIIC sPLA2
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
PLA2G2A
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60-2C6Y] | |||||
| Function |
Catalyzes the calcium-dependent hydrolysis of the 2-acyl groups in 3-sn-phosphoglycerides. Thought to participate in the regulation of phospholipid metabolism in biomembranes including eicosanoid biosynthesis. Independent of its catalytic activity, acts as a ligand for integrins. Binds to and activates integrins ITGAV:ITGB3, ITGA4:ITGB1 and ITGA5:ITGB1. Binds to a site (site 2) which is distinct from the classical ligand-binding site (site 1) and induces integrin conformational changes and enhanced ligand binding to site 1. Induces cell proliferation in an integrin-dependent manner.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Carboxylic ester hydrolase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 3.1.1.4
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MKTLLLLAVIMIFGLLQAHGNLVNFHRMIKLTTGKEAALSYGFYGCHCGVGGRGSPKDAT
DRCCVTHDCCYKRLEKRGCGTKFLSYKFSNSGSRITCAKQDSCRSQLCECDKAAATCFAR NKTTYNKKYQYYSNKHCRGSTPRC Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T40LTN | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | KH064 | Drug Info | Clinical trial | Breast cancer | [1] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 16 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | KH064 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | 1,4-Butanediol | Drug Info | [2] | |||
| 3 | 2-(4-phenoxyphenoxy)ethanamine | Drug Info | [3] | |||
| 4 | 2-Propanol, Isopropanol | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 5 | B-Octylglucoside | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 6 | BOLINAQUINONE | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 7 | CACOSPONGIONOLIDE | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 8 | CACOSPONGIONOLIDE B | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 9 | Cacospongionolide E | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 10 | DIDODECANOYLPHLOROGLUCINOL | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 11 | DYSIDINE | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 12 | Elaidoylamide | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 13 | Lauric Acid | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 14 | LUFFARIELLOLIDE | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 15 | N-Tridecanoic Acid | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 16 | Ochnaflavone | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: KH064 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | PANCREATIC SECRETORY PHOSPHOLIPASE A2 (IIa) WITH ANTI-INFLAMMATORY ACTIVITY | PDB:1J1A | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.20 Å | Mutation | No | [1] |
| PDB Sequence |
NLVNFHRMIK
10 LTTGKEAALS20 YGFYGCHCGV30 GGRGSPKDAT40 DRCCVTHDCC50 YKRLEKRGCG 60 TKFLSYKFSN70 SGSRITCAKQ80 DSCRSQLCEC90 DKAAATCFAR100 NKTTYNKKYQ 110 YYSNKHCRGS120 TPRC
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Ligand Name: 3-(5'-Benzyl-2'-Carbamoylbiphenyl-3-Yl)propanoic Acid | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Discovery of a novel secreted phospholipase A2 (sPLA2) inhibitor. | PDB:5G3N | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.80 Å | Mutation | Yes | [11] |
| PDB Sequence |
ALVNFHRMIK
10 LTTGKEAALS20 YGFYGCHCGV30 GGRGSPKDAT40 DRCCVTHDCC50 YKRLEKRGCG 60 TKFLSYKFSN70 SGSRISCAKQ80 DSCRSQLCEC90 DKAAATCFAR100 NKTTYNKKYQ 110 YYSNKHCRGS120 TPRCGHH
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|






| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glycerophospholipid metabolism | hsa00564 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Lipid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Ether lipid metabolism | hsa00565 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Lipid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
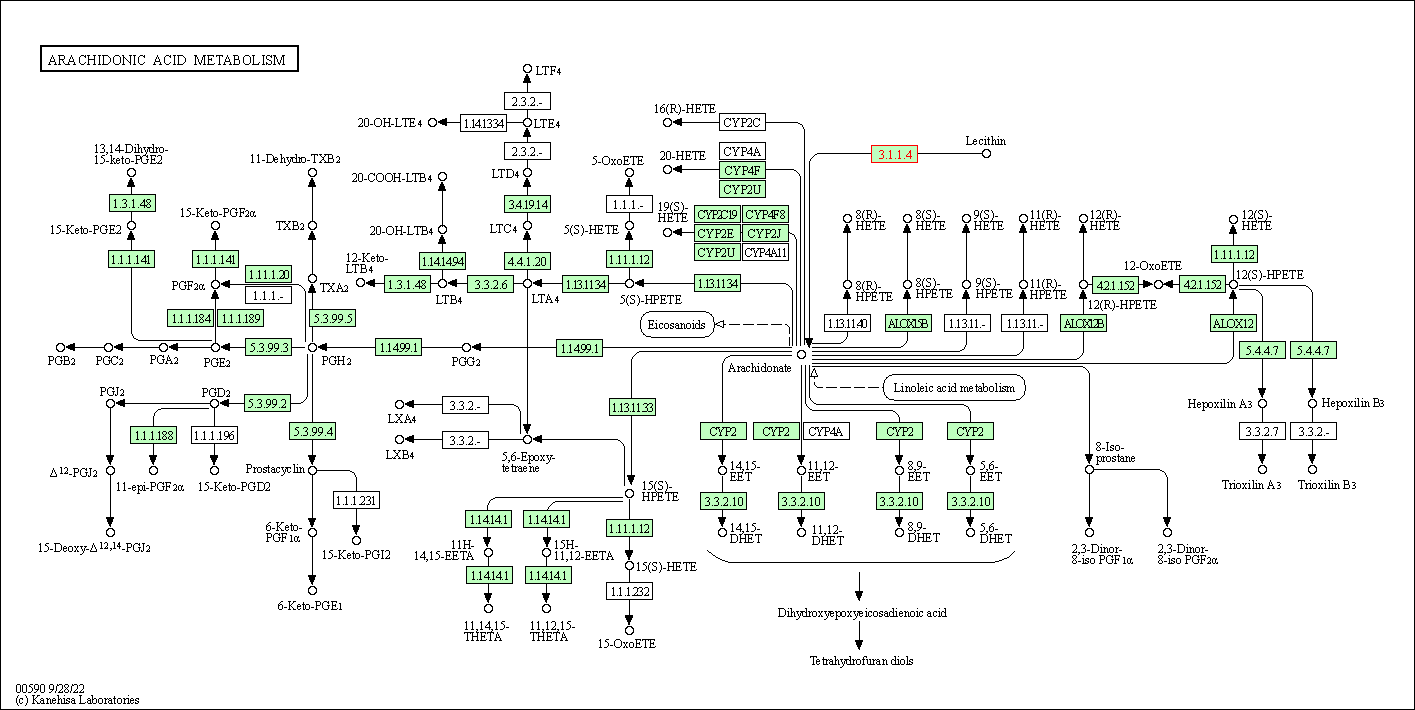
| Arachidonic acid metabolism | hsa00590 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Lipid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Linoleic acid metabolism | hsa00591 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Lipid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| alpha-Linolenic acid metabolism | hsa00592 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Lipid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
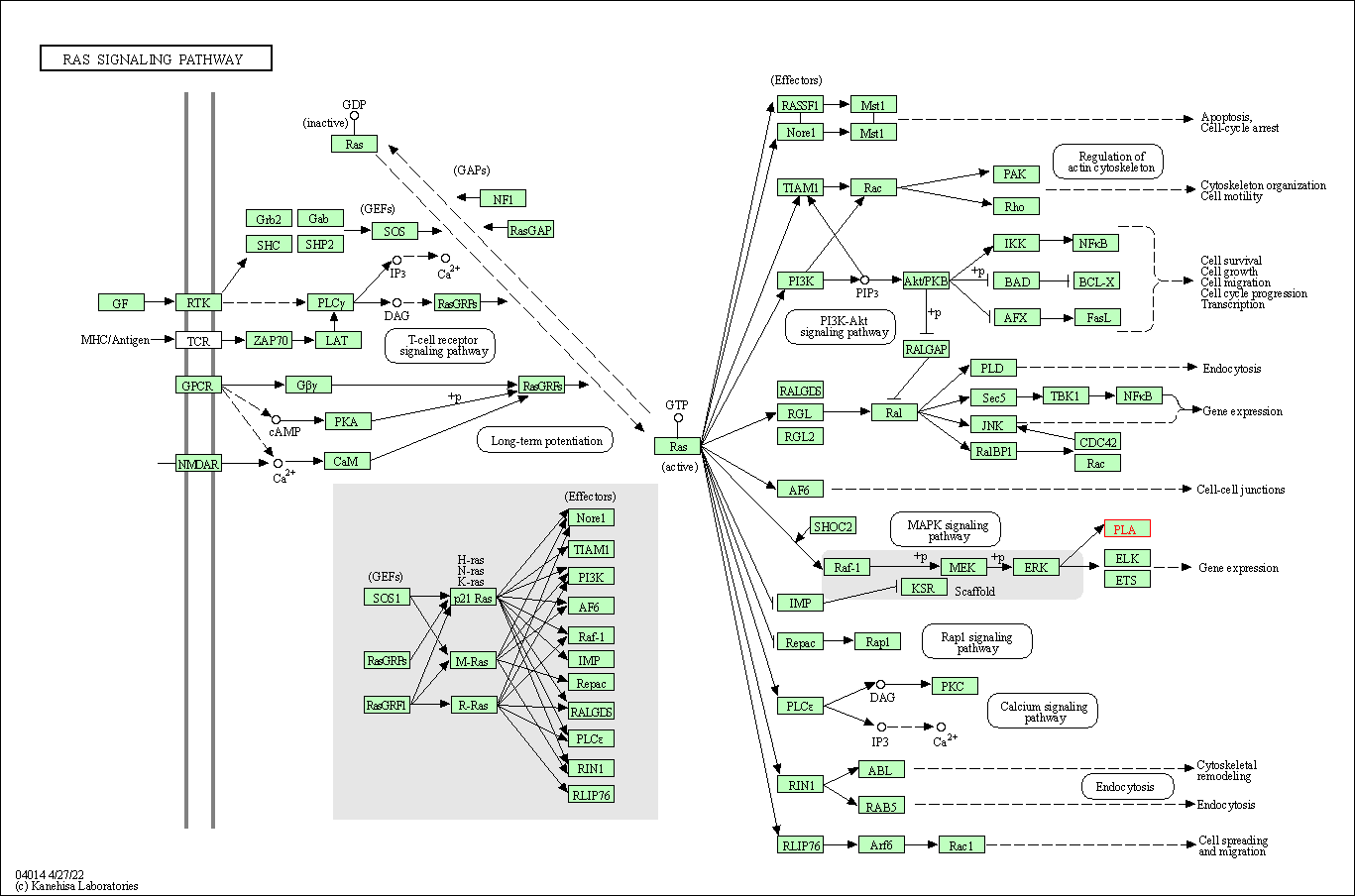
| Ras signaling pathway | hsa04014 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Vascular smooth muscle contraction | hsa04270 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Circulatory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
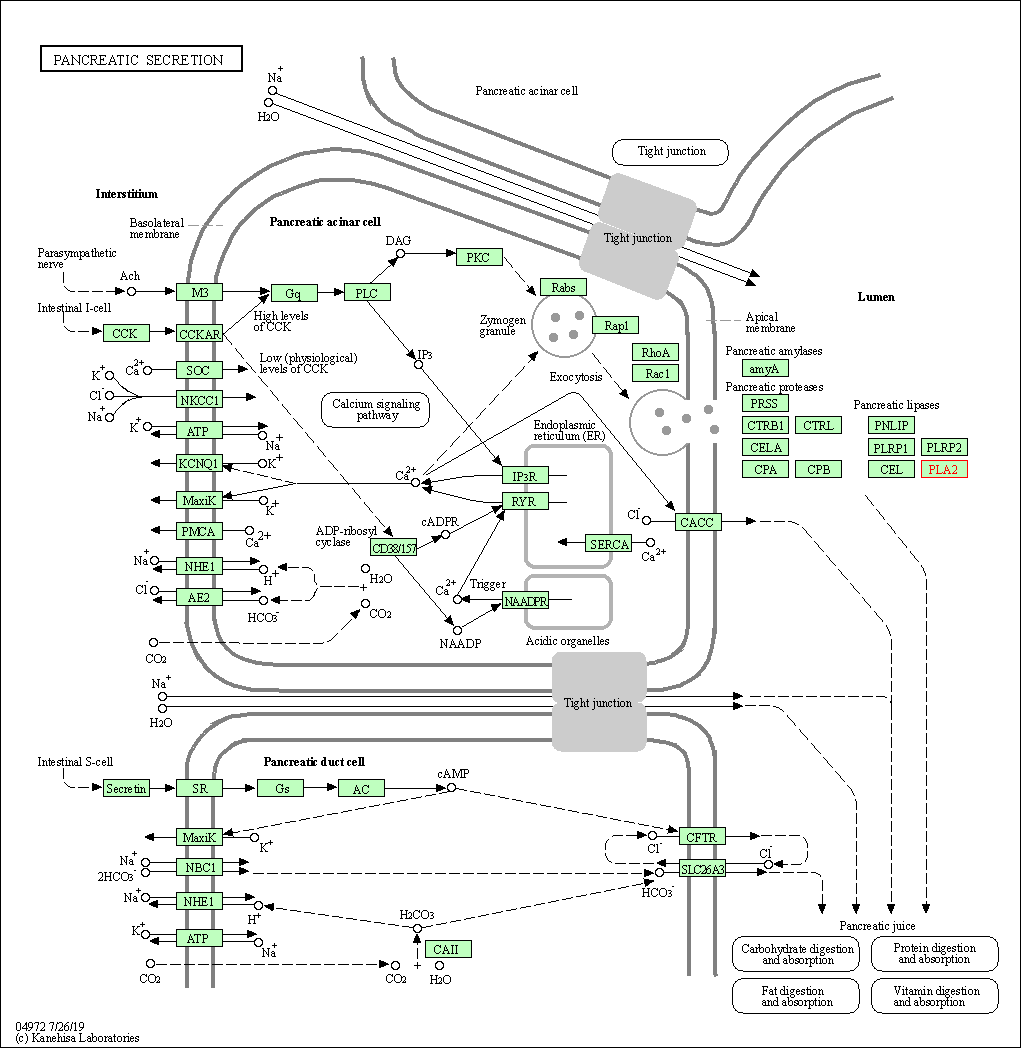
| Pancreatic secretion | hsa04972 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Fat digestion and absorption | hsa04975 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 2 | Degree centrality | 2.15E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 1.01E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.81E-01 | Radiality | 1.30E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 0.00E+00 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 1.10E+01 | Topological coefficient | 5.00E-01 | Eccentricity | 13 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BioCyc | [+] 1 BioCyc Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Phospholipases | |||||
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 10 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Glycerophospholipid metabolism | |||||
| 2 | Ether lipid metabolism | |||||
| 3 | Arachidonic acid metabolism | |||||
| 4 | Linoleic acid metabolism | |||||
| 5 | alpha-Linolenic acid metabolism | |||||
| 6 | Metabolic pathways | |||||
| 7 | Ras signaling pathway | |||||
| 8 | Vascular smooth muscle contraction | |||||
| 9 | Pancreatic secretion | |||||
| 10 | Fat digestion and absorption | |||||
| PID Pathway | [+] 1 PID Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Glypican 1 network | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 3 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Acyl chain remodelling of PC | |||||
| 2 | Acyl chain remodelling of PE | |||||
| 3 | Acyl chain remodelling of PI | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 6 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Cardiac Hypertrophic Response | |||||
| 2 | Glycerophospholipid biosynthesis | |||||
| 3 | Glycerophospholipid Biosynthetic Pathway | |||||
| 4 | Spinal Cord Injury | |||||
| 5 | Eicosanoid Synthesis | |||||
| 6 | MicroRNAs in cardiomyocyte hypertrophy | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | D-Tyrosine as a chiral precusor to potent inhibitors of human nonpancreatic secretory phospholipase A2 (IIa) with antiinflammatory activity. Chembiochem. 2003 Mar 3;4(2-3):181-5. | |||||
| REF 2 | Drosophila metabolize 1,4-butanediol into gamma-hydroxybutyric acid in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003 Jul 25;473(2-3):149-52. | |||||
| REF 3 | Discovery of multitarget inhibitors by combining molecular docking with common pharmacophore matching. J Med Chem. 2008 Dec 25;51(24):7882-8. | |||||
| REF 4 | The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1;28(1):235-42. | |||||
| REF 5 | How many drug targets are there Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. | |||||
| REF 6 | New sesquiterpene derivatives from the sponge Dysidea species with a selective inhibitor profile against human phospholipase A2 and other leukocyte... J Nat Prod. 2001 May;64(5):612-5. | |||||
| REF 7 | A new cacospongionolide inhibitor of human secretory phospholipase A2 from the Tyrrhenian sponge Fasciospongia cavernosa and absolute configuration... J Nat Prod. 1998 Jul;61(7):931-5. | |||||
| REF 8 | Simplified YM-26734 inhibitors of secreted phospholipase A2 group IIA. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008 Oct 15;18(20):5415-9. | |||||
| REF 9 | Phospholipase A2 inhibitors from marine organisms. J Nat Prod. 1992 Dec;55(12):1701-17. | |||||
| REF 10 | Synthesis of phospholipase A2 inhibitory biflavonoids. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006 May 1;16(9):2373-5. | |||||
| REF 11 | Discovery of AZD2716: A Novel Secreted Phospholipase A(2) (sPLA(2)) Inhibitor for the Treatment of Coronary Artery Disease. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2016 Aug 9;7(10):884-889. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

