Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T52522
(Former ID: TTDS00037)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Adrenergic receptor beta-2 (ADRB2)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Beta-2 adrenoreceptor; Beta-2 adrenoceptor; Beta-2 adrenergic receptor; B2AR; ADRB2R
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
ADRB2
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 5 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Asthma [ICD-11: CA23] | |||||
| 2 | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [ICD-11: CA22] | |||||
| 3 | Conduction disorder [ICD-11: BC63] | |||||
| 4 | Preterm labour/delivery [ICD-11: JB00] | |||||
| 5 | Sleep-related breathing disorder [ICD-11: 7A4Z] | |||||
| Function |
The beta-2-adrenergic receptor binds epinephrine with an approximately 30-fold greater affinity than it does norepinephrine. Beta-adrenergic receptors mediate the catecholamine-induced activation of adenylate cyclase through the action of G proteins.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
GPCR rhodopsin
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MGQPGNGSAFLLAPNGSHAPDHDVTQERDEVWVVGMGIVMSLIVLAIVFGNVLVITAIAK
FERLQTVTNYFITSLACADLVMGLAVVPFGAAHILMKMWTFGNFWCEFWTSIDVLCVTAS IETLCVIAVDRYFAITSPFKYQSLLTKNKARVIILMVWIVSGLTSFLPIQMHWYRATHQE AINCYANETCCDFFTNQAYAIASSIVSFYVPLVIMVFVYSRVFQEAKRQLQKIDKSEGRF HVQNLSQVEQDGRTGHGLRRSSKFCLKEHKALKTLGIIMGTFTLCWLPFFIVNIVHVIQD NLIRKEVYILLNWIGYVNSGFNPLIYCRSPDFRIAFQELLCLRRSSLKAYGNGYSSNGNT GEQSGYHVEQEKENKLLCEDLPGTEDFVGHQGTVPSDNIDSQGRNCSTNDSLL Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| ADReCS ID | BADD_A02053 ; BADD_A04210 ; BADD_A06316 | |||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T92UWJ | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 19 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Arformoterol | Drug Info | Approved | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | [2], [3] | |
| 2 | Bambuterol | Drug Info | Approved | Asthma | [4], [5] | |
| 3 | Clenbuterol | Drug Info | Approved | Chronic breathing disorder | [6] | |
| 4 | Fenoterol | Drug Info | Approved | Asthma | [7], [8] | |
| 5 | Formoterol | Drug Info | Approved | Asthma | [9], [10] | |
| 6 | GW642444 | Drug Info | Approved | Asthma | [11], [12] | |
| 7 | Indacaterol | Drug Info | Approved | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | [13], [14] | |
| 8 | Isoetharine | Drug Info | Approved | Asthma | [15], [16] | |
| 9 | Isoproterenol | Drug Info | Approved | Heart block | [17] | |
| 10 | Levalbuterol | Drug Info | Approved | Asthma | [18], [19] | |
| 11 | Metaproterenol Sulfate | Drug Info | Approved | Asthma | [18], [20], [21] | |
| 12 | Olodaterol | Drug Info | Approved | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | [22], [23] | |
| 13 | Pirbuterol | Drug Info | Approved | Asthma | [24], [5] | |
| 14 | Procaterol | Drug Info | Approved | Asthma | [25], [26] | |
| 15 | Ritodrine | Drug Info | Approved | Premature labour | [27], [28] | |
| 16 | Salbutamol | Drug Info | Approved | Acute asthma | [29], [30] | |
| 17 | Salmeterol | Drug Info | Approved | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | [31], [5] | |
| 18 | Terbutaline | Drug Info | Approved | Asthma | [32], [33] | |
| 19 | Vilanterol | Drug Info | Approved | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | [18], [34], [35] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 17 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | GSK642444 | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | [36] | |
| 2 | ICI 118,551 | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Gastric adenocarcinoma | [37] | |
| 3 | PT005 | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | [38] | |
| 4 | QVA-149 | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | [39] | |
| 5 | BUCINDOLOL | Drug Info | Phase 2/3 | Atrial fibrillation | [40] | |
| 6 | APD-209 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Cachexia | [41] | |
| 7 | AZD-2115 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | [42] | |
| 8 | AZD-3199 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Asthma | [43] | |
| 9 | Carmoterol | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | [44], [36] | |
| 10 | GSK961081 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | [45] | |
| 11 | LAS 100977 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | [46] | |
| 12 | MN-221 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Exacerbation of acute asthma | [47] | |
| 13 | R-salbutamol sulphate | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Skin infection | [48] | |
| 14 | TA-2005 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | [3] | |
| 15 | THRX-198321 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | [49] | |
| 16 | KUL-7211 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Neurogenic bladder dysfunction | [50] | |
| 17 | L-796568 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Obesity | [51] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 12 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Meluadrine | Drug Info | Discontinued in Preregistration | Premature ejaculation | [52] | |
| 2 | Broxaterol | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 3 | Asthma | [53] | |
| 3 | Sibenadet | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 3 | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | [54] | |
| 4 | GSK-159797 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | [3] | |
| 5 | GSK159802 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Asthma | [55] | |
| 6 | Milveterol | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Asthma | [36] | |
| 7 | Milveterol+Fluticasone | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | [56] | |
| 8 | PF-610355 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | [57] | |
| 9 | Picumeterol | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Asthma | [58] | |
| 10 | AR-C-89855 | Drug Info | Terminated | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | [59] | |
| 11 | DPI-201-106 | Drug Info | Terminated | Cardiovascular disease | [60] | |
| 12 | RP-58802B | Drug Info | Terminated | Asthma | [61] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 4 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Agonist | [+] 31 Agonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Arformoterol | Drug Info | [62], [63] | |||
| 2 | Bambuterol | Drug Info | [64] | |||
| 3 | Clenbuterol | Drug Info | [65], [66] | |||
| 4 | Fenoterol | Drug Info | [67], [68] | |||
| 5 | Formoterol | Drug Info | [69], [70], [71] | |||
| 6 | GW642444 | Drug Info | [72] | |||
| 7 | Indacaterol | Drug Info | [36], [3] | |||
| 8 | Pirbuterol | Drug Info | [77], [78] | |||
| 9 | Procaterol | Drug Info | [79], [80] | |||
| 10 | Salbutamol | Drug Info | [81] | |||
| 11 | Salmeterol | Drug Info | [82] | |||
| 12 | Terbutaline | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 13 | GSK642444 | Drug Info | [11], [12], [36] | |||
| 14 | PT005 | Drug Info | [84] | |||
| 15 | QVA-149 | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 16 | APD-209 | Drug Info | [88] | |||
| 17 | AZD-2115 | Drug Info | [89] | |||
| 18 | AZD-3199 | Drug Info | [90] | |||
| 19 | Carmoterol | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 20 | LAS 100977 | Drug Info | [92] | |||
| 21 | MN-221 | Drug Info | [93] | |||
| 22 | R-salbutamol sulphate | Drug Info | [94] | |||
| 23 | TA-2005 | Drug Info | [3] | |||
| 24 | GSK-159797 | Drug Info | [3] | |||
| 25 | GSK159802 | Drug Info | [72] | |||
| 26 | Milveterol | Drug Info | [72] | |||
| 27 | Milveterol+Fluticasone | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 28 | PF-610355 | Drug Info | [102] | |||
| 29 | Picumeterol | Drug Info | [103] | |||
| 30 | AR-C-89855 | Drug Info | [104] | |||
| 31 | D 2343 | Drug Info | [112] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 14 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Isoetharine | Drug Info | [73] | |||
| 2 | Isoproterenol | Drug Info | [74], [73] | |||
| 3 | Metaproterenol Sulfate | Drug Info | [76], [73] | |||
| 4 | Olodaterol | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 5 | Ritodrine | Drug Info | [73] | |||
| 6 | Vilanterol | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| 7 | BUCINDOLOL | Drug Info | [85], [86], [87] | |||
| 8 | GSK961081 | Drug Info | [91] | |||
| 9 | THRX-198321 | Drug Info | [95] | |||
| 10 | KUL-7211 | Drug Info | [96], [97] | |||
| 11 | Meluadrine | Drug Info | [99] | |||
| 12 | Broxaterol | Drug Info | [100] | |||
| 13 | Sibenadet | Drug Info | [101] | |||
| 14 | RP-58802B | Drug Info | [107] | |||
| Antagonist | [+] 3 Antagonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Levalbuterol | Drug Info | [75] | |||
| 2 | ICI 118,551 | Drug Info | [83] | |||
| 3 | Butoxamine | Drug Info | [111] | |||
| Inhibitor | [+] 12 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | L-796568 | Drug Info | [98] | |||
| 2 | DPI-201-106 | Drug Info | [105] | |||
| 3 | L-755507 | Drug Info | [106] | |||
| 4 | (R,R)-(-)-fenoterol | Drug Info | [108] | |||
| 5 | (R,S)-(-)-fenoterol | Drug Info | [108] | |||
| 6 | (S,R)-(+)-fenoterol | Drug Info | [108] | |||
| 7 | 1-(2-allylphenoxy)-3-morpholinopropan-2-ol | Drug Info | [109] | |||
| 8 | 1-(2-isopropylphenoxy)-3-morpholinopropan-2-ol | Drug Info | [109] | |||
| 9 | 2-fluoronorepinehprine | Drug Info | [110] | |||
| 10 | Dichloroisoproterenol | Drug Info | [113] | |||
| 11 | GNF-PF-1694 | Drug Info | [105] | |||
| 12 | [3H]CGP12177 | Drug Info | [106] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Salbutamol | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Cryo-EM structure of the partial agonist salbutamol-bound beta2 adrenergic receptor-Gs protein complex. | PDB:7DHI | ||||
| Method | Electron microscopy | Resolution | 3.26 Å | Mutation | Yes | [114] |
| PDB Sequence |
EVWVVGMGIV
39 MSLIVLAIVF49 GNVLVITAIA59 KFERLQTVTN69 YFITSLAVAD79 LVMGLAVVPF 89 GAAHILTKTW99 TFGNFWCEFW109 TSIDVLCVTA119 SIWTLVVIAV129 DRYFAITSPF 139 KYQSLLTKNK149 ARVIILMVWI159 VSGLTSFLPI169 QMHWYRATHQ179 EAINCYAEET 189 CCDFFTNQAY199 AIASSIVSFY209 VPLVIMVFVY219 SRVFQEAKRQ229 LQKIDKSEGR 239 FHVALKEHKA271 LKTLGIIMGT281 FTLAWLPFFI291 VNIVHVIQDN301 LIRKEVYILL 311 NWIGYVNSGF321 NPLIYSRSPD331 FRIAFQELLC341
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: Isoproterenol | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Cryo-EM structure of the full agonist isoprenaline-bound beta2 adrenergic receptor-Gs protein complex. | PDB:7DHR | ||||
| Method | Electron microscopy | Resolution | 3.80 Å | Mutation | Yes | [114] |
| PDB Sequence |
EVWVVGMGIV
39 MSLIVLAIVF49 GNVLVITAIA59 KFERLQTVTN69 YFITSLAVAD79 LVMGLAVVPF 89 GAAHILTKTW99 TFGNFWCEFW109 TSIDVLCVTA119 SIWTLVVIAV129 DRYFAITSPF 139 KYQSLLTKNK149 ARVIILMVWI159 VSGLTSFLPI169 QMHWYRAHQE180 AINCYAEETC 190 CDFFTNQAYA200 IASSIVSFYV210 PLVIMVFVYS220 RVFQEAKRQL230 QKIDKSEGRF 240 LKEHKALKTL275 GIIMGTFTLA285 WLPFFIVNIV295 HVIQDNLIRK305 EVYILLNWIG 315 YVNSGFNPLI325 YSRSPDFRIA335 FQEL
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium signaling pathway | hsa04020 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | hsa04022 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| cAMP signaling pathway | hsa04024 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | hsa04080 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
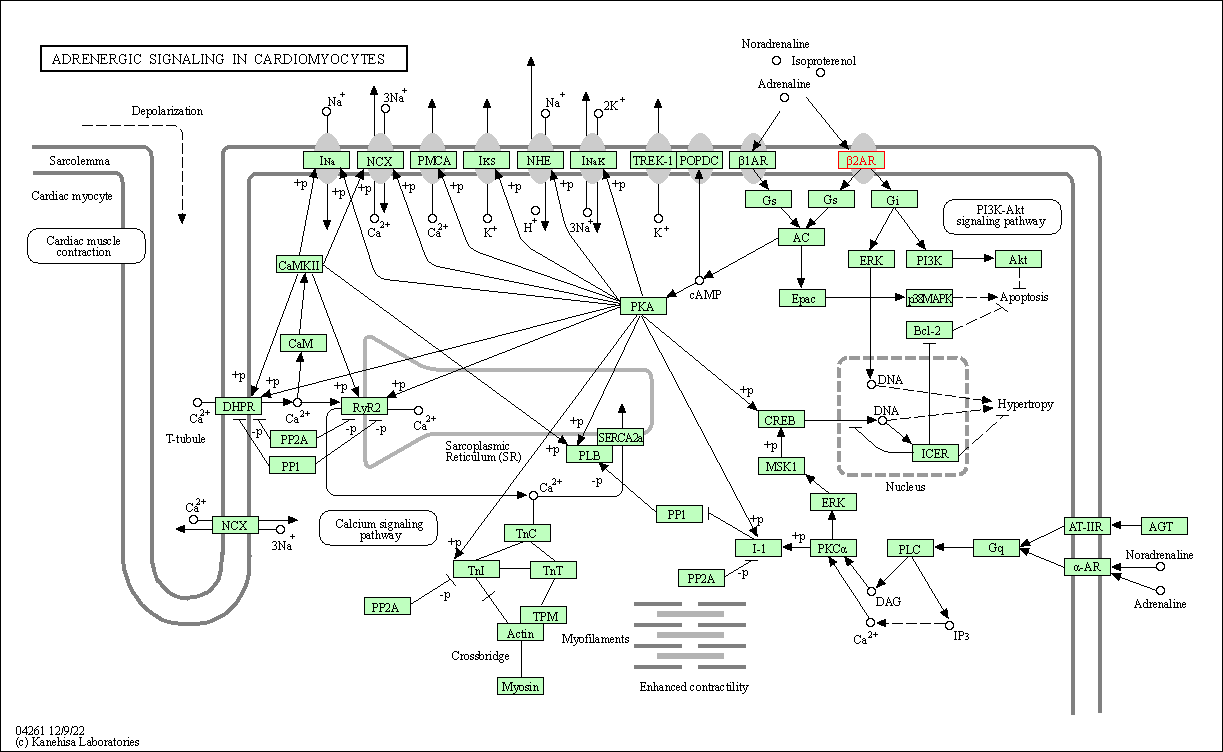
| Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes | hsa04261 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Circulatory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
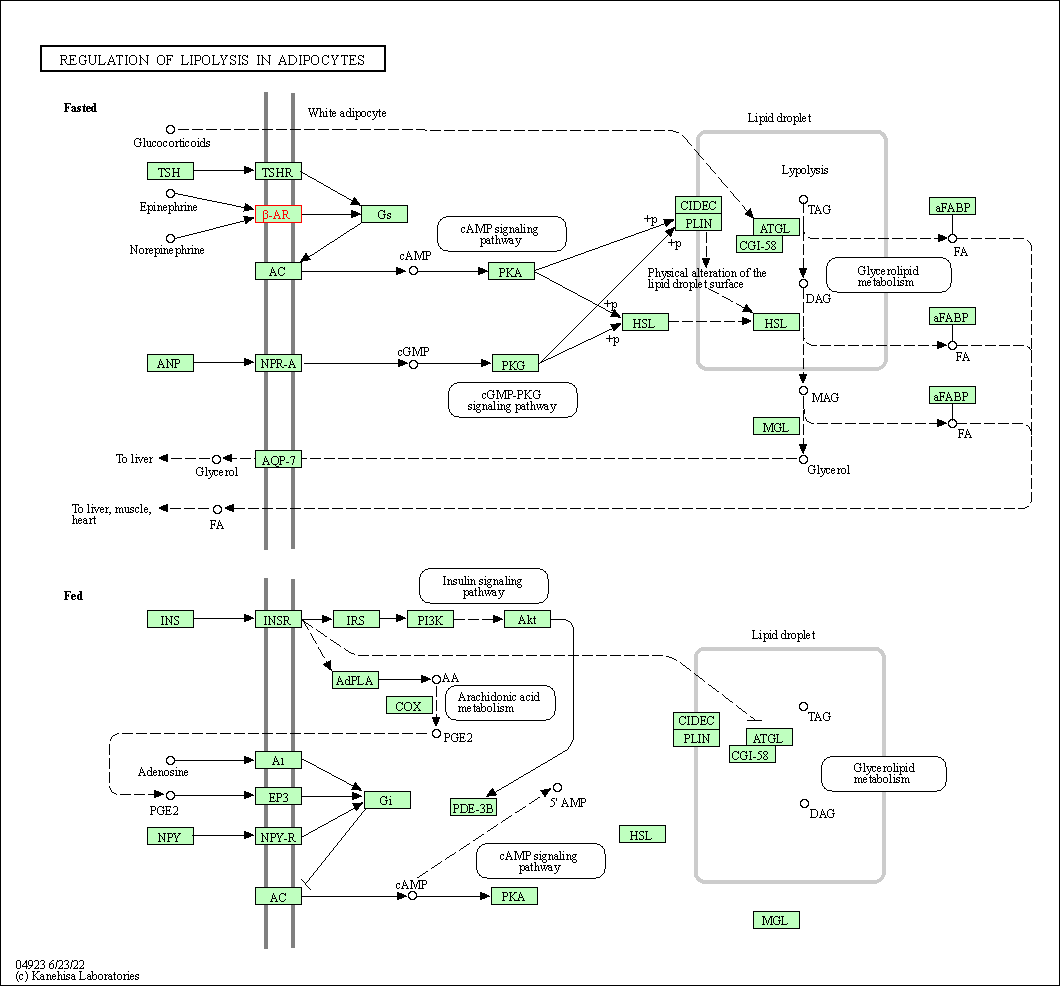
| Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes | hsa04923 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
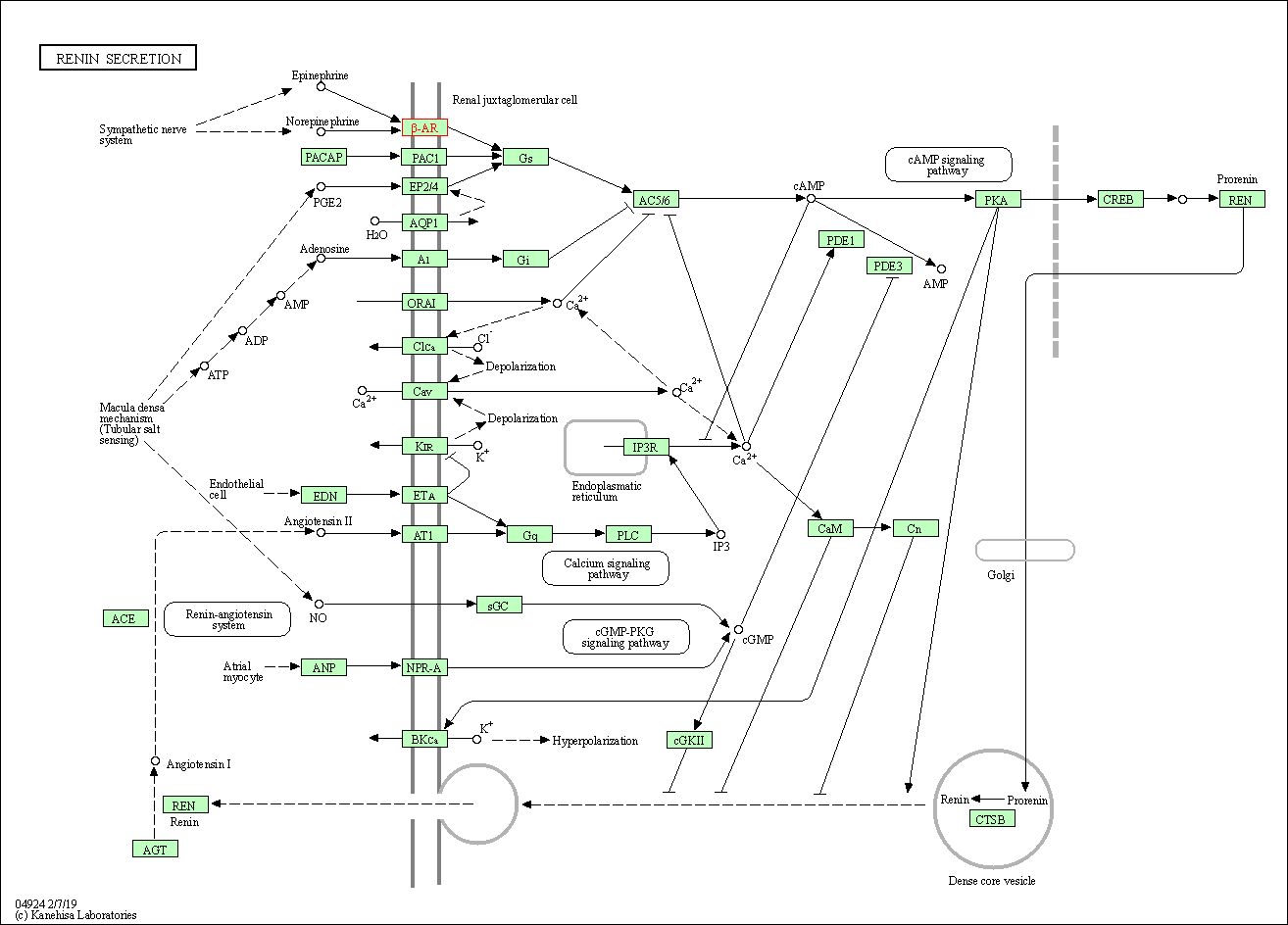
| Renin secretion | hsa04924 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
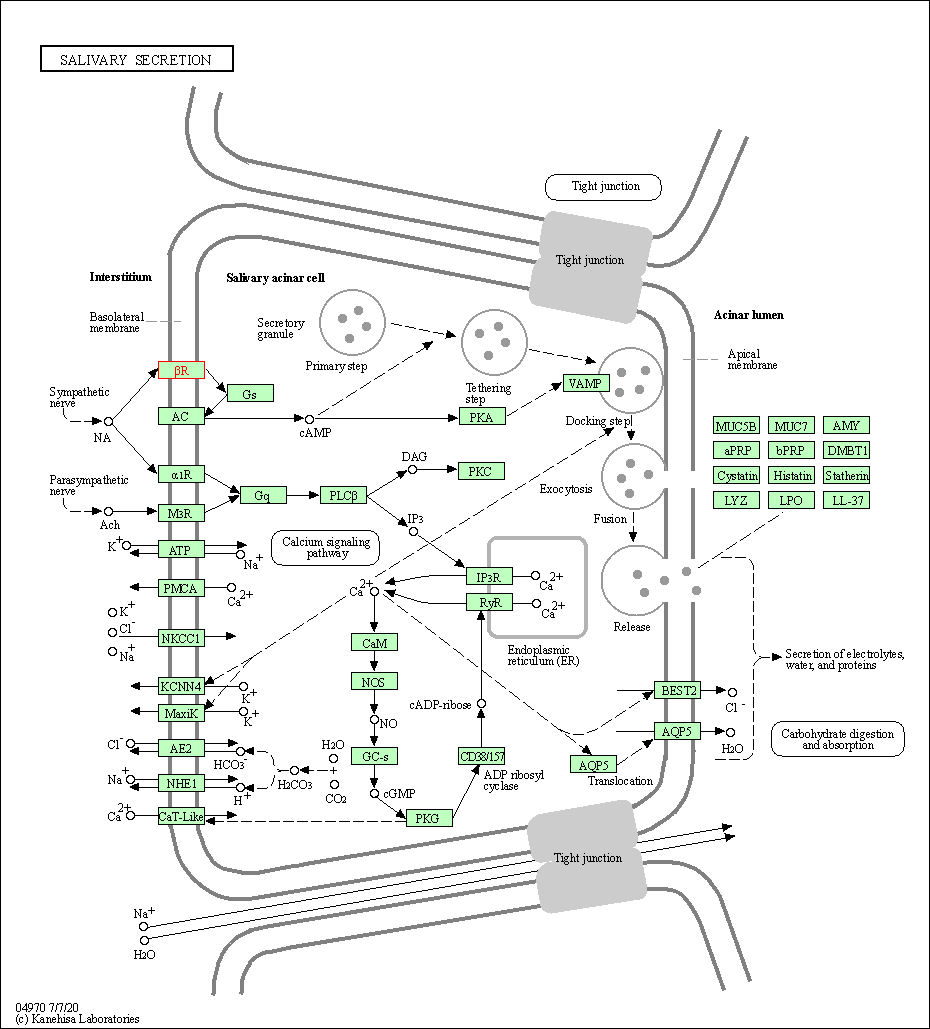
| Salivary secretion | hsa04970 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 19 | Degree centrality | 2.04E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 3.33E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.40E-01 | Radiality | 1.42E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 9.36E-02 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.48E+01 | Topological coefficient | 7.27E-02 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 7 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Calcium signaling pathway | |||||
| 2 | cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | |||||
| 3 | cAMP signaling pathway | |||||
| 4 | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | |||||
| 5 | Endocytosis | |||||
| 6 | Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes | |||||
| 7 | Salivary secretion | |||||
| NetPath Pathway | [+] 1 NetPath Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | TCR Signaling Pathway | |||||
| Panther Pathway | [+] 2 Panther Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Heterotrimeric G-protein signaling pathway-Gi alpha and Gs alpha mediated pathway | |||||
| 2 | Beta2 adrenergic receptor signaling pathway | |||||
| PID Pathway | [+] 2 PID Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Arf6 trafficking events | |||||
| 2 | Arf6 signaling events | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 2 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Adrenoceptors | |||||
| 2 | G alpha (s) signalling events | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 7 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Monoamine GPCRs | |||||
| 2 | Calcium Regulation in the Cardiac Cell | |||||
| 3 | GPCRs, Class A Rhodopsin-like | |||||
| 4 | Vitamin D Receptor Pathway | |||||
| 5 | GPCR ligand binding | |||||
| 6 | GPCR downstream signaling | |||||
| 7 | GPCRs, Other | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Evaluation of a new oral beta2-adrenoceptor stimulant bronchodilator, terbutaline. Pharmacology. 1975;13(3):201-11. | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7479). | |||||
| REF 3 | Emerging drugs for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2006 May;11(2):275-91. | |||||
| REF 4 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6601). | |||||
| REF 5 | Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod. 2007 Mar;70(3):461-77. | |||||
| REF 6 | Drug information of Clenbuterol, 2008. eduDrugs. | |||||
| REF 7 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 557). | |||||
| REF 8 | Acute clenbuterol overdose resulting in supraventricular tachycardia and atrial fibrillation. J Med Toxicol. 2007 Jun;3(2):56-60. | |||||
| REF 9 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 3465). | |||||
| REF 10 | Long duration of airway but not systemic effects of inhaled formoterol in asthmatic patients. Respir Med. 2008 Mar;102(3):449-56. | |||||
| REF 11 | Radium 223 dichloride for prostate cancer treatment. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017 Sep 6;11:2643-2651. | |||||
| REF 12 | Vilanterol trifenatate, a novel inhaled long-acting beta2 adrenoceptor agonist, is well tolerated in healthy subjects and demonstrates prolonged bronchodilation in subjects with asthma and COPD. PulmPharmacol Ther. 2013 Apr;26(2):256-64. | |||||
| REF 13 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7455). | |||||
| REF 14 | 2011 FDA drug approvals. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012 Feb 1;11(2):91-4. | |||||
| REF 15 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7205). | |||||
| REF 16 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (ANDA) 086711. | |||||
| REF 17 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (ANDA) 083346. | |||||
| REF 18 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 19 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800005434) | |||||
| REF 20 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7250). | |||||
| REF 21 | Drug information of Orciprenaline, 2008. eduDrugs. | |||||
| REF 22 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7543). | |||||
| REF 23 | 2014 FDA drug approvals. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015 Feb;14(2):77-81. | |||||
| REF 24 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7272). | |||||
| REF 25 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 3464). | |||||
| REF 26 | Drug information of Procaterol, 2008. eduDrugs. | |||||
| REF 27 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7294). | |||||
| REF 28 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (ANDA) 071438. | |||||
| REF 29 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 558). | |||||
| REF 30 | Emerging therapies for treatment of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2007 Sep;12(3):461-77. | |||||
| REF 31 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 559). | |||||
| REF 32 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 560). | |||||
| REF 33 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (ANDA) 075877. | |||||
| REF 34 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7353). | |||||
| REF 35 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01936649) Open-label, Test-retest Study Assessing Reproducibility of Quantitative Measurements of Myocardial Uptake of AdreView.. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 36 | Emerging drugs in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2009 Mar;14(1):181-94. | |||||
| REF 37 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 38 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02343458) Study to Assess the Efficacy and Safety of PT003, PT005, and PT001 in Subjects With Moderate to Very Severe COPD. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 39 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Novartis. | |||||
| REF 40 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 41 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01977443) Therapeutic Efficacy of APD-209 Eye Drops in Treatment of Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis (EKC). U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 42 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02109406) Efficacy and Safety Study of Two Dose Levels of AZD2115 in Subjects With Moderate to Severe COPD. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 43 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00736489) Single-dose Crossover Study to Investigate Pharmacodynamics of AZD3199. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 44 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7582). | |||||
| REF 45 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800024247) | |||||
| REF 46 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800026746) | |||||
| REF 47 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00683449) Study Evaluating the Safety and Effects of MN-221 in Subjects Experiencing an Acute Exacerbation of Asthma. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 48 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00625521) Efficacy and Safety of ASF-1096 Cream 0.5% in the Treatment of Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE) Lesions. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 49 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Theravance. | |||||
| REF 50 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800013676) | |||||
| REF 51 | Effect of a 28-d treatment with L-796568, a novel beta(3)-adrenergic receptor agonist, on energy expenditure and body composition in obese men. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002 Oct;76(4):780-8. | |||||
| REF 52 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800003111) | |||||
| REF 53 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800000105) | |||||
| REF 54 | Anti-obesity drugs and neural circuits of feeding. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Apr;29(4):208-17. | |||||
| REF 55 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800021784) | |||||
| REF 56 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of GlaxoSmithKline. | |||||
| REF 57 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800025582) | |||||
| REF 58 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800002942) | |||||
| REF 59 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800013263) | |||||
| REF 60 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800000134) | |||||
| REF 61 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800001694) | |||||
| REF 62 | Arformoterol tartrate in the treatment of bronchoconstriction in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Drugs Today (Barc). 2009 Jan;45(1):3-9. | |||||
| REF 63 | Arformoterol: (R,R)-eformoterol, (R,R)-formoterol, arformoterol tartrate, eformoterol-sepracor, formoterol-sepracor, R,R-eformoterol, R,R-formoterol. Drugs R D. 2004;5(1):25-7. | |||||
| REF 64 | Enantiomeric separation of beta2-agonists on macrocyclic antibiotic chiral stationary phases in high performance liquid chromatography. Pharmazie. 2007 Nov;62(11):836-40. | |||||
| REF 65 | Postischemic brain injury is attenuated in mice lacking the beta2-adrenergic receptor. Anesth Analg. 2009 Jan;108(1):280-7. | |||||
| REF 66 | Beta(2)-adrenoceptor stimulation enhances latent transforming growth factor-beta-binding protein-1 and transforming growth factor-beta1 expression in rat hippocampus after transient forebrain ischemia. Neuroscience. 2001;107(4):593-602. | |||||
| REF 67 | Functional alpha1- and beta2-adrenergic receptors in human osteoblasts. J Cell Physiol. 2009 Jul;220(1):267-75. | |||||
| REF 68 | Effect of fenoterol-induced constitutive beta(2)-adrenoceptor activity on contractile receptor function in airway smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001 Nov 23;431(3):353-9. | |||||
| REF 69 | Long-acting beta2-agonists for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients with poorly reversible airflow limitation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(3):CD001104. | |||||
| REF 70 | Tocolytic effects of a long-acting beta2-adrenoceptor agonist, formoterol, in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2000 Nov;52(11):1417-23. | |||||
| REF 71 | Long-acting beta2-agonists for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;(2):CD001104. | |||||
| REF 72 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of GlaxoSmithKline (2009). | |||||
| REF 73 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | |||||
| REF 74 | Current therapeutic uses and potential of beta-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1998 Feb;53(6):389-404. | |||||
| REF 75 | Beta-blockers in the treatment of hypertension: are there clinically relevant differences Postgrad Med. 2009 May;121(3):90-8. | |||||
| REF 76 | Male--female differences in the impact of beta-adrenoceptor stimulation on resistance to experimental metastasis: exploring the effects of age and ... J Neuroimmunol. 2008 Jan;193(1-2):113-9. | |||||
| REF 77 | Inhaled beta agonists. Respir Care. 2007 Jul;52(7):820-32. | |||||
| REF 78 | A chemical biology approach identifies a beta-2 adrenergic receptor agonist that causes human tumor regression by blocking the Raf-1/Mek-1/Erk1/2 p... Oncogene. 2007 May 31;26(26):3777-88. | |||||
| REF 79 | Inhalation and incubation with procaterol increases diaphragm muscle contractility in mice. Allergol Int. 2007 Sep;56(3):285-91. | |||||
| REF 80 | beta 2-adrenoceptor polymorphism and effect of inhaled beta 2-stimulant (procaterol) on airway resistance measured by body plethysmography in healthy volunteers. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2002 Aug;40(8):637-43. | |||||
| REF 81 | Potential of beta2-adrenoceptor agonists as add-on therapy for multiple sclerosis: focus on salbutamol (albuterol). CNS Drugs. 2002;16(1):1-8. | |||||
| REF 82 | Pharmacogenetic tests in asthma therapy. Clin Lab Med. 2008 Dec;28(4):645-65. | |||||
| REF 83 | Selective beta 2-adrenoceptor antagonists: derivatives of ICI 118,551 and a binary aryloxypropanolamine. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;40(11):803-5. | |||||
| REF 84 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Pearl Therapeutics. | |||||
| REF 85 | Bucindolol has serotonin and alpha-adrenoceptor blocking properties. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1985;7 Suppl 7:S67-9. | |||||
| REF 86 | Bucindolol, a nonselective beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptor antagonist, decreases beta-adrenergic receptor density in cultured embryonic chic... J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2001 Jun;37(6):678-91. | |||||
| REF 87 | Bucindolol: new hopes from reviewing past data.Drugs Today (Barc).2011 May;47(5):347-51. | |||||
| REF 88 | Drugs in development for treatment of patients with cancer-related anorexia and cachexia syndrome. Retraction in: Drug Des Devel Ther. 2013; 7: 1385. | |||||
| REF 89 | Evaluation of WO-2012085582 and WO-2012085583 two identified MABAs: backups to AZD-2115. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2012 Nov;22(11):1377-83. | |||||
| REF 90 | Clinical pharmacokinetics of AZD3199, an inhaled ultra-long-acting beta2-adrenoreceptor agonist (uLABA). Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015; 9: 753-762. | |||||
| REF 91 | Pharmacologic characterization of GSK-961081 (TD-5959), a first-in-class inhaled bifunctional bronchodilator possessing muscarinic receptor antagonist and 2-adrenoceptor agonist properties.J Pharmacol Exp Ther.2014 Oct;351(1):190-9. | |||||
| REF 92 | Pharmacological characterization of abediterol, a novel inhaled beta(2)-adrenoceptor agonist with long duration of action and a favorable safety profile in preclinical models. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012 Aug;342(2):497-509. | |||||
| REF 93 | Investigation of beta(2)-adrenoceptor subtype selectivity and organ specificity for bedoradrine (KUR-1246), a novel tocolytic beta-adrenergic receptor stimulant. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2009 Jun;35(3):405-13. | |||||
| REF 94 | Pharmacokinetics and extrapulmonary beta 2 adrenoceptor activity of nebulised racemic salbutamol and its R and S isomers in healthy volunteers. Thorax. 1997 Oct;52(10):849-52. | |||||
| REF 95 | THRX-198321 is a bifunctional muscarinic receptor antagonist and beta2-adrenoceptor agonist (MABA) that binds in a bimodal and multivalent manner. Mol Pharmacol. 2011 Mar;79(3):389-99. | |||||
| REF 96 | The potency of KUL-7211, a selective ureteral relaxant, in isolated canine ureter: comparison with various spasmolytics.Urol Res.2005 Dec;33(6):409-14. | |||||
| REF 97 | Pharmacological profile of KUL-7211, a selective beta-adrenoceptor agonist, in isolated ureteral smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Sci. 2003 Aug;92(4):411-9. | |||||
| REF 98 | Heterocyclic acetamide and benzamide derivatives as potent and selective beta3-adrenergic receptor agonists with improved rodent pharmacokinetic pr... Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Mar 15;20(6):1895-9. | |||||
| REF 99 | Effects of meluadrine tartrate and ritodrine hydrochloride on oxytocin-induced uterine contraction, uterine arterial blood flow and maternal cardiovascular function in pregnant goats. Jpn J Pharmacol. 2002 Oct;90(2):107-13. | |||||
| REF 100 | Broxaterol, a new beta 2-adrenoceptor agonist compared to salbutamol in asthmatics, oral and inhalation treatment. Respiration. 1989;55 Suppl 2:15-9. | |||||
| REF 101 | The role of the novel D2/beta2-agonist, Viozan (sibenadet HCl), in the treatment of symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: results of a... Respir Med. 2003 Jan;97 Suppl A:S23-33. | |||||
| REF 102 | Inhalation by design: novel ultra-long-acting beta(2)-adrenoreceptor agonists for inhaled once-daily treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease that utilize a sulfonamide agonist headgroup. J Med Chem. 2010 Sep 23;53(18):6640-52. | |||||
| REF 103 | Picumeterol: dissociation of improvement in lung function and reduction of airways hyperresponsiveness in asthmatics. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1997 Feb;43(2):169-76. | |||||
| REF 104 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800013263) | |||||
| REF 105 | Use of the X-ray structure of the beta2-adrenergic receptor for drug discovery. Part 2: Identification of active compounds. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008 Oct 15;18(20):5391-5. | |||||
| REF 106 | (4-Piperidin-1-yl)phenyl amides: potent and selective human beta(3) agonists. J Med Chem. 2001 Apr 26;44(9):1456-66. | |||||
| REF 107 | RP 58802B, a long-acting beta 2-adrenoceptor agonist: assessment of antiasthma activity in the guinea-pig in vivo. Pulm Pharmacol. 1992 Sep;5(3):203-12. | |||||
| REF 108 | Comparative molecular field analysis of the binding of the stereoisomers of fenoterol and fenoterol derivatives to the beta2 adrenergic receptor. J Med Chem. 2007 Jun 14;50(12):2903-15. | |||||
| REF 109 | A vHTS approach for the identification of beta-adrenoceptor ligands. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Jun 1;20(11):3399-404. | |||||
| REF 110 | Structural basis of the selectivity of the beta(2)-adrenergic receptor for fluorinated catecholamines. Bioorg Med Chem. 2009 Dec 1;17(23):7987-92. | |||||
| REF 111 | Partial agonistic effects of carteolol on atypical beta-adrenoceptors in the guinea pig gastric fundus. Jpn J Pharmacol. 2000 Nov;84(3):287-92. | |||||
| REF 112 | A new beta 2-adrenoceptor agonist--D 2343--with long duration. Inhalation comparison with terbutaline in asthmatics. Allergy. 1984 Aug;39(6):485-9. | |||||
| REF 113 | The [(methyloxy)imino]methyl moiety as a bioisoster of aryl. A novel class of completely aliphatic beta-adrenergic receptor antagonists. J Med Chem. 1994 May 13;37(10):1518-25. | |||||
| REF 114 | Different Conformational Responses of the beta2-Adrenergic Receptor-Gs Complex upon Binding of the Partial Agonist Salbutamol or the Full Agonist Isoprenaline. doi:10.1093/nsr/nwaa284. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

