Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T53389
(Former ID: TTDR00998)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
TGF-beta receptor type I (TGFBR1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Type I TGFbeta receptor kinase; Transforming growth factor-beta receptor type I; TbetaRI; TbetaR-I; TGFR-1; TGF-beta type I receptor; TGF-beta receptor type-1; Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor R4; SKR4; Activin receptor-like kinase 5; Activin A receptor type II-like protein kinase of 53kD; ALK5; ALK-5
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
TGFBR1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Arterial occlusive disease [ICD-11: BD40] | |||||
| 2 | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||||
| Function |
Transduces the TGFB1, TGFB2 and TGFB3 signal from the cell surface to the cytoplasm and is thus regulating a plethora of physiological and pathological processes including cell cycle arrest in epithelial and hematopoietic cells, control of mesenchymal cell proliferation and differentiation, wound healing, extracellular matrix production, immunosuppression and carcinogenesis. The formation of the receptor complex composed of 2 TGFBR1 and 2 TGFBR2 molecules symmetrically bound to the cytokine dimer results in the phosphorylation and the activation of TGFBR1 by the constitutively active TGFBR2. Activated TGFBR1 phosphorylates SMAD2 which dissociates from the receptor and interacts with SMAD4. The SMAD2-SMAD4 complex is subsequently translocated to the nucleus where it modulates the transcription of the TGF-beta-regulated genes. This constitutes the canonical SMAD-dependent TGF-beta signaling cascade. Also involved in non-canonical, SMAD-independent TGF-beta signaling pathways. For instance, TGFBR1 induces TRAF6 autoubiquitination which in turn results in MAP3K7 ubiquitination and activation to trigger apoptosis. Also regulates epithelial to mesenchymal transition through a SMAD-independent signaling pathway through PARD6A phosphorylation and activation. Transmembrane serine/threonine kinase forming with the TGF-beta type II serine/threonine kinase receptor, TGFBR2, the non-promiscuous receptor for the TGF-beta cytokines TGFB1, TGFB2 and TGFB3.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.30
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MEAAVAAPRPRLLLLVLAAAAAAAAALLPGATALQCFCHLCTKDNFTCVTDGLCFVSVTE
TTDKVIHNSMCIAEIDLIPRDRPFVCAPSSKTGSVTTTYCCNQDHCNKIELPTTVKSSPG LGPVELAAVIAGPVCFVCISLMLMVYICHNRTVIHHRVPNEEDPSLDRPFISEGTTLKDL IYDMTTSGSGSGLPLLVQRTIARTIVLQESIGKGRFGEVWRGKWRGEEVAVKIFSSREER SWFREAEIYQTVMLRHENILGFIAADNKDNGTWTQLWLVSDYHEHGSLFDYLNRYTVTVE GMIKLALSTASGLAHLHMEIVGTQGKPAIAHRDLKSKNILVKKNGTCCIADLGLAVRHDS ATDTIDIAPNHRVGTKRYMAPEVLDDSINMKHFESFKRADIYAMGLVFWEIARRCSIGGI HEDYQLPYYDLVPSDPSVEEMRKVVCEQKLRPNIPNRWQSCEALRVMAKIMRECWYANGA ARLTALRIKKTLSQLSQQEGIKM Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T71KM2 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 7 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | LY2157299 | Drug Info | Phase 2/3 | Arteriosclerosis | [2], [3] | |
| 2 | TEW-7197 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Myeloproliferative neoplasm | [4] | |
| 3 | Metelimumab | Drug Info | Phase 1/2 | Scleroderma | [5] | |
| 4 | LY3200882 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [6] | |
| 5 | P-2745 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Chronic myelogenous leukaemia | [7] | |
| 6 | PF-06952229 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [8] | |
| 7 | TP-0184 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [9] | |
| Preclinical Drug(s) | [+] 1 Preclinical Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | SB-431542 | Drug Info | Preclinical | Pulmonary fibrosis | [10] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 2 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | LF-984 | Drug Info | Terminated | Fibrosis | [11] | |
| 2 | SM-16 | Drug Info | Terminated | Fibrosis | [12] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 3 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Modulator | [+] 5 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | LY2157299 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | TEW-7197 | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 3 | P-2745 | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 4 | PTL-101 | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 5 | WilVent | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| Inhibitor | [+] 25 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | LY3200882 | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 2 | PF-06952229 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 3 | TP-0184 | Drug Info | [17] | |||
| 4 | SB-431542 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 5 | LF-984 | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 6 | SM-16 | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| 7 | 2-phenyl-N-(pyridin-4-yl)quinazolin-4-amine | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 8 | 4-Pyridin-2-yl-5-quinolin-2-yl-thiazol-2-ylamine | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 9 | 4-Pyridin-2-yl-5-quinolin-4-yl-thiazol-2-ylamine | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 10 | 4-Pyridin-3-yl-5-quinolin-4-yl-thiazol-2-ylamine | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 11 | 5''-Quinolin-4-yl-[2,4'']bithiazolyl-2''-ylamine | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 12 | ACE-435 | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 13 | DRP-049 | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 14 | GW-788388 | Drug Info | [24] | |||
| 15 | HTS-466284 | Drug Info | [25], [26] | |||
| 16 | IN-1130 | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 17 | IN-1166 | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| 18 | LDN-214117 | Drug Info | [29] | |||
| 19 | LY2109761 | Drug Info | [30] | |||
| 20 | PMID16539403C15b | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 21 | PMID23639540C13d | Drug Info | [31] | |||
| 22 | PMID23639540C13r | Drug Info | [31] | |||
| 23 | SB-505124 | Drug Info | [32] | |||
| 24 | SB-525334 | Drug Info | [32] | |||
| 25 | SD-208 | Drug Info | [33] | |||
| Antagonist | [+] 1 Antagonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | TGF-beta Shield | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: SB-431542 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | TGF-beta Receptor type 1 in complex with SB431542 | PDB:3TZM | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.70 Å | Mutation | No | [34] |
| PDB Sequence |
TIARTIVLQE
209 SIGKGRFGEV219 WRGKWRGEEV229 AVKIFSSREE239 RSWFREAEIY249 QTVMLRHENI 259 LGFIAADNKD269 NGTWTQLWLV279 SDYHEHGSLF289 DYLNRYTVTV299 EGMIKLALST 309 ASGLAHLHME319 IVGTQGKPAI329 AHRDLKSKNI339 LVKKNGTCCI349 ADLGLAVRHD 359 SATDTIDIAP369 RVGTKRYMAP381 EVLDDSINMK391 HFESFKRADI401 YAMGLVFWEI 411 ARRCSIGGIH421 EDYQLPYYDL431 VPSDPSVEEM441 RKVVCEQKLR451 PNIPNRWQSC 461 EALRVMAKIM471 RECWYANGAA481 RLTALRIKKT491 LSQLS
|
|||||
|
|
ILE211
3.642
LYS213
4.467
GLY214
3.653
ARG215
3.814
VAL219
4.020
ALA230
3.283
VAL231
4.181
LYS232
3.091
GLU245
3.973
TYR249
4.592
LEU260
3.818
LEU278
3.542
VAL279
4.200
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: HTS-466284 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal Structure of TGF-beta receptor I kinase with inhibitor | PDB:1PY5 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.30 Å | Mutation | No | [35] |
| PDB Sequence |
TIARTIVLQE
209 SIGKGRFGEV219 WRGKWRGEEV229 AVKIFSSREE239 RSWFREAEIY249 QTVMLRHENI 259 LGFIAADNKD269 NGTWTQLWLV279 SDYHEHGSLF289 DYLNRYTVTV299 EGMIKLALST 309 ASGLAHLHME319 IVGTQGKPAI329 AHRDLKSKNI339 LVKKNGTCCI349 ADLGLAVRHD 359 SATDTIDIAP369 NHRVGTKRYM379 APEVLDDSIN389 MKHFESFKRA399 DIYAMGLVFW 409 EIARRCSIGG419 IHEDYQLPYY429 DLVPSDPSVE439 EMRKVVCEQK449 LRPNIPNRWQ 459 SCEALRVMAK469 IMRECWYANG479 AARLTALRIK489 KTLSQLSQQE499 G |
|||||
|
|
ILE211
3.173
VAL219
3.784
ALA230
3.469
VAL231
3.670
LYS232
3.567
GLU245
4.005
TYR249
4.751
LEU260
3.532
LEU278
3.148
VAL279
4.174
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
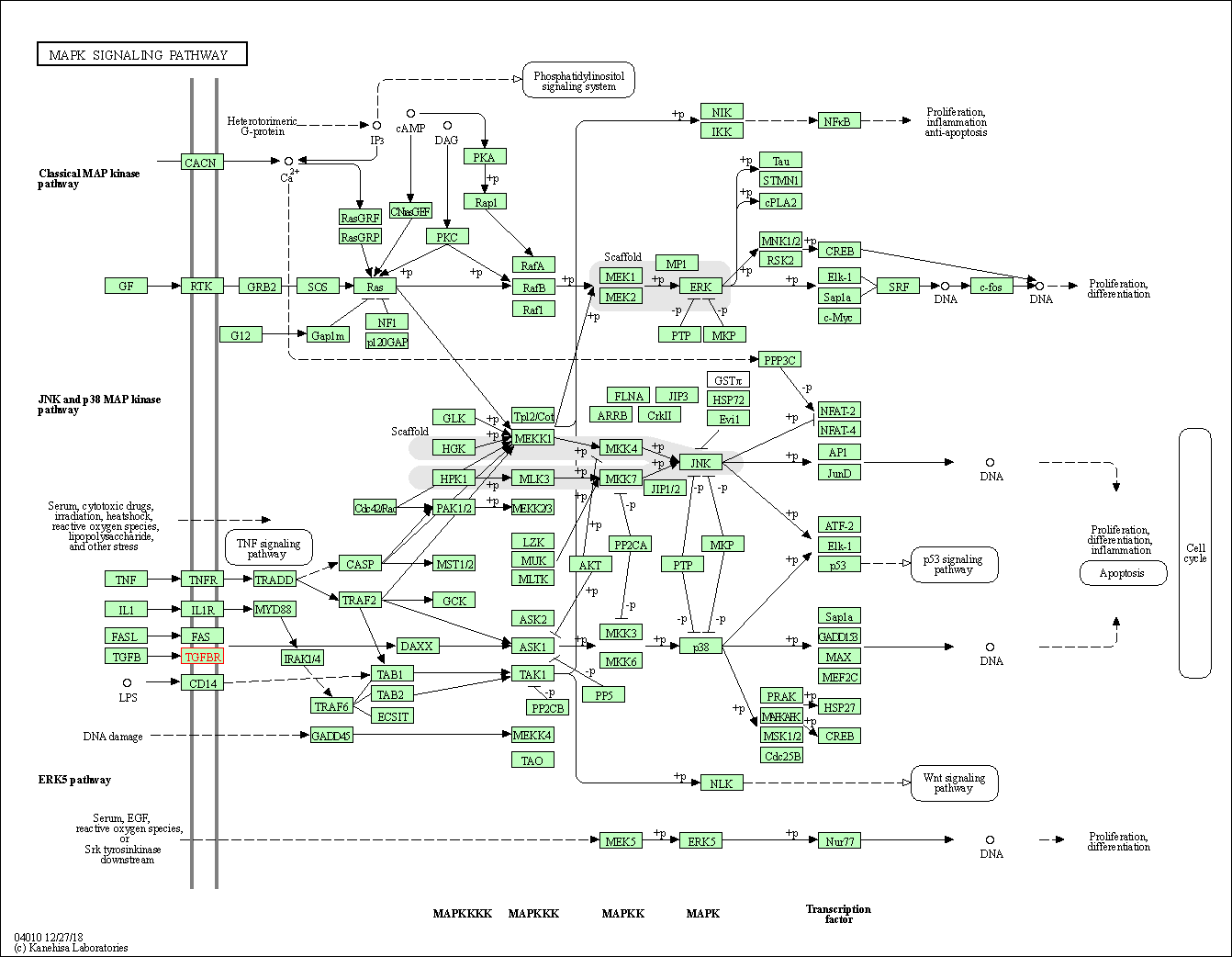
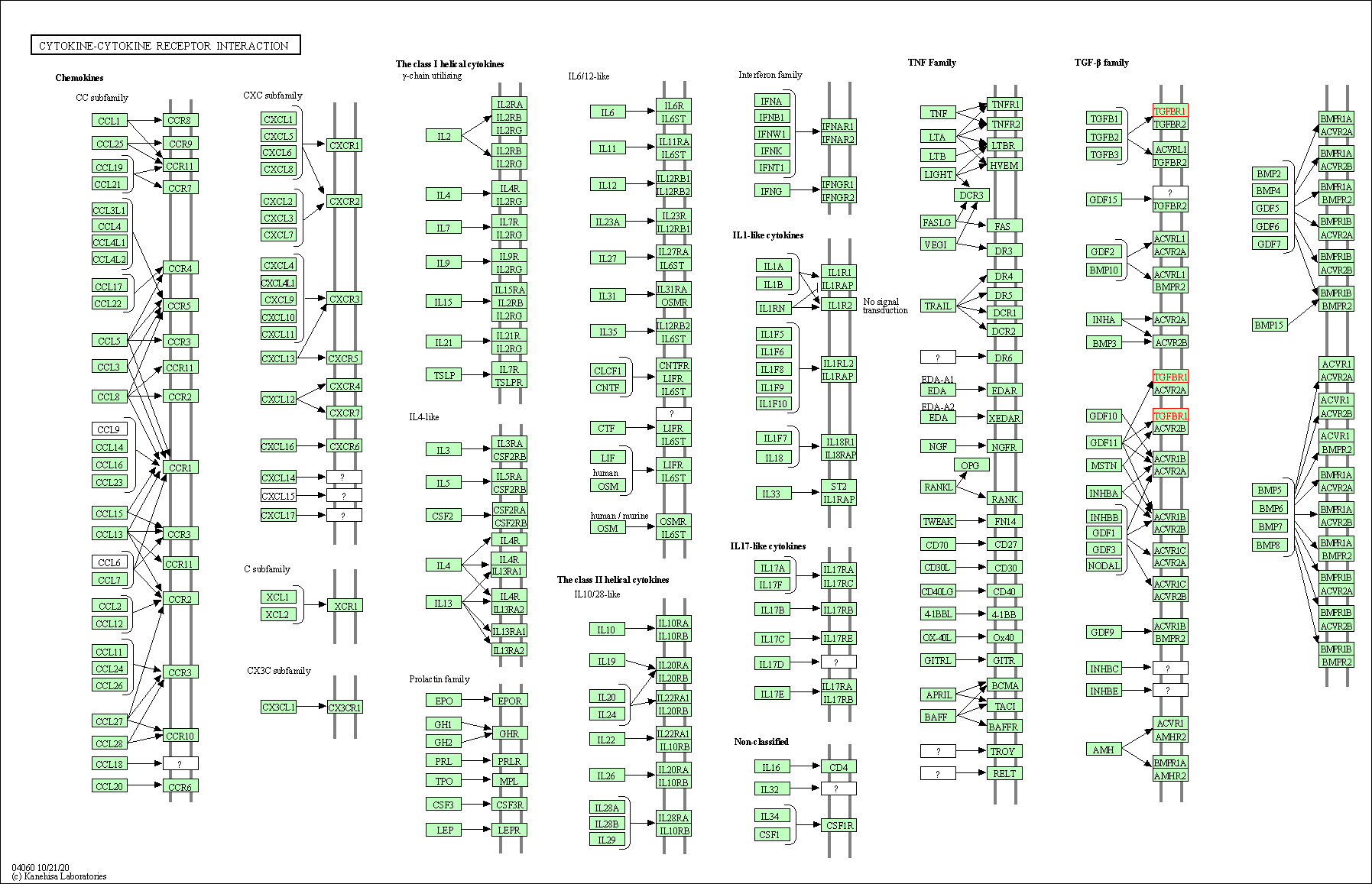
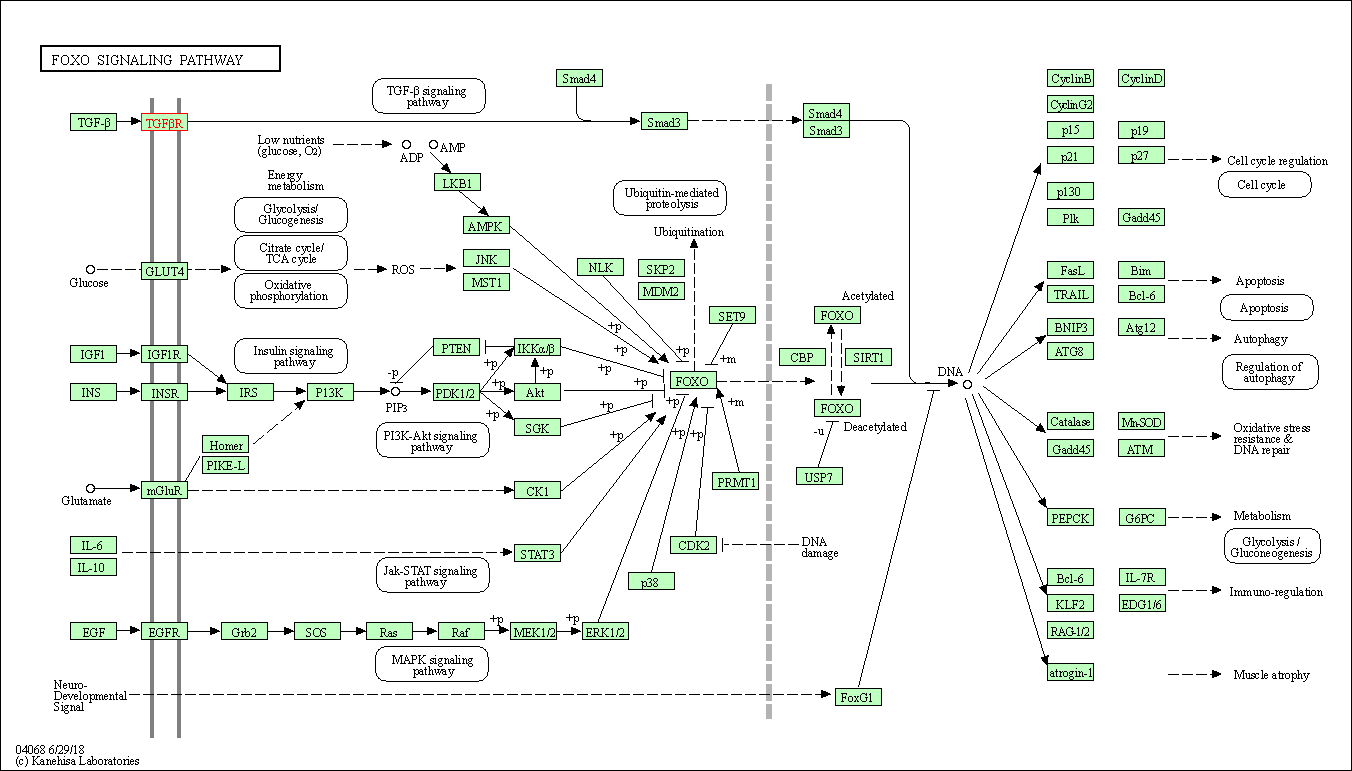
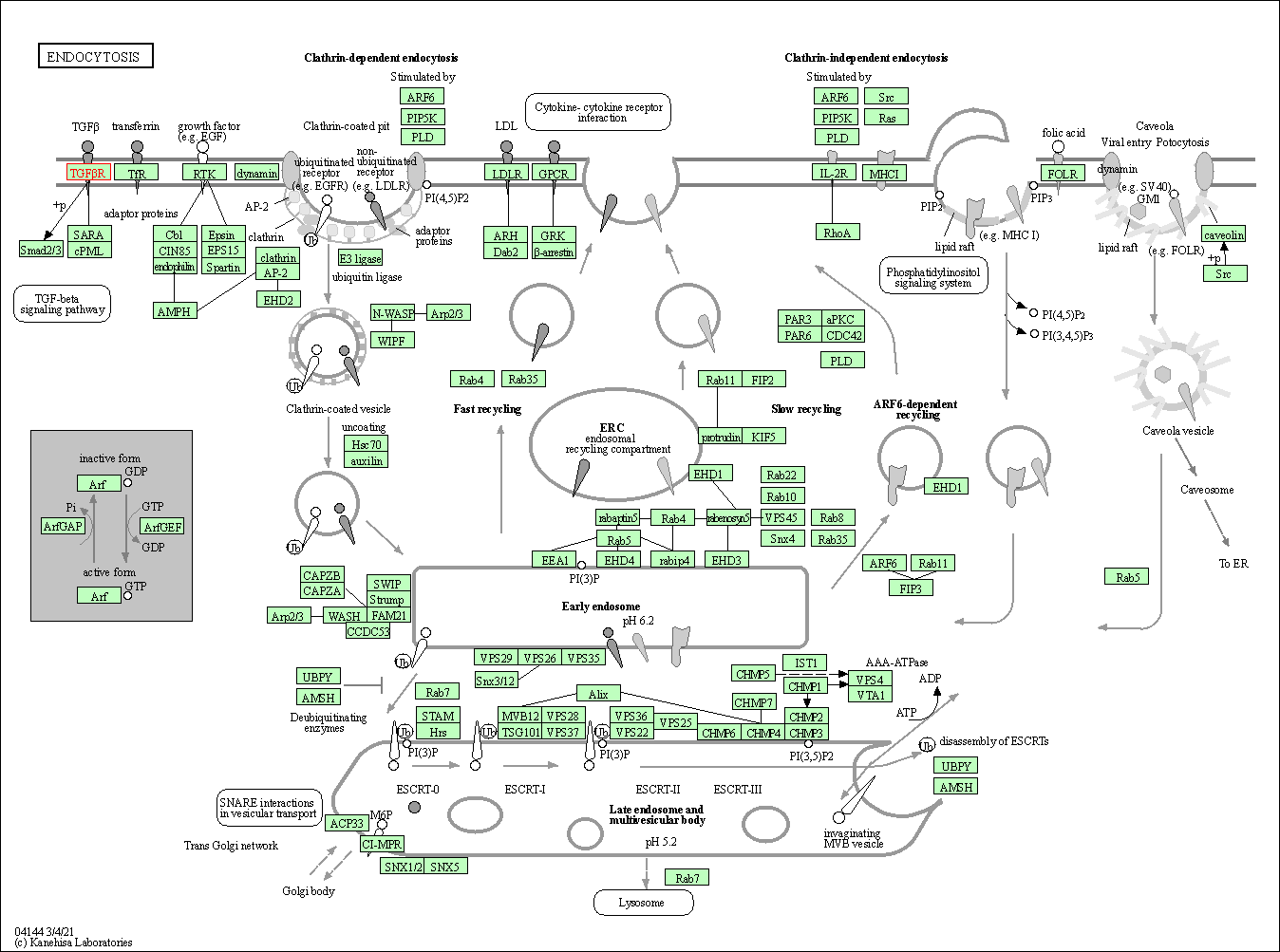
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | hsa04060 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| FoxO signaling pathway | hsa04068 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Endocytosis | hsa04144 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
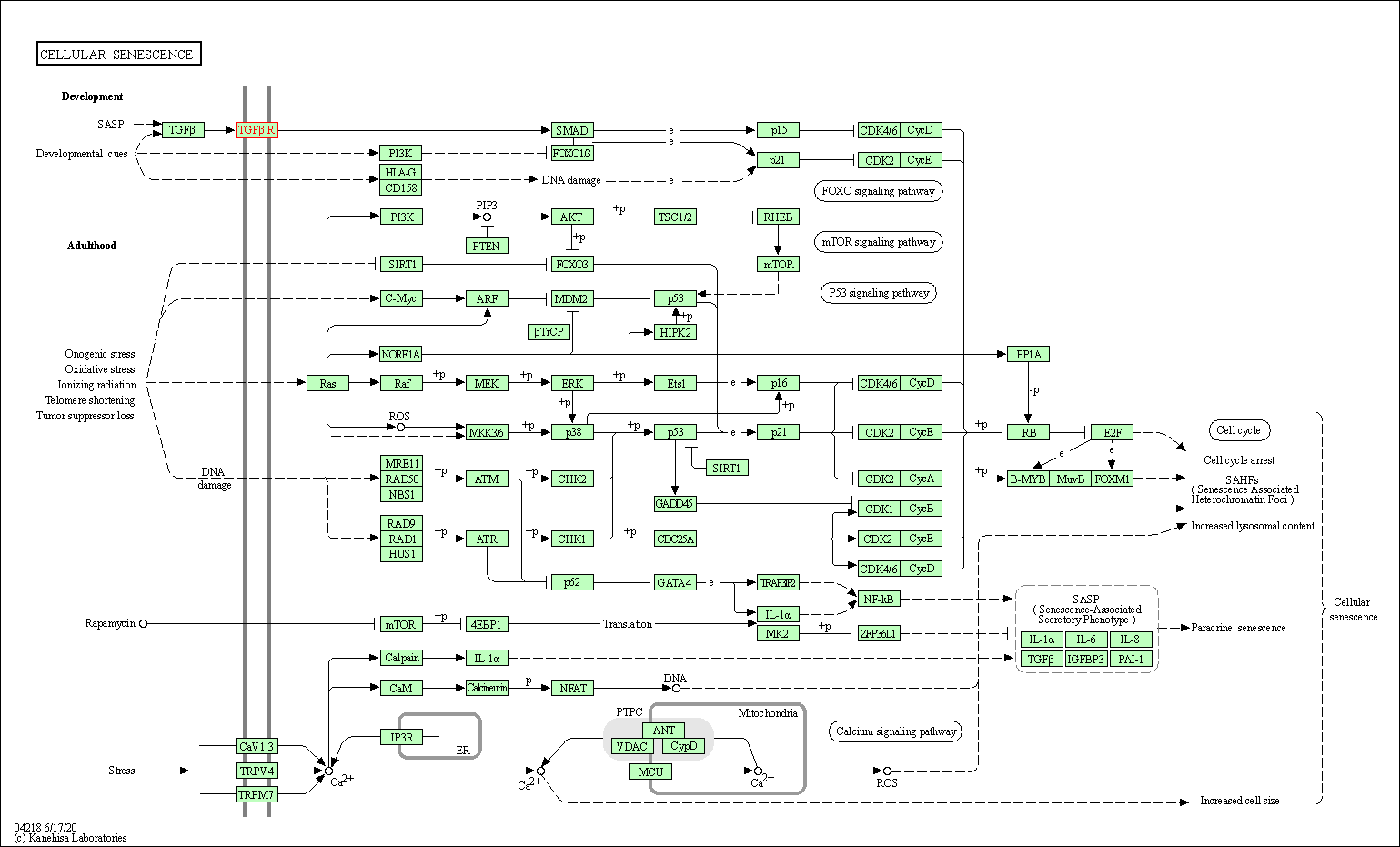
| Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
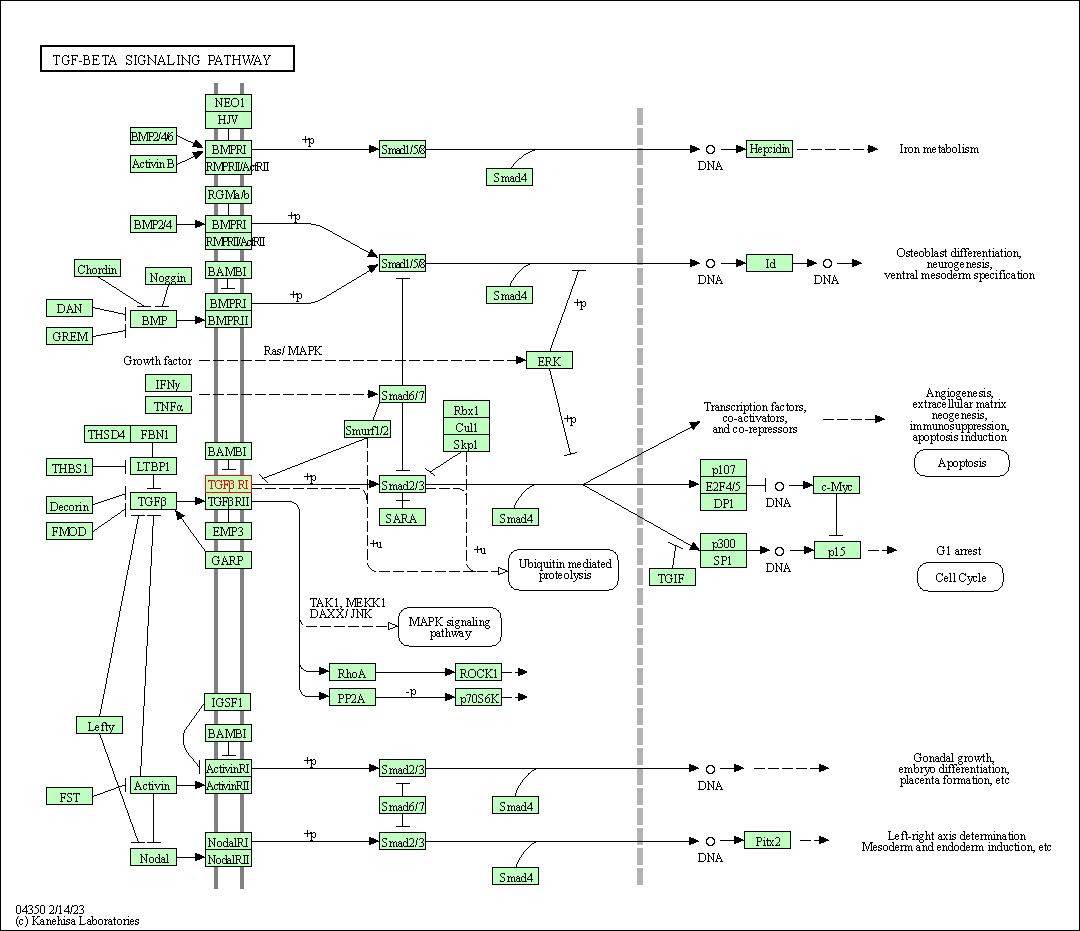
| TGF-beta signaling pathway | hsa04350 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
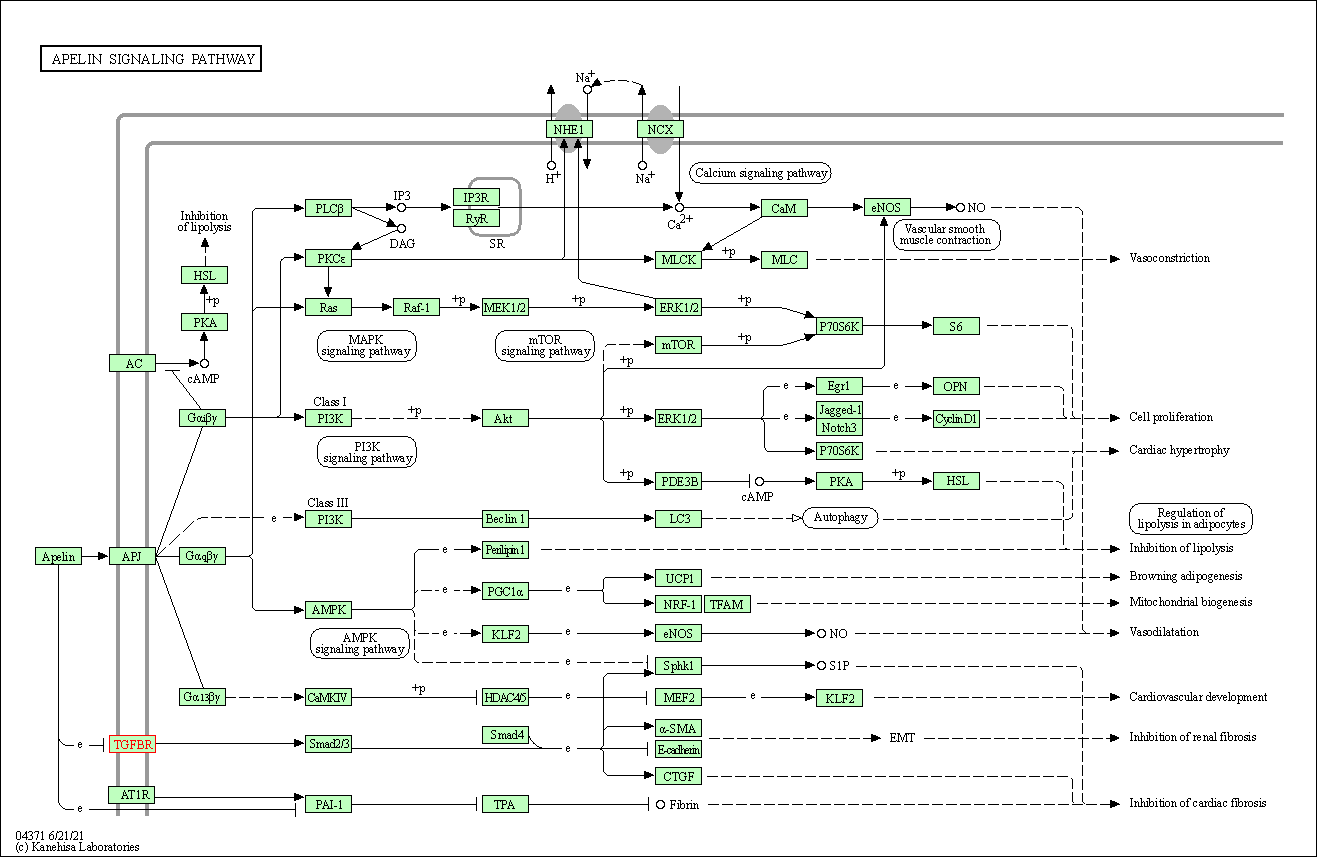
| Apelin signaling pathway | hsa04371 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
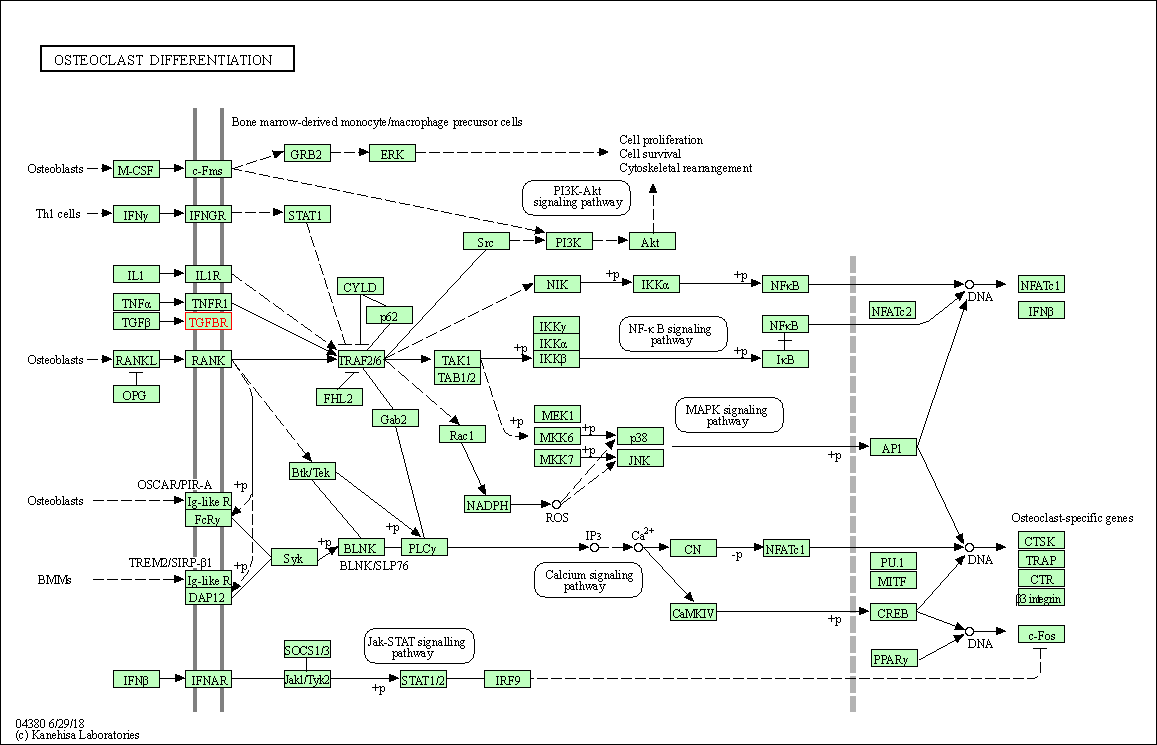
| Osteoclast differentiation | hsa04380 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Development and regeneration | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
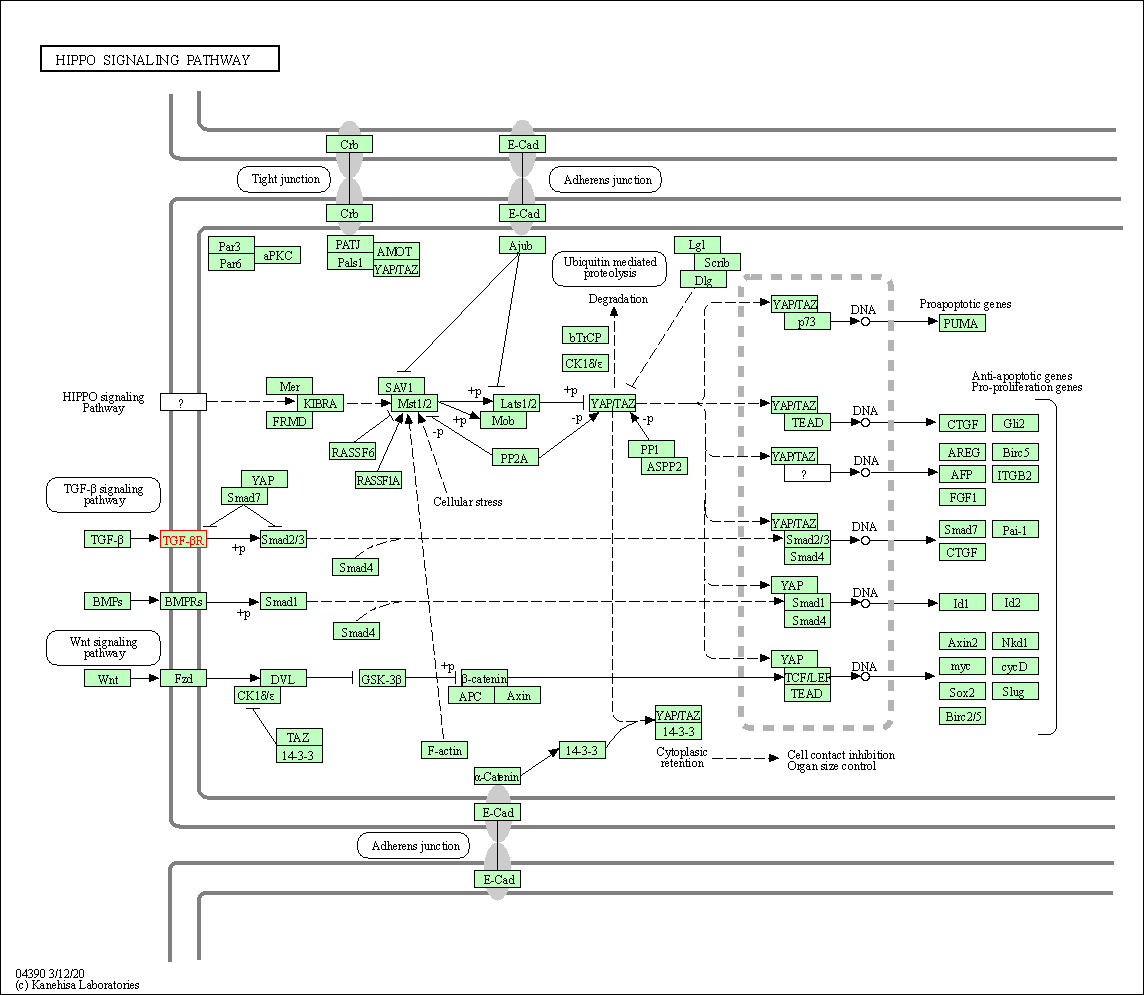
| Hippo signaling pathway | hsa04390 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
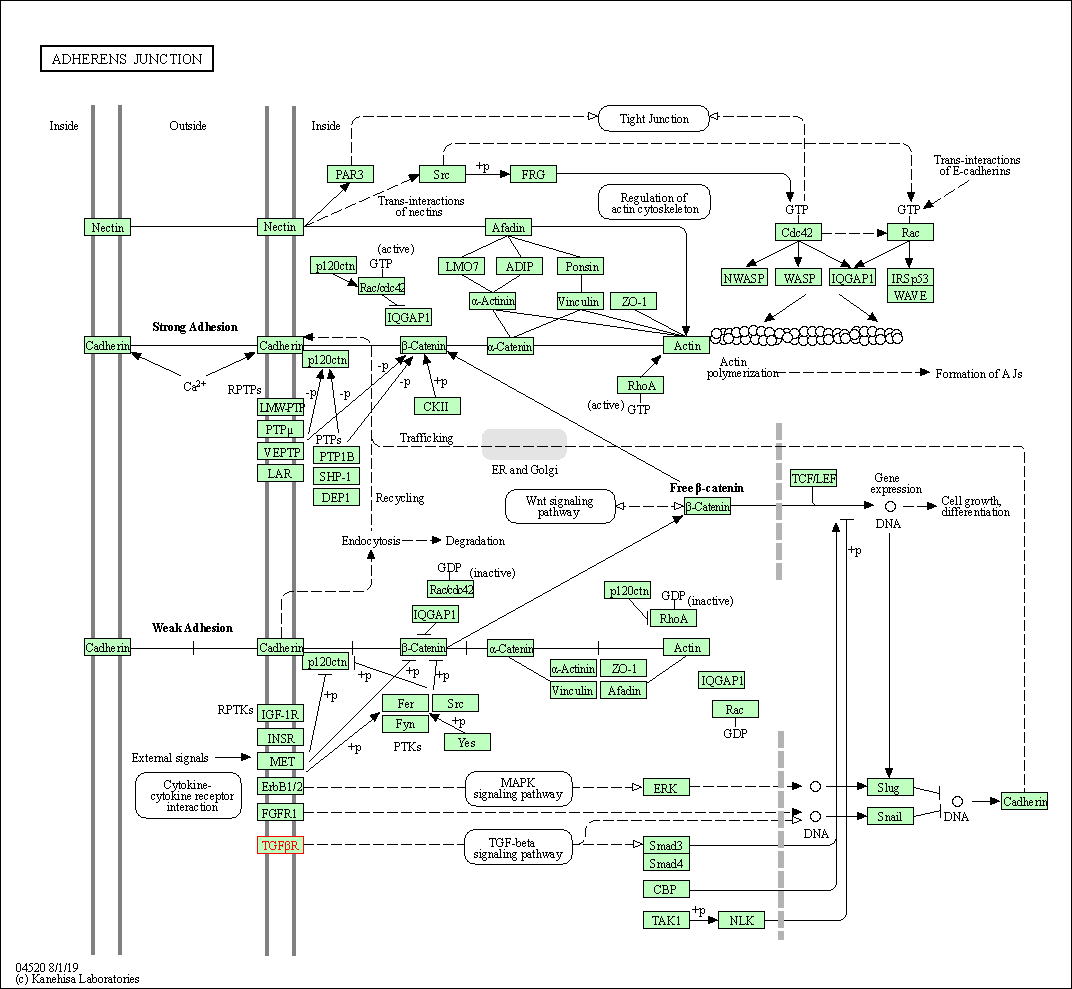
| Adherens junction | hsa04520 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
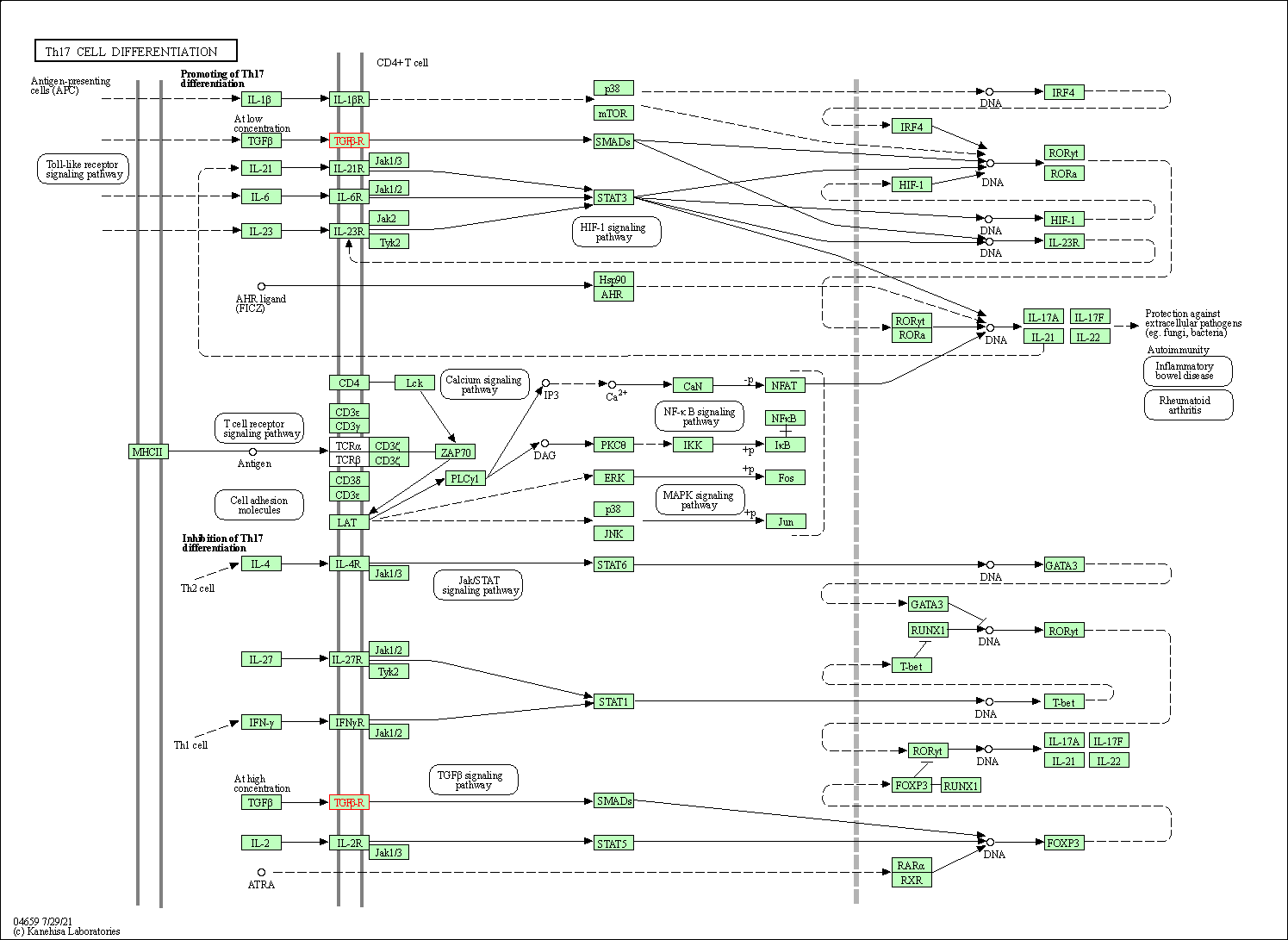
| Th17 cell differentiation | hsa04659 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
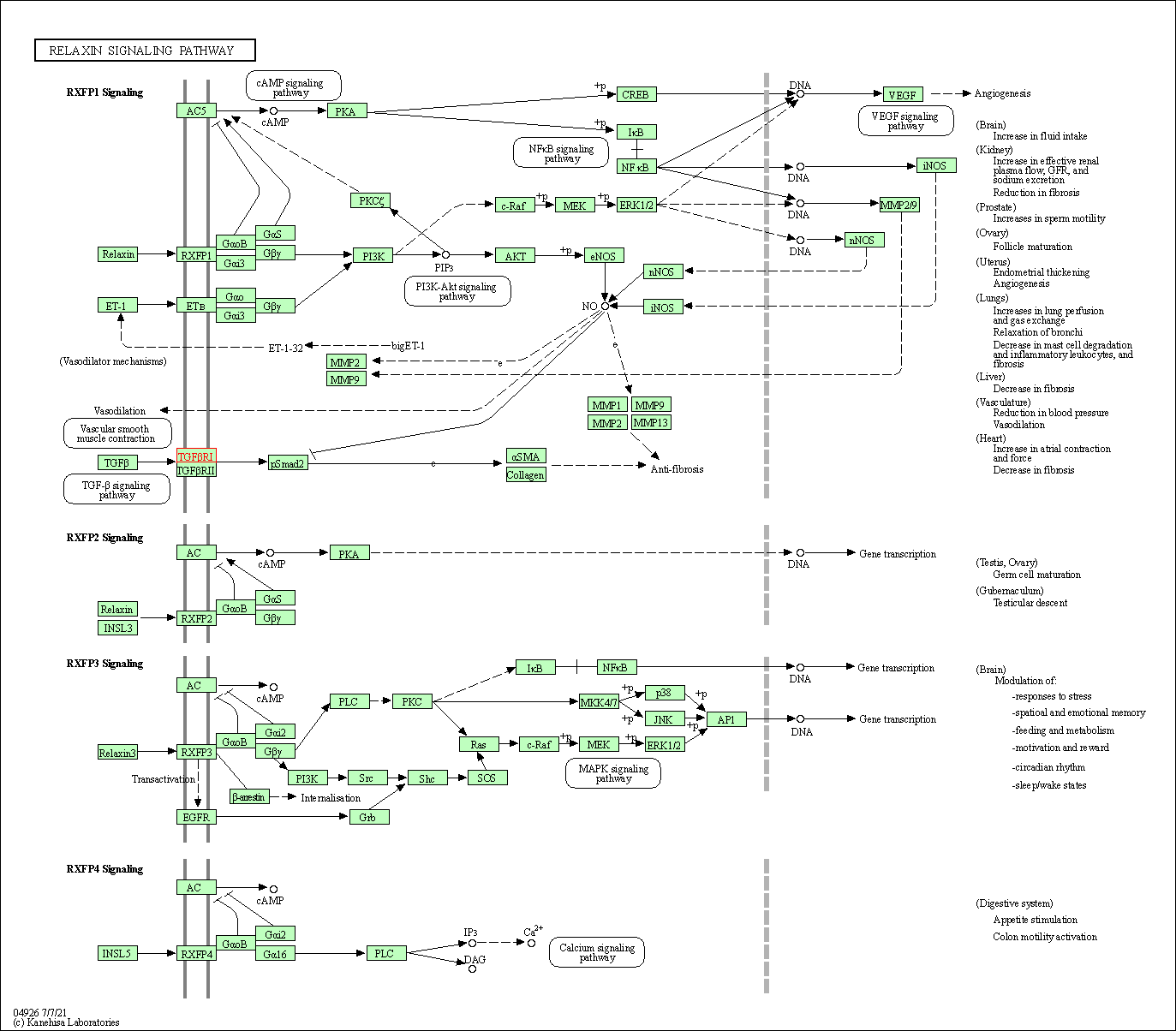
| Relaxin signaling pathway | hsa04926 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 37 | Degree centrality | 3.98E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 2.11E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.55E-01 | Radiality | 1.44E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.86E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.85E+01 | Topological coefficient | 5.13E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Cardiac Safety of TGF-beta Receptor I Kinase Inhibitor LY2157299 Monohydrate in Cancer Patients in a First-in-Human Dose Study. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2015 Oct;15(4):309-23. | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7797). | |||||
| REF 3 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02008318) A Study of LY2157299 in Participants With Myelodysplastic Syndromes. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 4 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04103645) Intra-patient Dose Escalation Study to Investigate Safety and Feasibility of Vactosertib in Treating Anemic MPN Patients. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 5 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00043706) Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of CAT-192 (Human Anti-TGF-Beta1 Monoclonal Antibody) in Patients With Early Stage Diffuse Systemic Sclerosis. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 6 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 7 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800037259) | |||||
| REF 8 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03685591) PF-06952229 Treatment in Adult Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 9 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03429218) First-in-human Study of Oral TP-0184 in Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 10 | Drugs and Targets in Fibrosis. Front Pharmacol. 2017 Nov 23;8:855. | |||||
| REF 11 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800012957) | |||||
| REF 12 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800026469) | |||||
| REF 13 | Interpreting expression profiles of cancers by genome-wide survey of breadth of expression in normal tissues. Genomics 2005 Aug;86(2):127-41. | |||||
| REF 14 | Development of TGF-beta signalling inhibitors for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004 Dec;3(12):1011-22. | |||||
| REF 15 | Novel potent inhibitor of Bcr-Abl mutated imatinib resistant chronic myeloid leukemia cell lines. Cancer Research. 06/2012; 72(8 Supplement):1822-1822. | |||||
| REF 16 | Targeting the TGF pathway for cancer therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Mar;147:22-31. | |||||
| REF 17 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma. | |||||
| REF 18 | Pyrazolone based TGFbetaR1 kinase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Jan 1;20(1):326-9. | |||||
| REF 19 | US patent application no. 2013,0028,978, Compositions and methods for wound treatment. | |||||
| REF 20 | TGF-beta type I receptor kinase inhibitor down-regulates rheumatoid synoviocytes and prevents the arthritis induced by type II collagen antibody. Int Immunol. 2007 Feb;19(2):117-26. | |||||
| REF 21 | Design of novel quinazoline derivatives and related analogues as potent and selective ALK5 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Apr 15;19(8):2277-81. | |||||
| REF 22 | Identification of 1,5-naphthyridine derivatives as a novel series of potent and selective TGF-beta type I receptor inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2004 Aug 26;47(18):4494-506. | |||||
| REF 23 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 1788). | |||||
| REF 24 | Discovery of 4-{4-[3-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]pyridin-2-yl}-N-(tetrahydro-2H- pyran-4-yl)benzamide (GW788388): a potent, selective, and orall... J Med Chem. 2006 Apr 6;49(7):2210-21. | |||||
| REF 25 | The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1;28(1):235-42. | |||||
| REF 26 | Dihydropyrrolopyrazole transforming growth factor-beta type I receptor kinase domain inhibitors: a novel benzimidazole series with selectivity vers... J Med Chem. 2006 Mar 23;49(6):2138-42. | |||||
| REF 27 | Synthesis and biological evaluation of 4(5)-(6-methylpyridin-2-yl)imidazoles and -pyrazoles as transforming growth factor-beta type 1 receptor kina... Bioorg Med Chem. 2010 Jun 15;18(12):4459-67. | |||||
| REF 28 | Synthesis and biological evaluation of 4(5)-(6-alkylpyridin-2-yl)imidazoles as transforming growth factor-beta type 1 receptor kinase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2007 Jun 28;50(13):3143-7. | |||||
| REF 29 | Structure-activity relationship of 3,5-diaryl-2-aminopyridine ALK2 inhibitors reveals unaltered binding affinity for fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva causing mutants. J Med Chem. 2014 Oct 9;57(19):7900-15. | |||||
| REF 30 | LY2109761, a novel transforming growth factor beta receptor type I and type II dual inhibitor, as a therapeutic approach to suppressing pancreatic cancer metastasis. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Apr;7(4):829-40. | |||||
| REF 31 | Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of a novel and selective bone morphogenetic protein receptor (BMP) inhibitor derived from the pyrazolo[1.5-a]pyrimidine scaffold of dorsomorphin: the discovery of ML347 as an ALK2 versus ALK3 selective MLPCN probe. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013 Jun 1;23(11):3248-52. | |||||
| REF 32 | Synthesis and biological evaluation of 2-pyridyl-substituted pyrazoles and imidazoles as transforming growth factor-beta type 1 receptor kinase inhibitors, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 20(14):4228-4232 (2010). | |||||
| REF 33 | Evaluation of the anti-hepatitis C virus effect of novel potent, selective, and orally bioavailable JNK and VEGFR kinase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 Apr 1;17(7):1843-9. | |||||
| REF 34 | Structural basis for specificity of TGFbeta family receptor small molecule inhibitors. Cell Signal. 2012 Feb;24(2):476-483. | |||||
| REF 35 | Synthesis and activity of new aryl- and heteroaryl-substituted 5,6-dihydro-4H-pyrrolo[1,2-b]pyrazole inhibitors of the transforming growth factor-beta type I receptor kinase domain. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004 Jul 5;14(13):3581-4. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

