Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T55729
(Former ID: TTDR00352)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Stress-activated protein kinase 2b (p38 beta)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Stress-activated protein kinase-2; SAPK2b; SAPK2; PRKM11; P38b; P38-2; P38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase beta; Mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 beta; Mitogen-activated protein kinase 11; MAPK 11; MAP kinase p38 beta; MAP kinase 11
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
MAPK11
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Alzheimer disease [ICD-11: 8A20] | |||||
| 2 | Rheumatoid arthritis [ICD-11: FA20] | |||||
| Function |
MAPK11 is one of the four p38 MAPKs which play an important role in the cascades of cellular responses evoked by extracellular stimuli such as proinflammatory cytokines or physical stress leading to direct activation of transcription factors. Accordingly, p38 MAPKs phosphorylate a broad range of proteins and it has been estimated that they may have approximately 200 to 300 substrates each. MAPK11 functions are mostly redundant with those of MAPK14. Some of the targets are downstream kinases which are activated through phosphorylation and further phosphorylate additional targets. RPS6KA5/MSK1 and RPS6KA4/MSK2 can directly phosphorylate and activate transcription factors such as CREB1, ATF1, the NF-kappa-B isoform RELA/NFKB3, STAT1 and STAT3, but can also phosphorylate histone H3 and the nucleosomal protein HMGN1. RPS6KA5/MSK1 and RPS6KA4/MSK2 play important roles in the rapid induction of immediate-early genes in response to stress or mitogenic stimuli, either by inducing chromatin remodeling or by recruiting the transcription machinery. On the other hand, two other kinase targets, MAPKAPK2/MK2 and MAPKAPK3/MK3, participate in the control of gene expression mostly at the post-transcriptional level, by phosphorylating ZFP36 (tristetraprolin) and ELAVL1, and by regulating EEF2K, which is important for the elongation of mRNA during translation. MKNK1/MNK1 and MKNK2/MNK2, two other kinases activated by p38 MAPKs, regulate protein synthesis by phosphorylating the initiation factor EIF4E2. In the cytoplasm, the p38 MAPK pathway is an important regulator of protein turnover. For example, CFLAR is an inhibitor of TNF-induced apoptosis whose proteasome-mediated degradation is regulated by p38 MAPK phosphorylation. Ectodomain shedding of transmembrane proteins is regulated by p38 MAPKs as well. In response to inflammatory stimuli, p38 MAPKs phosphorylate the membrane-associated metalloprotease ADAM17. Such phosphorylation is required for ADAM17-mediated ectodomain shedding of TGF-alpha family ligands, which results in the activation of EGFR signaling and cell proliferation. Additional examples of p38 MAPK substrates are the FGFR1. FGFR1 can be translocated from the extracellular space into the cytosol and nucleus of target cells, and regulates processes such as rRNA synthesis and cell growth. FGFR1 translocation requires p38 MAPK activation. In the nucleus, many transcription factors are phosphorylated and activated by p38 MAPKs in response to different stimuli. Classical examples include ATF1, ATF2, ATF6, ELK1, PTPRH, DDIT3, TP53/p53 and MEF2C and MEF2A. The p38 MAPKs are emerging as important modulators of gene expression by regulating chromatin modifiers and remodelers. The promoters of several genes involved in the inflammatory response, such as IL6, IL8 and IL12B, display a p38 MAPK-dependent enrichment of histone H3 phosphorylation on 'Ser-10' (H3S10ph) in LPS-stimulated myeloid cells. This phosphorylation enhances the accessibility of the cryptic NF-kappa-B-binding sites marking promoters for increased NF-kappa-B recruitment. Serine/threonine kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.24
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MSGPRAGFYRQELNKTVWEVPQRLQGLRPVGSGAYGSVCSAYDARLRQKVAVKKLSRPFQ
SLIHARRTYRELRLLKHLKHENVIGLLDVFTPATSIEDFSEVYLVTTLMGADLNNIVKCQ ALSDEHVQFLVYQLLRGLKYIHSAGIIHRDLKPSNVAVNEDCELRILDFGLARQADEEMT GYVATRWYRAPEIMLNWMHYNQTVDIWSVGCIMAELLQGKALFPGSDYIDQLKRIMEVVG TPSPEVLAKISSEHARTYIQSLPPMPQKDLSSIFRGANPLAIDLLGRMLVLDSDQRVSAA EALAHAYFSQYHDPEDEPEAEPYDESVEAKERTLEEWKELTYQEVLSFKPPEPPKPPGSL EIEQ Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| ADReCS ID | BADD_A03251 ; BADD_A05675 | |||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T67LQK | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | VX-745 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Rheumatoid arthritis | [2], [3], [4] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 1 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | SB 235699 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 1 | Psoriasis vulgaris | [5] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 15 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | VX-745 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | SB 235699 | Drug Info | [1], [6] | |||
| 3 | 4,5,6,7-tetrabromo-1H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazole | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 4 | Bisindolylmaleimide-I | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 5 | CI-1040 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 6 | KN-62 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 7 | KT-5720 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 8 | L-779450 | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 9 | ML-3163 | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 10 | ML-3375 | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 11 | ML-3403 | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 12 | RO-316233 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 13 | Ro31-8220 | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 14 | RWJ-68354 | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| 15 | STAUROSPORINONE | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Nilotinib | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal Structure of Human Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase 11 (p38 beta) in complex with Nilotinib | PDB:3GP0 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.90 Å | Mutation | No | [13] |
| PDB Sequence |
MRAGFYRQEL
13 NKTVWEVPQR23 LQGLRPVGSV38 CSAYDARLRQ48 KVAVKKLSRP58 FQSLIHARRT 68 YRELRLLKHL78 KHENVIGLLD88 VFTPATSIED98 FSEVYLVTTL108 MGADLNNIVK 118 CQALSDEHVQ128 FLVYQLLRGL138 KYIHSAGIIH148 RDLKPSNVAV158 NEDCELRILD 168 FGEEMGYVAT185 RWYRAPEIML195 NWMHYNQTVD205 IWSVGCIMAE215 LLQGKALFPG 225 SDYIDQLKRI235 MEVVGTPSPE245 VLAKISSEHA255 RTYIQSLPPM265 PQKDLSSIFR 275 GANPLAIDLL285 GRMLVLDSDQ295 RVSAAEALAH305 AYFSQYHDPE315 DEPEAEPYDE 325 SVEAKERTLE335 EWKELTYQEV345 LSF
|
|||||
|
|
VAL30
4.497
VAL38
3.876
ALA51
3.681
VAL52
3.913
LYS53
3.520
ARG67
3.452
ARG70
4.061
GLU71
2.778
LEU74
3.827
LEU75
3.792
LEU78
4.005
VAL83
3.525
ILE84
3.423
LEU104
3.711
VAL105
4.753
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: 5-(2-Chloro-4-Fluorophenyl)-1-(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)-7-[1-(1-Methylethyl)piperidin-4-Yl]-3,4-Dihydroquinazolin-2(1h)-One | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | The structure of p38beta C119S, C162S in complex with a dihydroquinazolinone inhibitor | PDB:3GC9 | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.05 Å | Mutation | Yes | [14] |
| PDB Sequence |
GPRAGFYRQE
12 LNKTVWEVPQ22 RLQGLRPVGS32 GAYGSVCSAY42 DARLRQKVAV52 KKLSRPFQSL 62 IHARRTYREL72 RLLKHLKHEN82 VIGLLDVFTP92 ATSIEDFSEV102 YLVTTLMGAD 112 LNNIVKSQAL122 SDEHVQFLVY132 QLLRGLKYIH142 SAGIIHRDLK152 PSNVAVNEDS 162 ELRILDFGLA172 ATRWYRAPEI193 MLNWMHYNQT203 VDIWSVGCIM213 AELLQGKALF 223 PGSDYIDQLK233 RIMEVVGTPS243 PEVLAKISSE253 HARTYIQSLP263 PMPQKDLSSI 273 FRGANPLAID283 LLGRMLVLDS293 DQRVSAAEAL303 AHAYFSQYHD313 PEDEPEAEPY 323 DESVEAKERT333 LEEWKELTYQ343 EVLSF
|
|||||
|
|
VAL30
3.570
ALA34
3.714
TYR35
3.625
VAL38
3.531
CYS39
4.533
ALA51
3.212
VAL52
3.741
LYS53
3.551
LEU75
3.939
ILE84
4.117
LEU86
3.974
LEU104
3.595
THR106
3.230
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Rap1 signaling pathway | hsa04015 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| FoxO signaling pathway | hsa04068 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Sphingolipid signaling pathway | hsa04071 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Oocyte meiosis | hsa04114 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cellular senescence | hsa04218 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes | hsa04261 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Circulatory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| VEGF signaling pathway | hsa04370 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Osteoclast differentiation | hsa04380 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Development and regeneration | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells | hsa04550 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Platelet activation | hsa04611 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neutrophil extracellular trap formation | hsa04613 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04620 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04621 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04622 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway | hsa04625 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
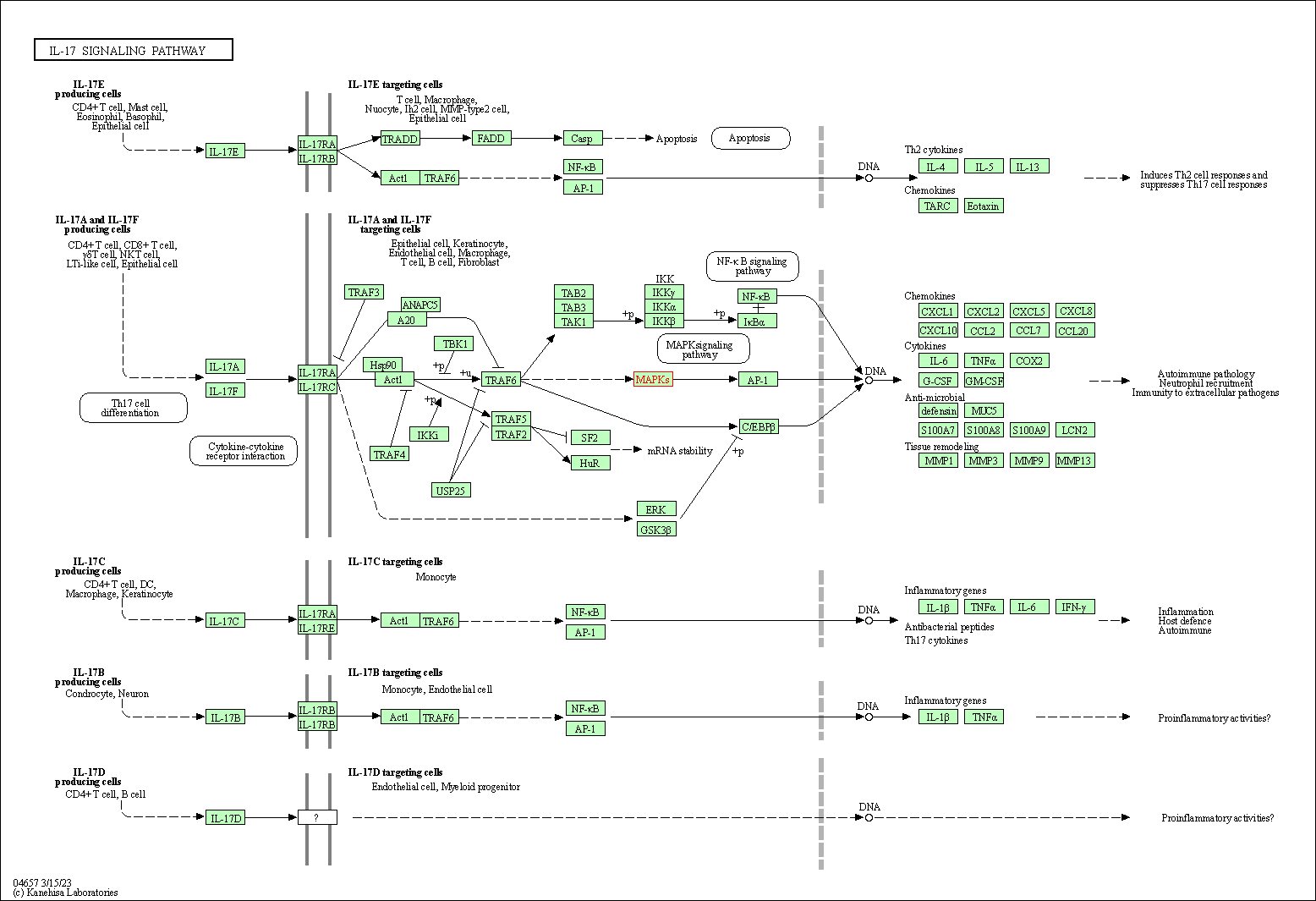
| IL-17 signaling pathway | hsa04657 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
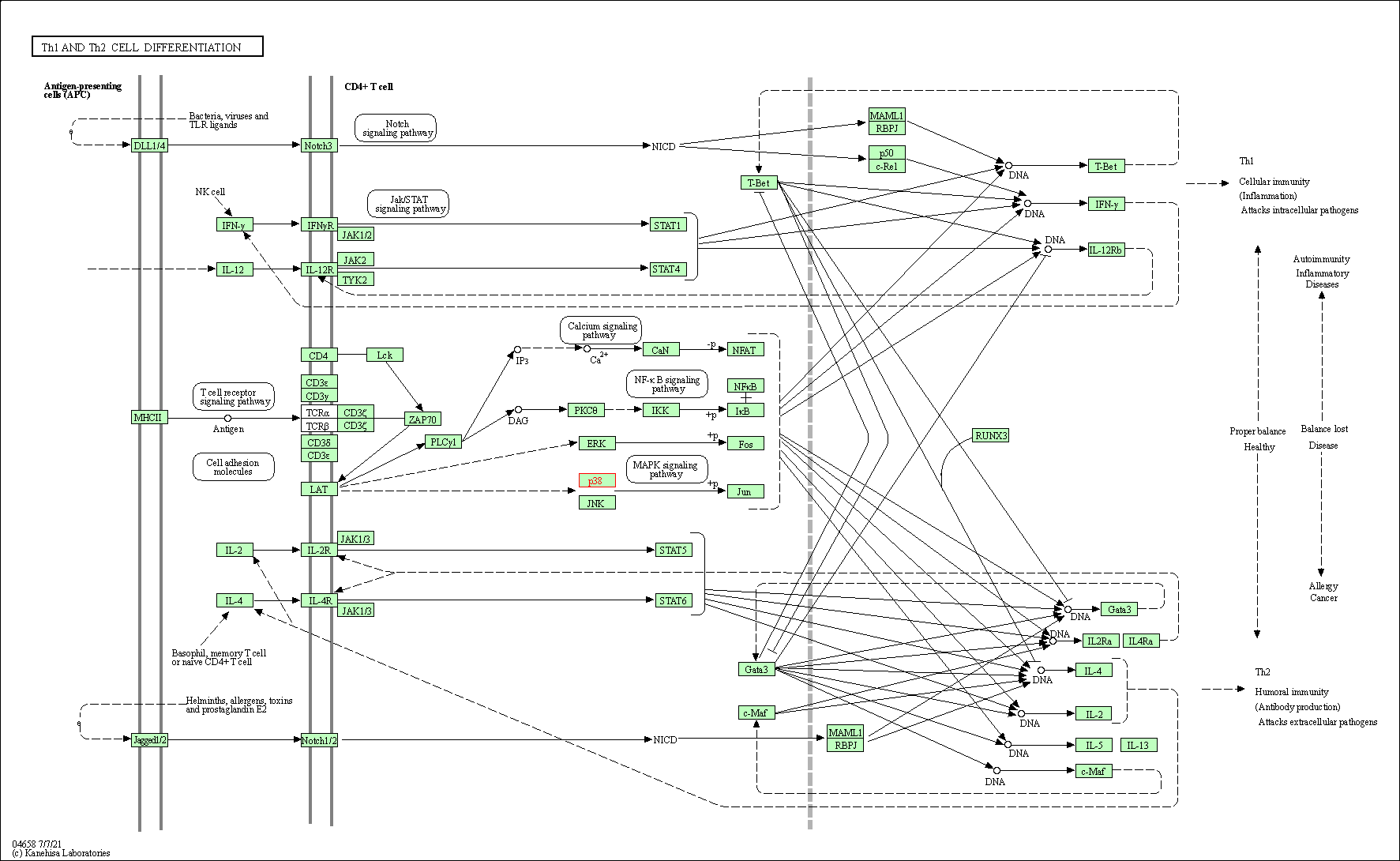
| Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation | hsa04658 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
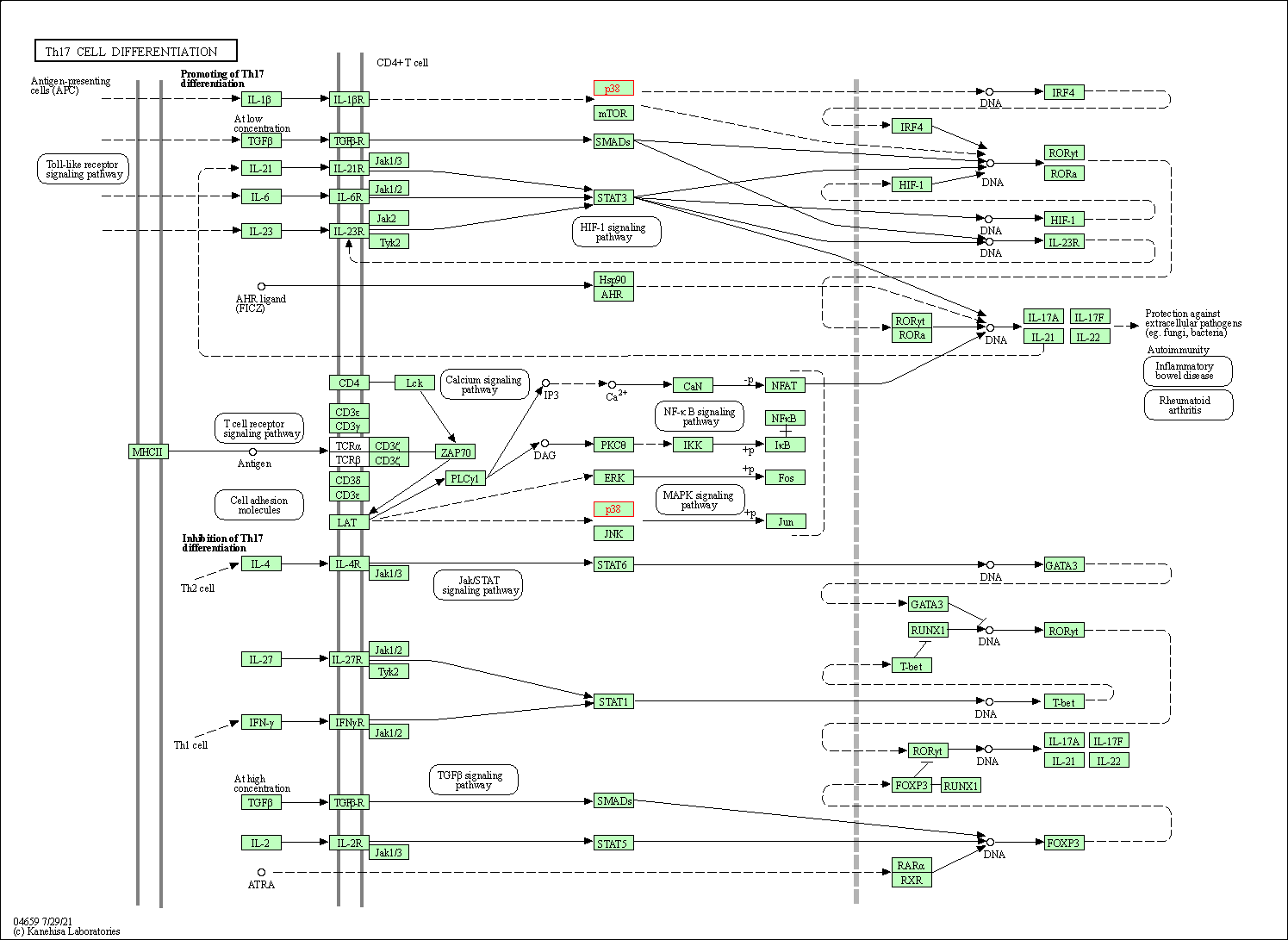
| Th17 cell differentiation | hsa04659 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
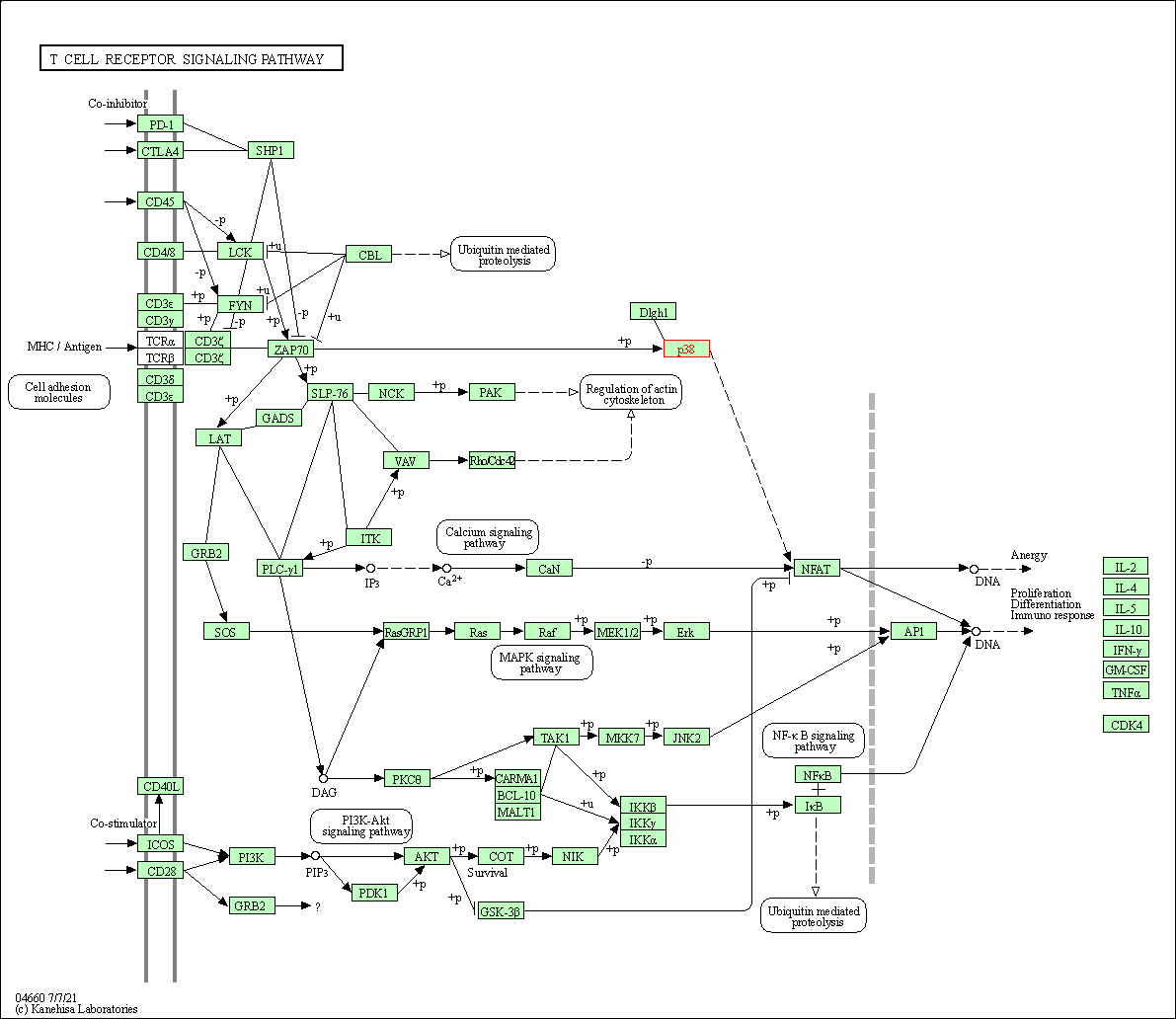
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04660 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway | hsa04664 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| TNF signaling pathway | hsa04668 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Leukocyte transendothelial migration | hsa04670 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Thermogenesis | hsa04714 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Environmental adaptation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | hsa04722 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling | hsa04723 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Dopaminergic synapse | hsa04728 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels | hsa04750 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Sensory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| GnRH signaling pathway | hsa04912 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation | hsa04914 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Prolactin signaling pathway | hsa04917 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Relaxin signaling pathway | hsa04926 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04935 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 16 | Degree centrality | 1.72E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 2.10E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.40E-01 | Radiality | 1.42E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 6.67E-02 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.27E+01 | Topological coefficient | 8.18E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Pharmacological inhibitors of MAPK pathways. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2002 Jan;23(1):40-5. | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 5719). | |||||
| REF 3 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02423200) Clinical Pharmacology of p38 MAP Kinase Inhibitor, VX-745, in Mild Cognitive Impairment Due to Alzheimer's Disease (AD) or Mild AD. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 4 | Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2011 January; 9(1): 30-56. | |||||
| REF 5 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800012315) | |||||
| REF 6 | Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of aminobenzophenones. A novel class of p38 MAP kinase inhibitors with high antiinflammatory activity. J Med Chem. 2003 Dec 18;46(26):5651-62. | |||||
| REF 7 | Optimization of protein kinase CK2 inhibitors derived from 4,5,6,7-tetrabromobenzimidazole. J Med Chem. 2004 Dec 2;47(25):6239-47. | |||||
| REF 8 | Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors. Biochem J. 2000 Oct 1;351(Pt 1):95-105. | |||||
| REF 9 | The identification of potent and selective imidazole-based inhibitors of B-Raf kinase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006 Jan 15;16(2):378-81. | |||||
| REF 10 | From imidazoles to pyrimidines: new inhibitors of cytokine release. J Med Chem. 2002 Jun 20;45(13):2733-40. | |||||
| REF 11 | Novel substituted pyridinyl imidazoles as potent anticytokine agents with low activity against hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes. J Med Chem. 2003 Jul 17;46(15):3230-44. | |||||
| REF 12 | Imidazopyrimidines, potent inhibitors of p38 MAP kinase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2003 Feb 10;13(3):347-50. | |||||
| REF 13 | Crystal Structure of Human Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase 11 (p38 beta) in complex with Nilotinib | |||||
| REF 14 | The three-dimensional structure of MAP kinase p38beta: different features of the ATP-binding site in p38beta compared with p38alpha. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2009 Aug;65(Pt 8):777-85. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

