Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T69375
(Former ID: TTDR00334)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Stress-activated protein kinase JNK2 (JNK2)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Stress-activated protein kinase 1a; SAPK1a; PRKM9; Mitogen-activated protein kinase 9; Mitogen-activated protein kinase 8-interacting protein 2; MAPK 9; MAP kinase 9; Jun-N-terminal kinase 2; JNK-interacting protein 2; JNK-55; JNK MAP kinase scaffold protein 2; JIP-2; Islet-brain-2; IB-2; C-jun-amino-terminal kinase interacting protein 2; C-Jun N-terminal kinase 2
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
MAPK9
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Preclinical target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Mature T-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A90] | |||||
| Function |
Extracellular stimuli such as proinflammatory cytokines or physical stress stimulate the stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinase (SAP/JNK) signaling pathway. In this cascade, two dual specificity kinases MAP2K4/MKK4 and MAP2K7/MKK7 phosphorylate and activate MAPK9/JNK2. In turn, MAPK9/JNK2 phosphorylates a number of transcription factors, primarily components of AP-1 such as JUN and ATF2 and thus regulates AP-1 transcriptional activity. In response to oxidative or ribotoxic stresses, inhibits rRNA synthesis by phosphorylating and inactivating the RNA polymerase 1-specific transcription initiation factor RRN3. Promotes stressed cell apoptosis by phosphorylating key regulatory factors including TP53 and YAP1. In T-cells, MAPK8 and MAPK9 are required for polarized differentiation of T-helper cells into Th1 cells. Upon T-cell receptor (TCR) stimulation, is activated by CARMA1, BCL10, MAP2K7 and MAP3K7/TAK1 to regulate JUN protein levels. Plays an important role in the osmotic stress-induced epithelial tight-junctions disruption. When activated, promotes beta-catenin/CTNNB1 degradation and inhibits the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Participates also in neurite growth in spiral ganglion neurons. Phosphorylates the CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1 heterodimer and plays a role in the regulation of the circadian clock. Phosphorylates POU5F1, which results in the inhibition of POU5F1's transcriptional activity and enhances its proteosomal degradation. Serine/threonine-protein kinase involved in various processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, transformation and programmed cell death.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.24
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MSDSKCDSQFYSVQVADSTFTVLKRYQQLKPIGSGAQGIVCAAFDTVLGINVAVKKLSRP
FQNQTHAKRAYRELVLLKCVNHKNIISLLNVFTPQKTLEEFQDVYLVMELMDANLCQVIH MELDHERMSYLLYQMLCGIKHLHSAGIIHRDLKPSNIVVKSDCTLKILDFGLARTACTNF MMTPYVVTRYYRAPEVILGMGYKENVDIWSVGCIMGELVKGCVIFQGTDHIDQWNKVIEQ LGTPSAEFMKKLQPTVRNYVENRPKYPGIKFEELFPDWIFPSESERDKIKTSQARDLLSK MLVIDPDKRISVDEALRHPYITVWYDPAEAEAPPPQIYDAQLEEREHAIEEWKELIYKEV MDWEERSKNGVVKDQPSDAAVSSNATPSQSSSINDISSMSTEQTLASDTDSSLDASTGPL EGCR Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T39WPZ | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preclinical Drug(s) | [+] 1 Preclinical Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | COR-D | Drug Info | Preclinical | T-cell leukaemia | [2] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 27 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | 7-azaindole derivative 1 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | 7-azaindole derivative 2 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 3 | 7-azaindole derivative 3 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 4 | 7-azaindole derivative 5 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 5 | PMID25991433-Compound-A1 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 6 | PMID25991433-Compound-A10 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 7 | PMID25991433-Compound-A11 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 8 | PMID25991433-Compound-A2 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 9 | PMID25991433-Compound-A3 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 10 | PMID25991433-Compound-A5 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 11 | PMID25991433-Compound-A6 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 12 | PMID25991433-Compound-A7 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 13 | PMID25991433-Compound-A8 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 14 | PMID25991433-Compound-A9 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 15 | PMID25991433-Compound-C1 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 16 | PMID25991433-Compound-D1 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 17 | PMID25991433-Compound-D2 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 18 | PMID25991433-Compound-F2 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 19 | PMID25991433-Compound-J2 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 20 | PMID25991433-Compound-J3 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 21 | PMID25991433-Compound-J5 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 22 | PMID25991433-Compound-O3 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 23 | PMID25991433-Compound-P1 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 24 | PMID25991433-Compound-P4 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 25 | PMID25991433-Compound-P5 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 26 | PMID25991433-Compound-P6 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 27 | 2,6-Dihydroanthra/1,9-Cd/Pyrazol-6-One | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| Activator | [+] 1 Activator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | COR-D | Drug Info | [3] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Adenosine monophosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal Structure of AMP-bound Human JNK2 | PDB:7N8T | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.69 Å | Mutation | No | [5] |
| PDB Sequence |
FYSVEVADST
19 FTVLKRYQQL29 KPIGSGAQGI39 VCAAFDTVLG49 INVAVKKLSR59 PFQNQTHAKR 69 AYRELVLLKC79 VNHKNIISLL89 NVFTPQKTLE99 EFQDVYLVME109 LMDANLCQVI 119 HMELDHERMS129 YLLYQMLCGI139 KHLHSAGIIH149 RDLKPSNIVV159 KSDCTLKILD 169 FGLARTACTN179 FMMTPYVVTR189 YYRAPEVILG199 MGYAANVDIW209 SVGCIMGELV 219 KGCVIFQGTD229 HIDQWNKVIE239 QLGTPSAEFM249 AALQPTVRNY259 VENRPKYPGI 269 KFEELFPDWI279 FPSESERDKI289 KTSQARDLLS299 KMLVIDPDKR309 ISVDEALRHP 319 YITVWYDPAE329 AEAPPPQIYD339 AQLEEREHAI349 EEWKELIYKE359 VMDWE |
|||||
|
|
ILE32
3.651
GLY33
3.595
SER34
3.544
GLY35
3.116
ALA36
4.237
VAL40
4.043
ALA53
3.541
LYS55
3.452
ILE86
3.785
MET108
4.023
GLU109
2.990
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: Doramapimod | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Crystal structure of JNK2 complexed with BIRB796 | PDB:3NPC | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.35 Å | Mutation | Yes | [6] |
| PDB Sequence |
DNQFYSVEVA
16 DSTFTVLKRY26 QQLKPIGSGA36 QGIVCAAFDT46 VLGINVAVKK56 LSRPFQNQTH 66 AKRAYRELVL76 LKCVNHKNII86 SLLNVFTPQK96 TLEEFQDVYL106 VMELMDANLC 116 QVIHMELDHE126 RMSYLLYQML136 CGIKHLHSAG146 IIHRDLKPSN156 IVVKSDCTLK 166 ILDFGLARTA176 CTNFMMTPYV186 VTRYYRAPEV196 ILGMGYAANV206 DIWSVGCIMG 216 ELVKGCVIFQ226 GTDHIDQWNK236 VIEQLGTPSA246 EFMAALQPTV256 RNYVENRPKY 266 PGIKFEELFP276 DWIFPSESER286 DKIKTSQARD296 LLSKMLVIDP306 DKRISVDEAL 316 RHPYITVWYD326 PAEAEAPPPQ336 IYDAQLEERE346 HAIEEWKELI356 YKEVMDW |
|||||
|
|
ILE32
3.963
GLN37
3.823
VAL40
3.565
ALA53
3.500
VAL54
4.551
LYS55
3.689
ARG69
3.519
ARG72
3.964
GLU73
2.817
LEU76
3.663
LEU77
3.836
VAL80
4.638
ILE85
4.241
ILE86
3.549
LEU88
4.402
LEU106
3.601
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|





| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| ErbB signaling pathway | hsa04012 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Ras signaling pathway | hsa04014 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| cAMP signaling pathway | hsa04024 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| FoxO signaling pathway | hsa04068 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Sphingolipid signaling pathway | hsa04071 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Mitophagy - animal | hsa04137 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Autophagy - animal | hsa04140 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum | hsa04141 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Genetic Information Processing => Folding, sorting and degradation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
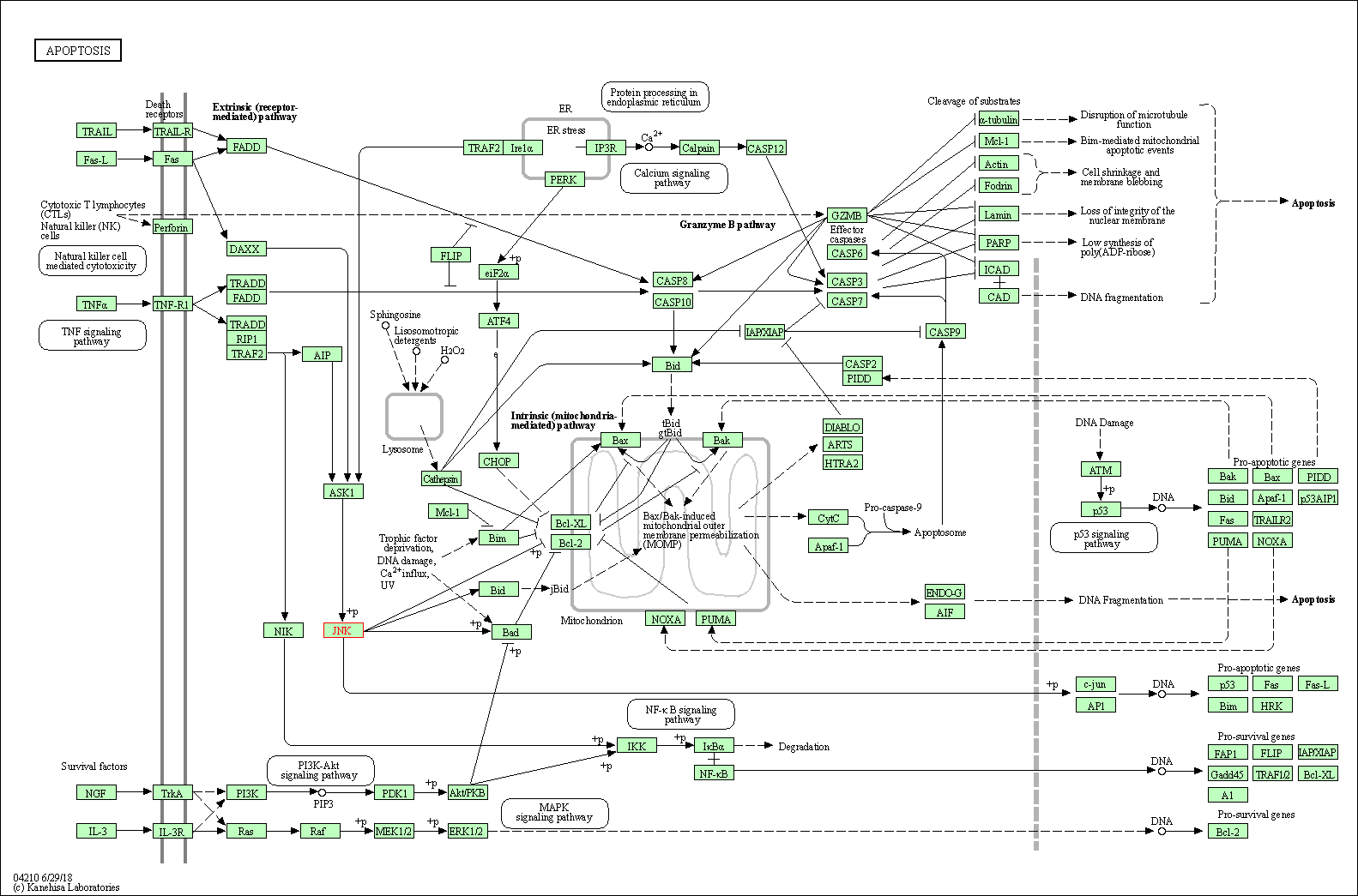
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
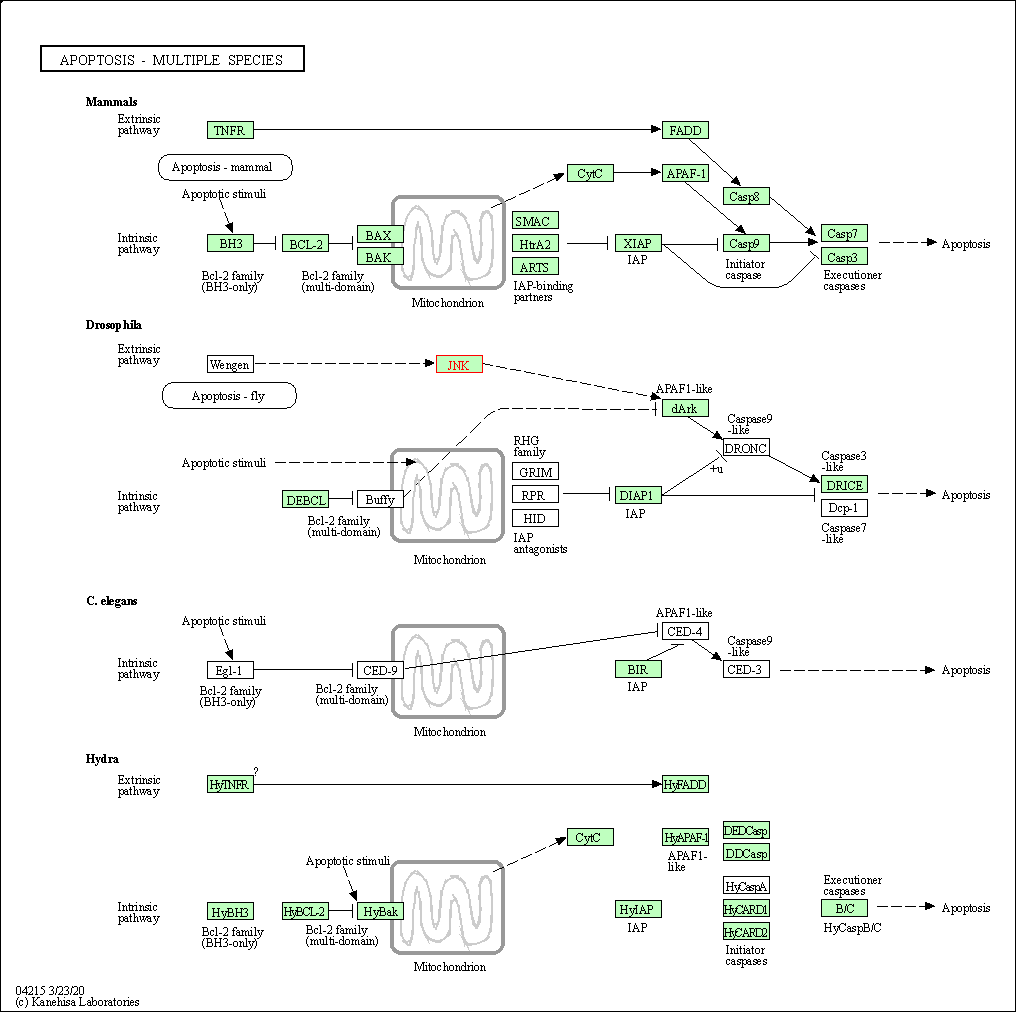
| Apoptosis - multiple species | hsa04215 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
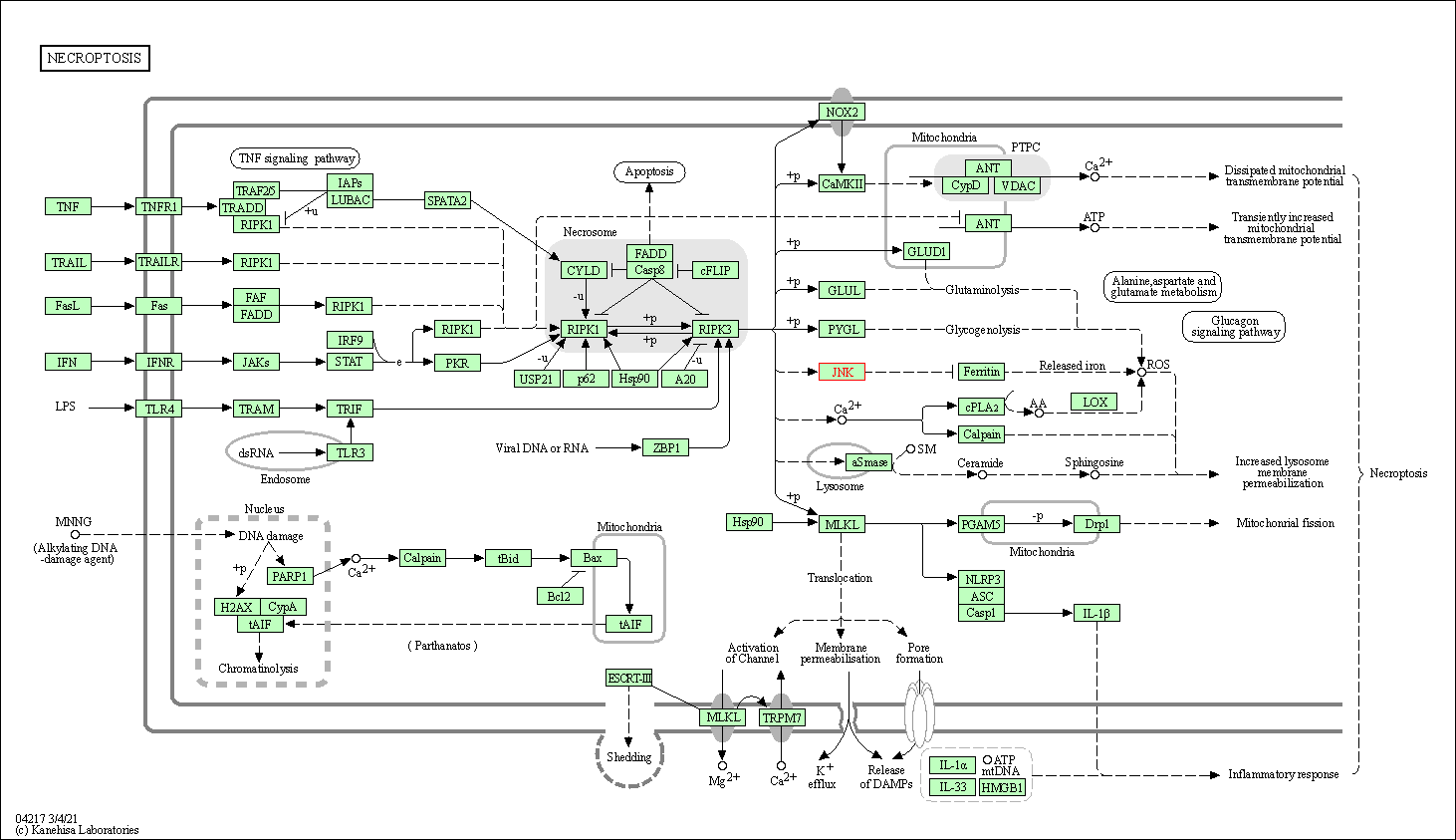
| Necroptosis | hsa04217 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
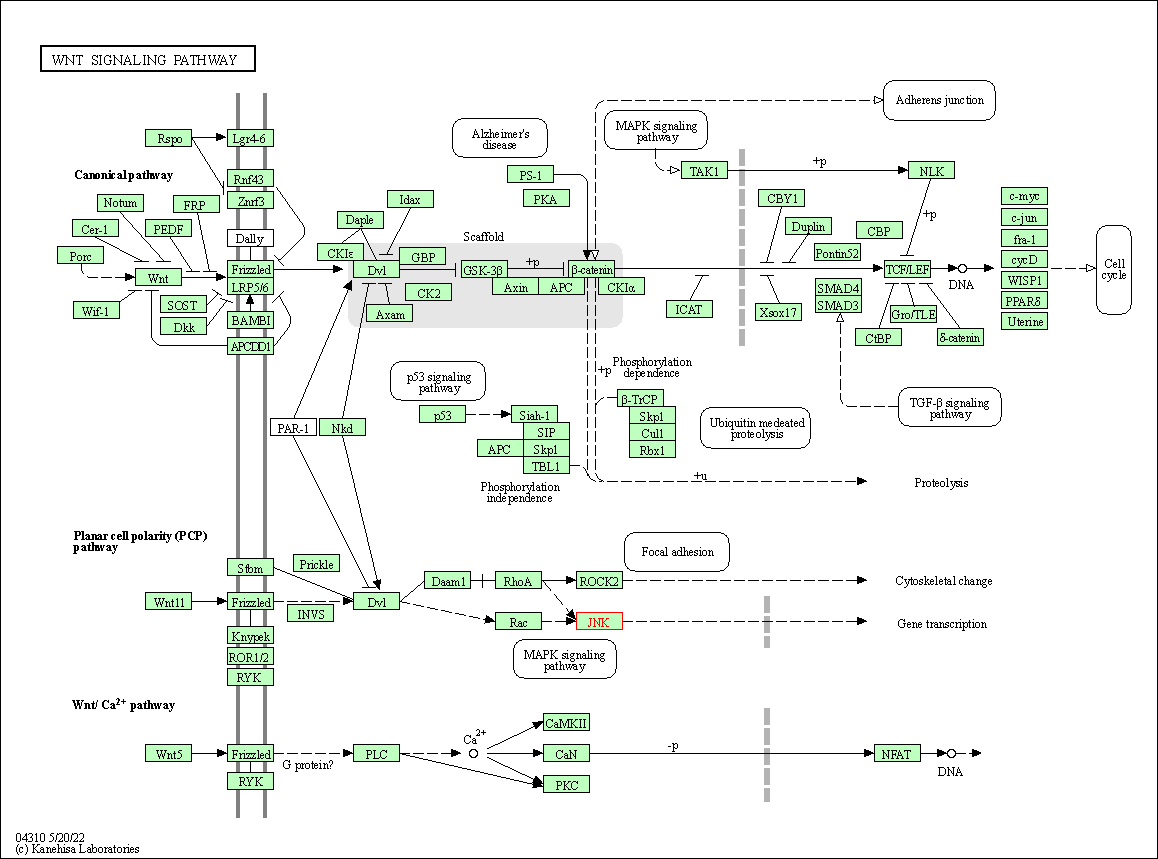
| Wnt signaling pathway | hsa04310 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
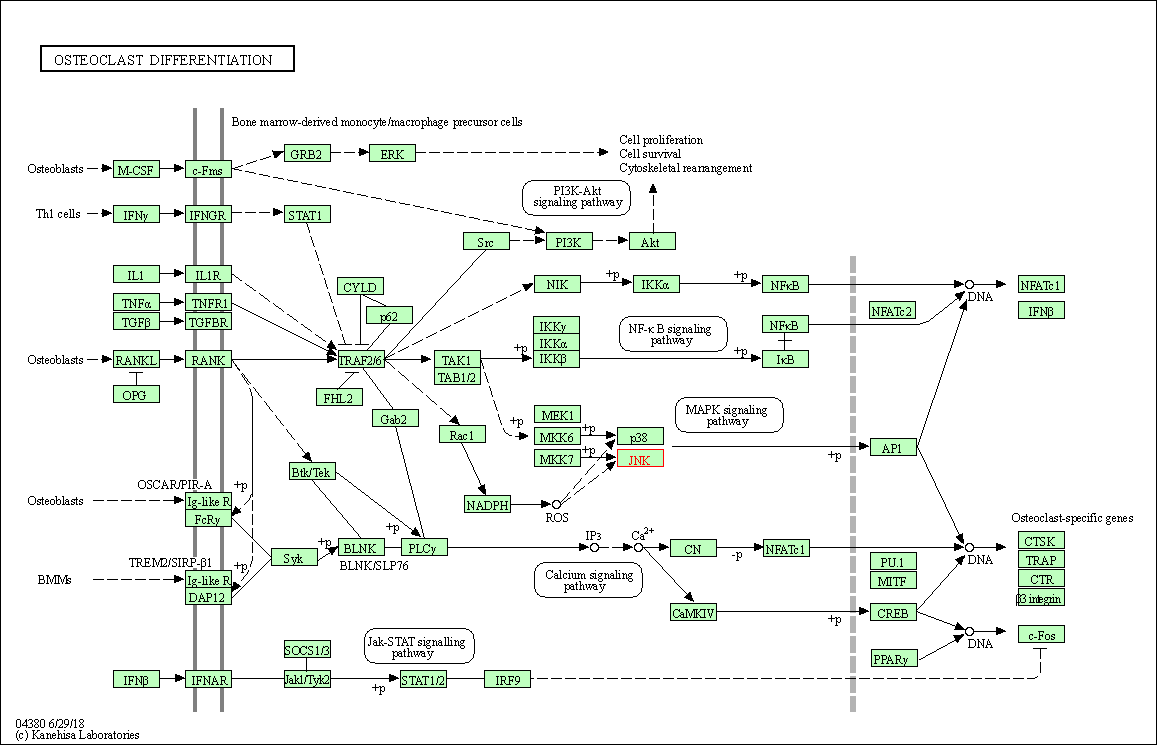
| Osteoclast differentiation | hsa04380 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Development and regeneration | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
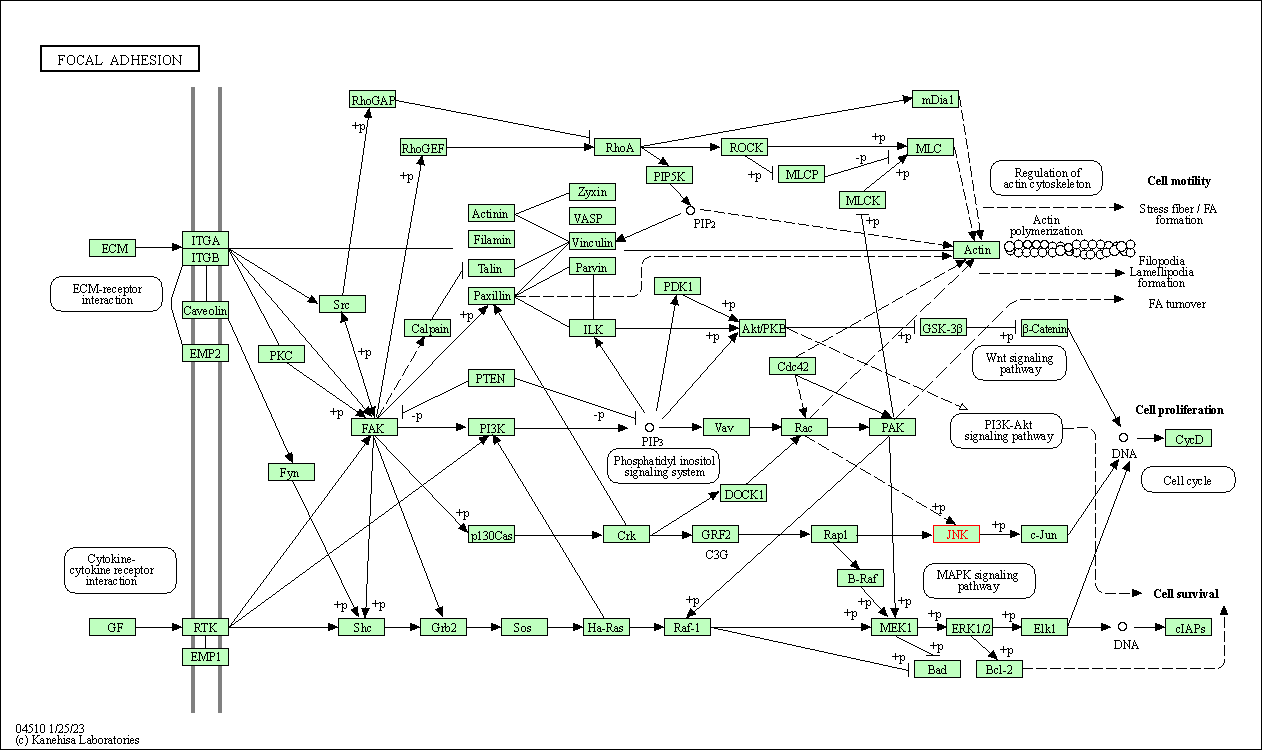
| Focal adhesion | hsa04510 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
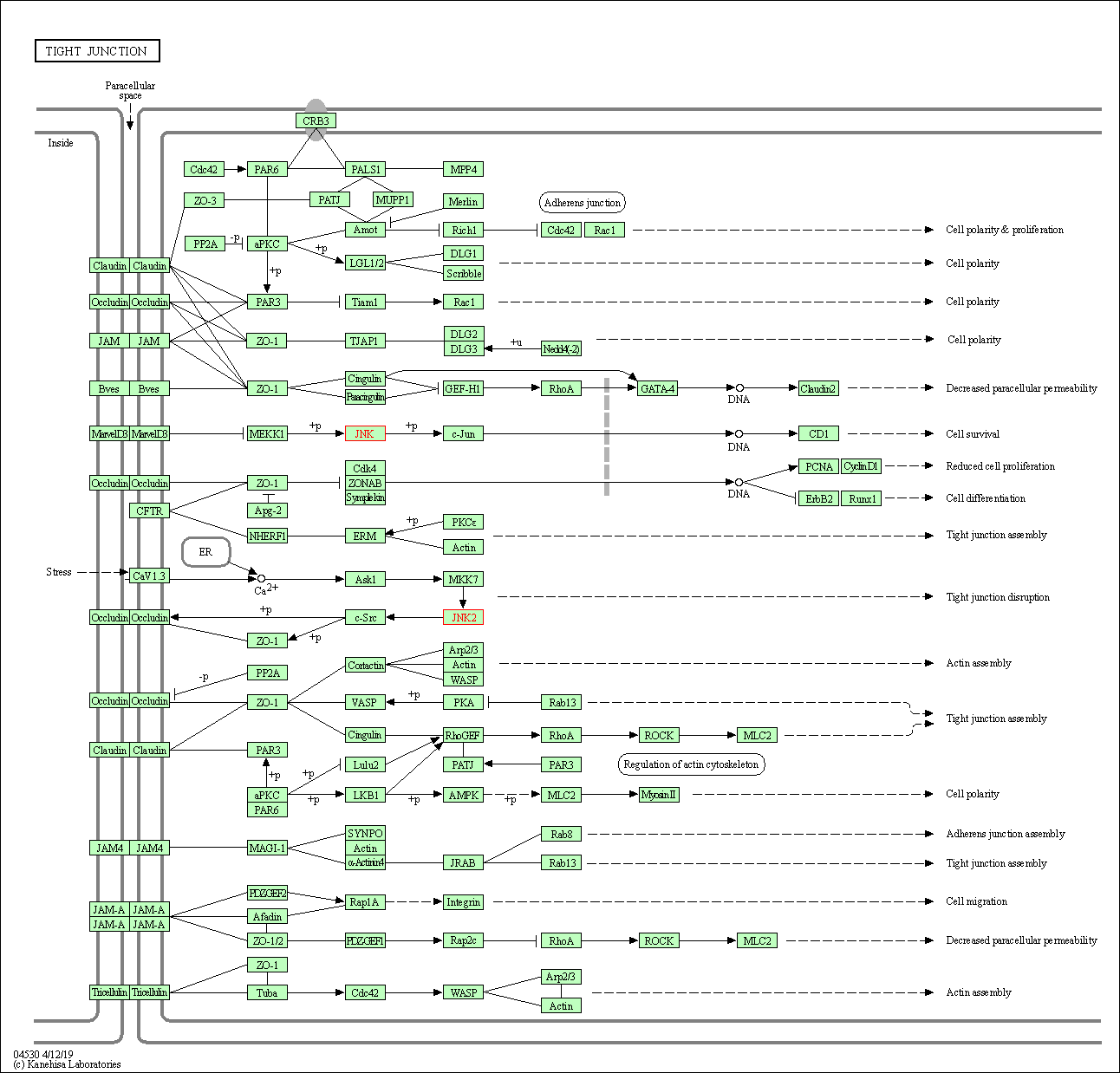
| Tight junction | hsa04530 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cellular community - eukaryotes | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
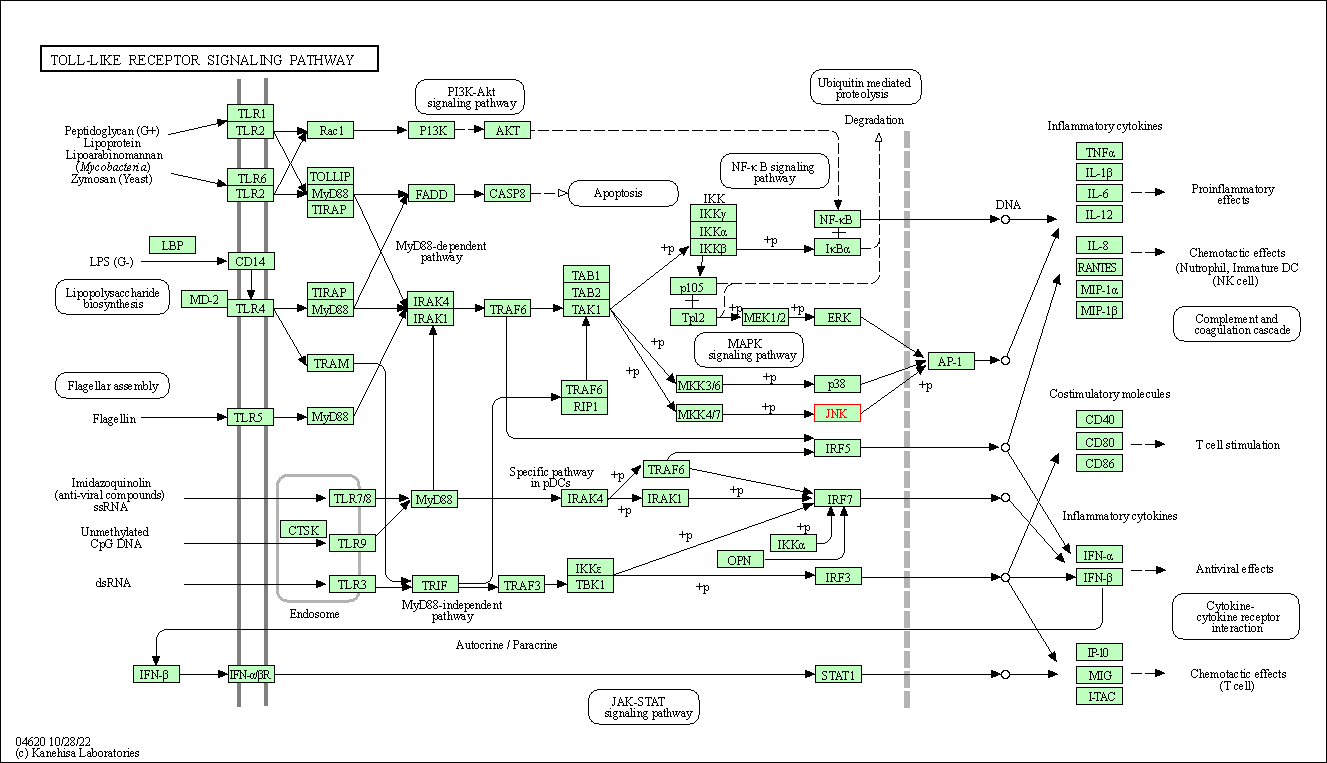
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04620 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
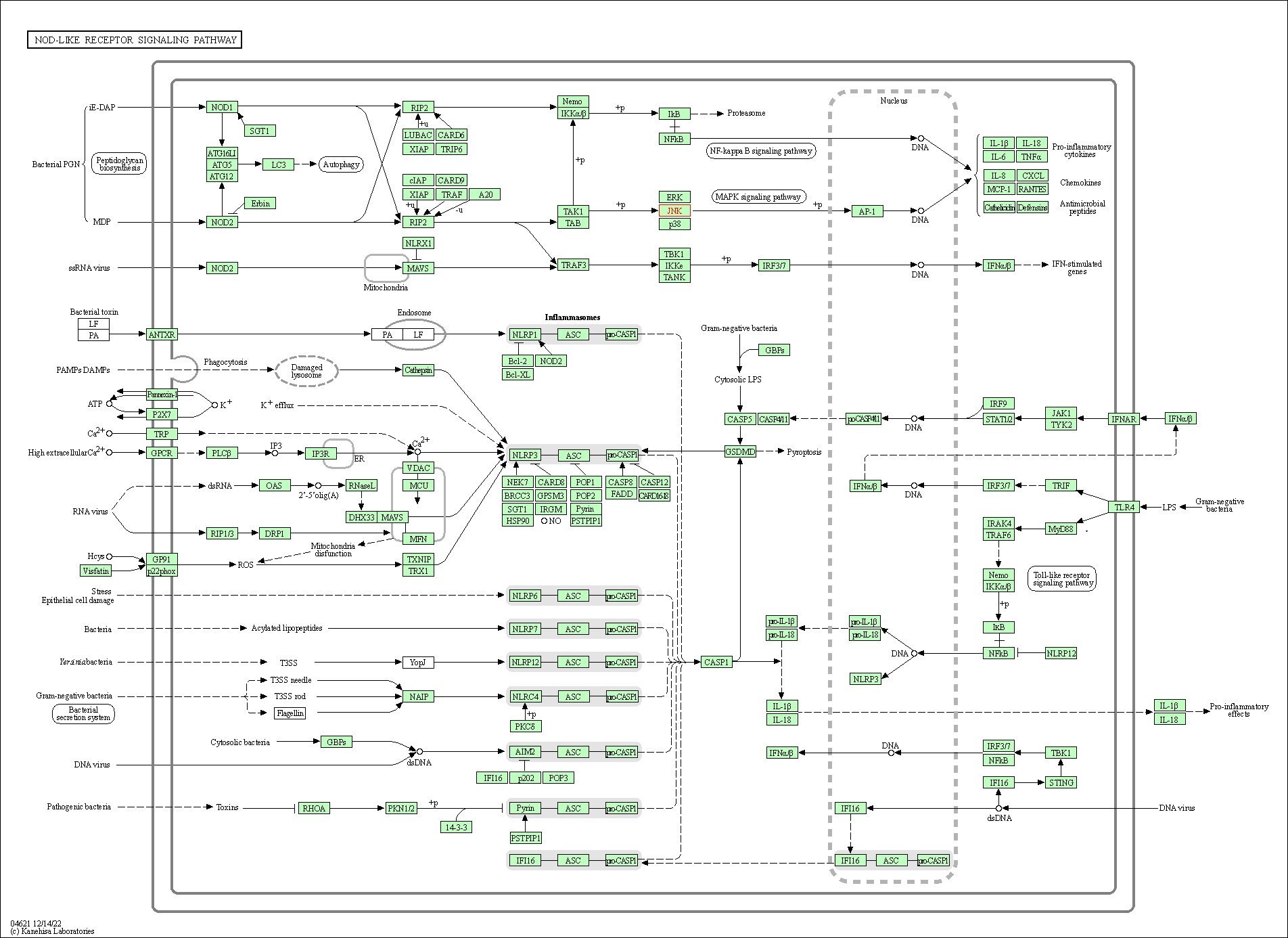
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04621 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04622 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
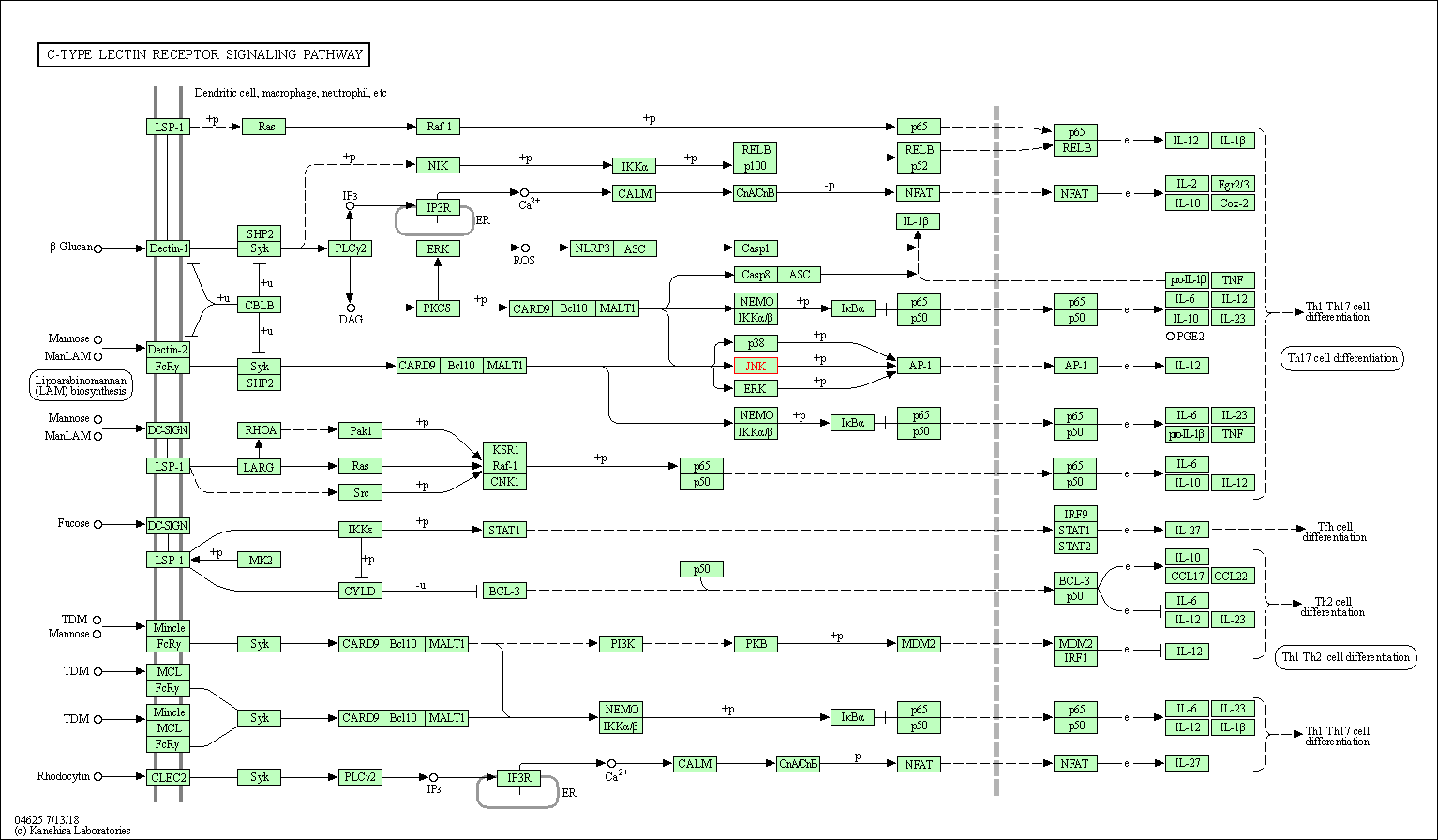
| C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway | hsa04625 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
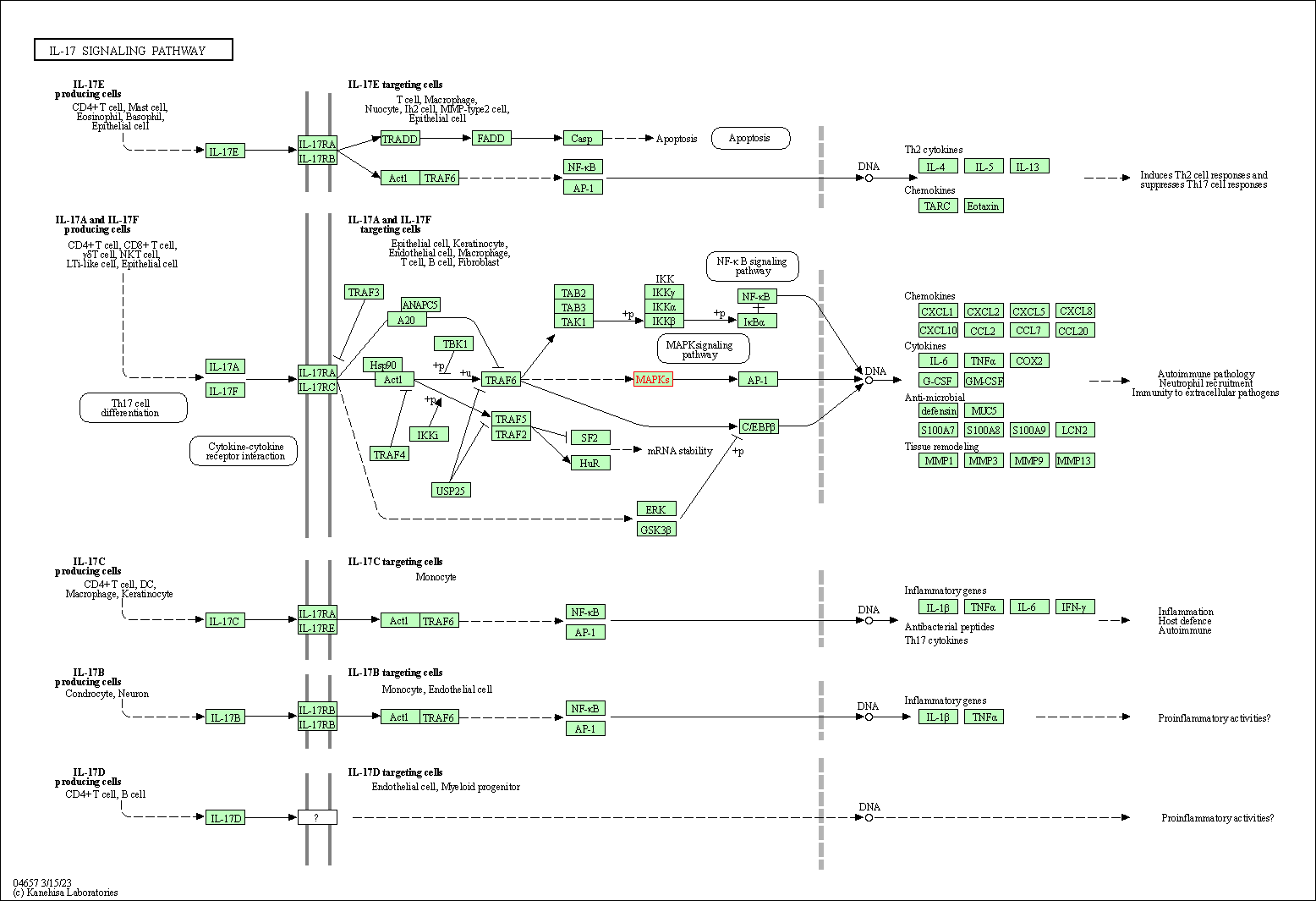
| IL-17 signaling pathway | hsa04657 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
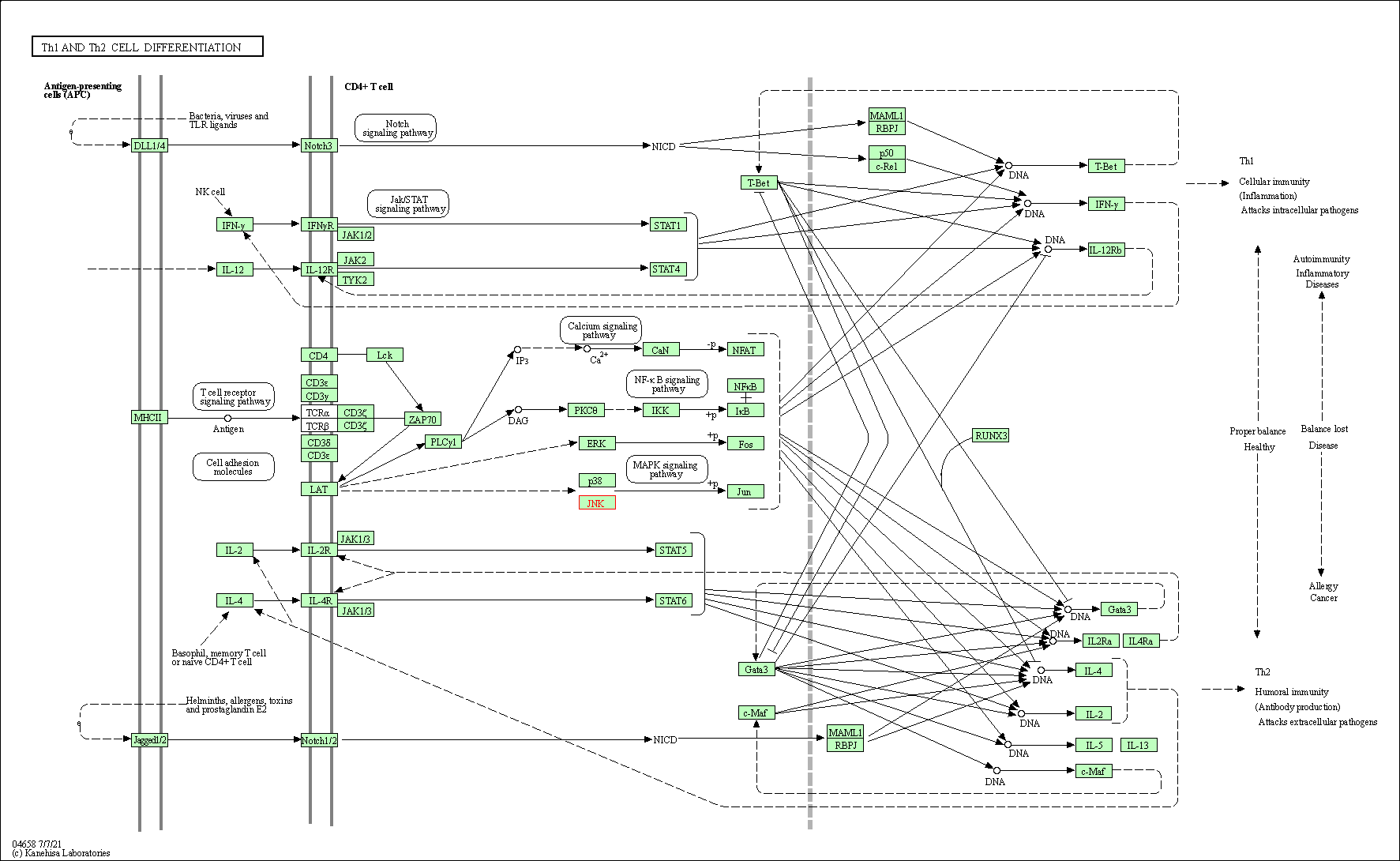
| Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation | hsa04658 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
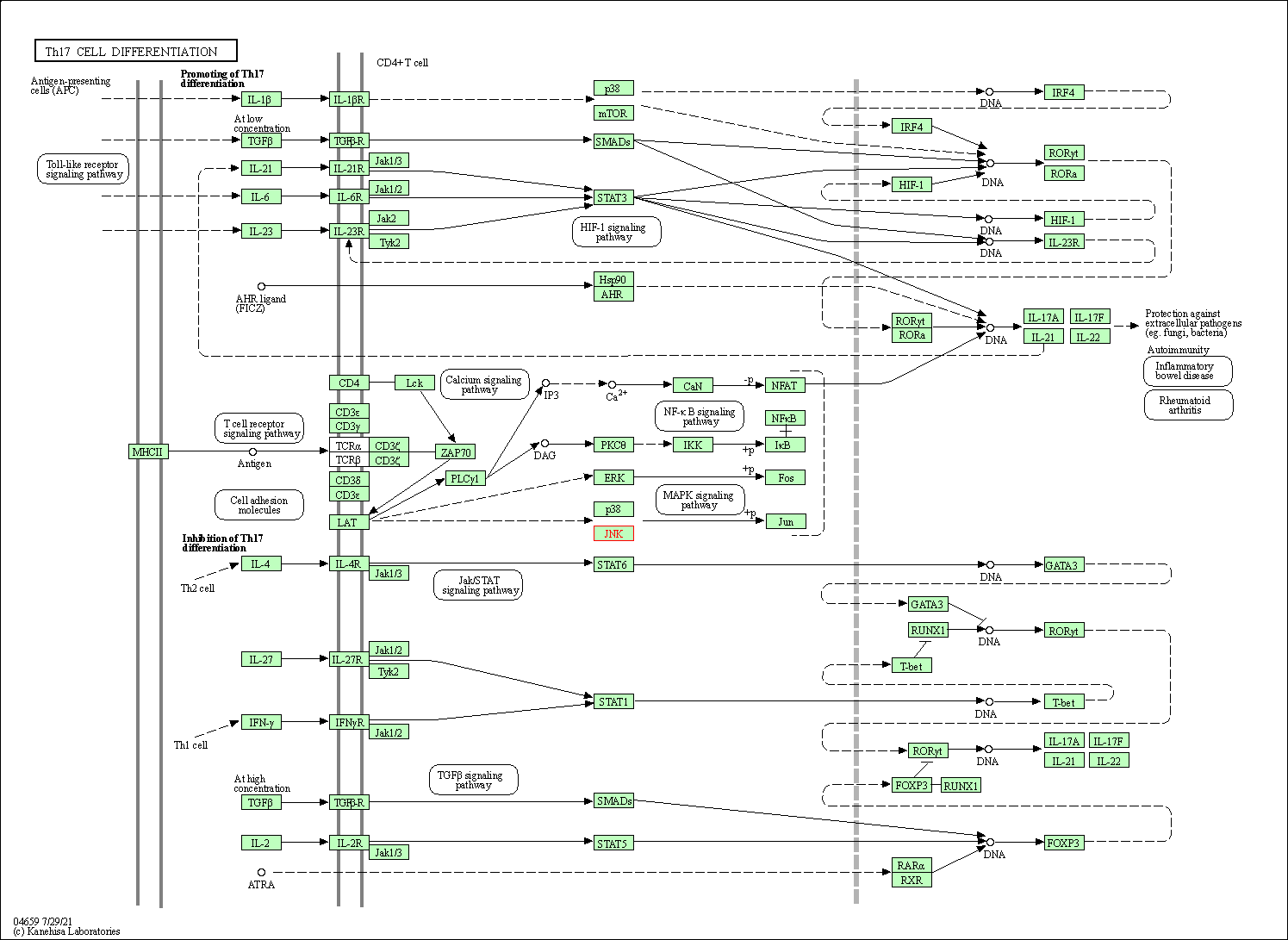
| Th17 cell differentiation | hsa04659 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
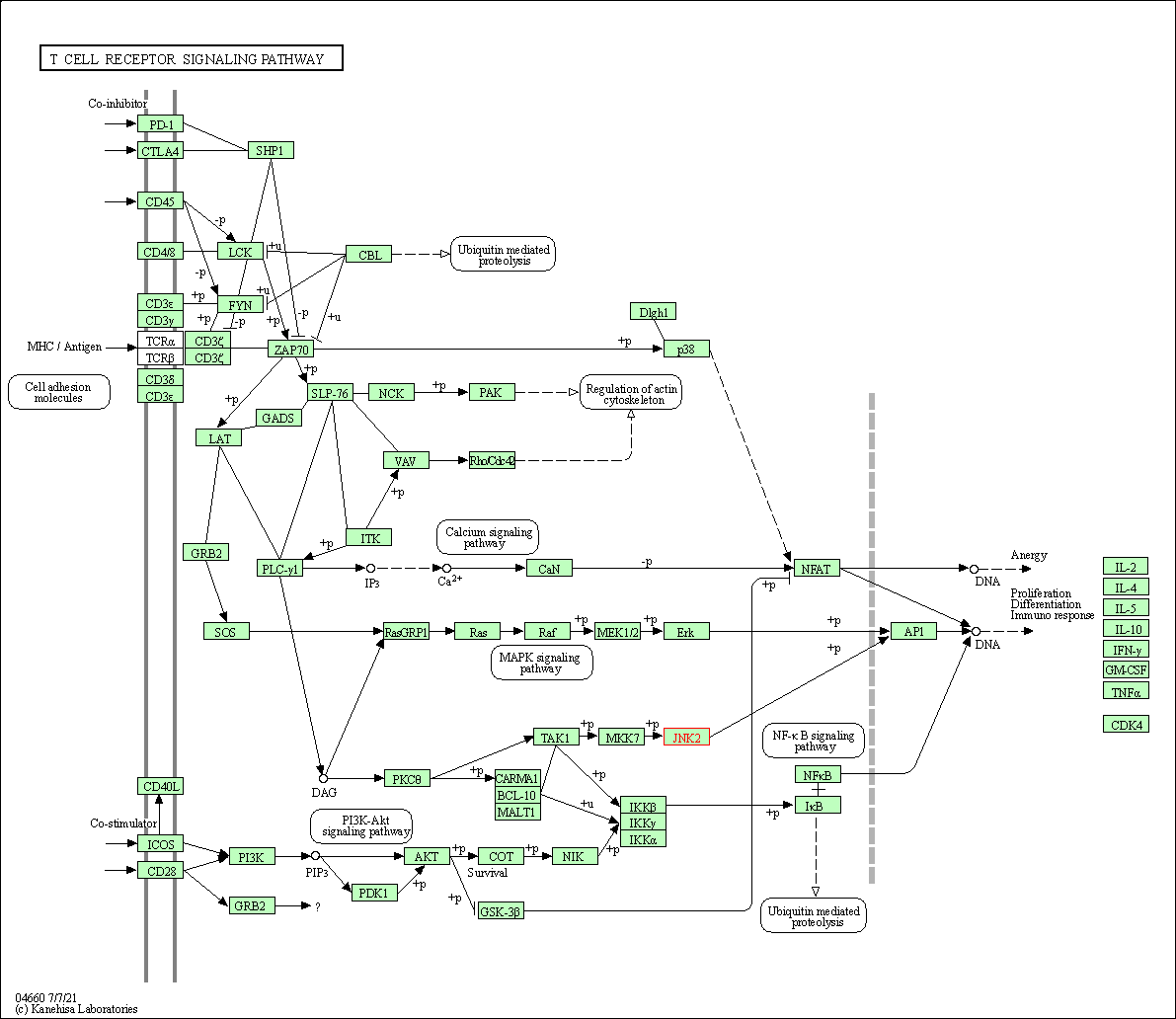
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04660 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
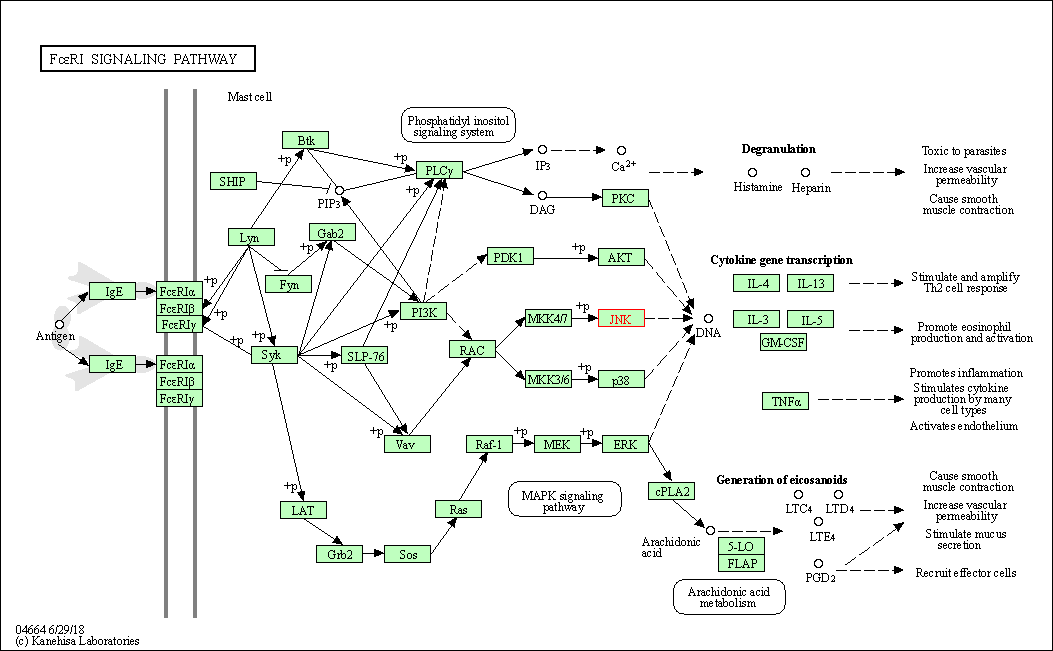
| Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway | hsa04664 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
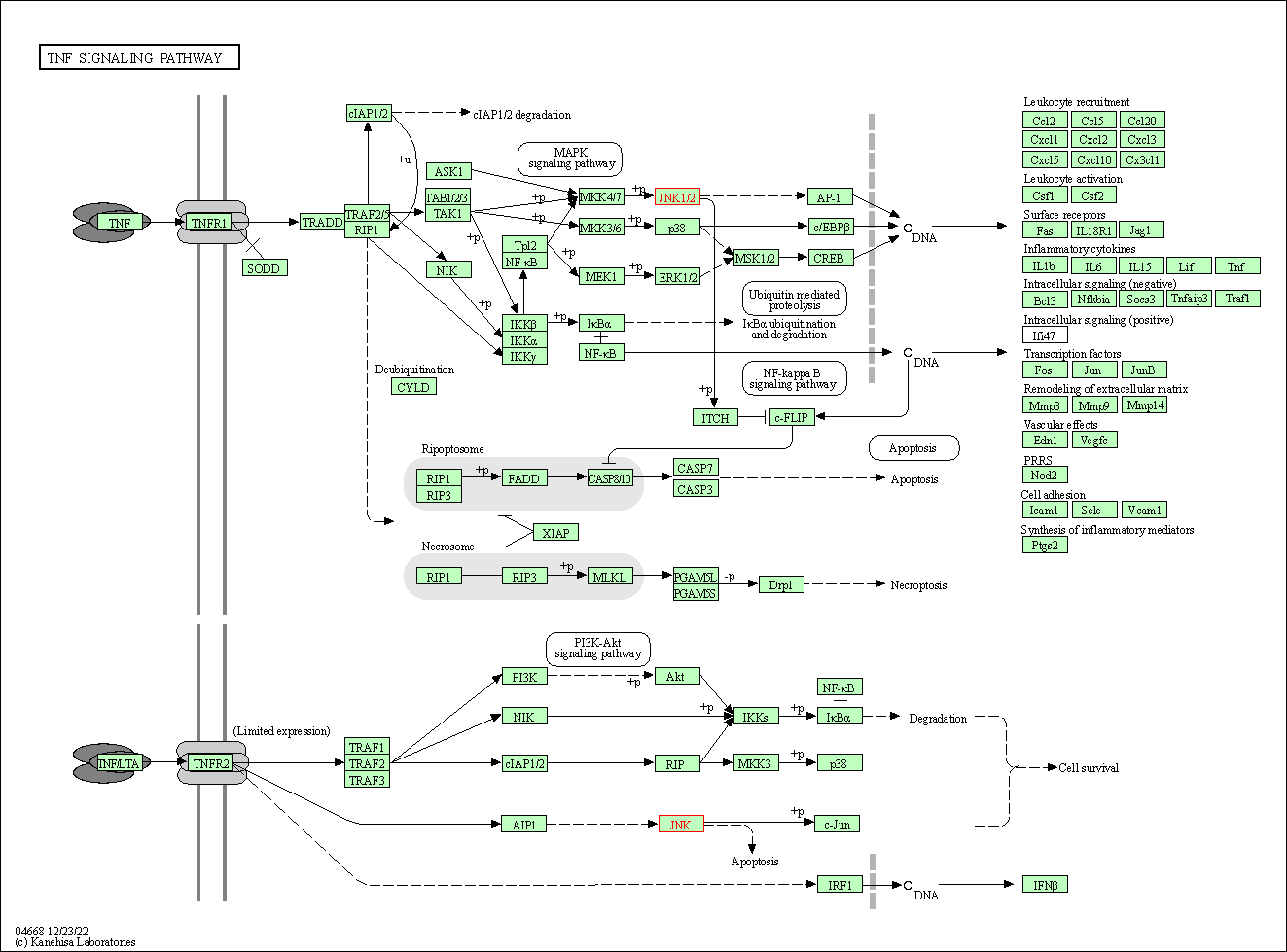
| TNF signaling pathway | hsa04668 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | hsa04722 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling | hsa04723 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Dopaminergic synapse | hsa04728 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels | hsa04750 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Sensory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Insulin signaling pathway | hsa04910 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| GnRH signaling pathway | hsa04912 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation | hsa04914 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Prolactin signaling pathway | hsa04917 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Adipocytokine signaling pathway | hsa04920 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Relaxin signaling pathway | hsa04926 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action | hsa04935 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 15 | Degree centrality | 1.61E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 3.59E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.53E-01 | Radiality | 1.44E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.00E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 6.29E+01 | Topological coefficient | 9.08E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitors: a patent review (2010 - 2014).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015;25(8):849-72. | |||||
| REF 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04022863) Ovarium Cancer Detection by TEP's and ctDNA. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 3 | Corchorusin-D directed apoptosis of K562 cells occurs through activation of mitochondrial and death receptor pathways and suppression of AKT/PKB pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2012;30(4):915-26. | |||||
| REF 4 | Pharmacological inhibitors of MAPK pathways. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2002 Jan;23(1):40-5. | |||||
| REF 5 | Development of a Covalent Inhibitor of c-Jun N-Terminal Protein Kinase (JNK) 2/3 with Selectivity over JNK1. J Med Chem. 2023 Mar 9;66(5):3356-3371. | |||||
| REF 6 | X-ray crystal structure of JNK2 complexed with the p38alpha inhibitor BIRB796: insights into the rational design of DFG-out binding MAP kinase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Sep 1;20(17):5217-20. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

