Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T80423
(Former ID: TTDI02613)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
von Hippel-Lindau disease tumor suppressor (VHL)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
pVHL; Protein G7
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
VHL
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Patented-recorded target
|
[1] | ||||
| Function |
Seems to act as a target recruitment subunit in the E3 ubiquitin ligase complex and recruits hydroxylated hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) under normoxic conditions. Involved in transcriptional repression through interaction with HIF1A, HIF1AN and histone deacetylases. Ubiquitinates, in an oxygen-responsive manner, ADRB2. Involved in the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation via the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitination complex.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MPRRAENWDEAEVGAEEAGVEEYGPEEDGGEESGAEESGPEESGPEELGAEEEMEAGRPR
PVLRSVNSREPSQVIFCNRSPRVVLPVWLNFDGEPQPYPTLPPGTGRRIHSYRGHLWLFR DAGTHDGLLVNQTELFVPSLNVDGQPIFANITLPVYTLKERCLQVVRSLVKPENYRRLDI VRSLYEDLEDHPNVQKDLERLTQERIAHQRMGD Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: trans-4-hydroxy-proline | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | pVHL:EloB:EloC in complex with (4-(1H-pyrrol-1-yl)phenyl)methanol | PDB:6GMR | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.75 Å | Mutation | No | [2] |
| PDB Sequence |
RPVLRSVNSR
69 EPSQVIFCNR79 SPRVVLPVWL89 NFDGEPQPYP99 TLPPGTGRRI109 HSYRGHLWLF 119 RDAGTHDGLL129 VNQTELFVPS139 LNVDGQPIFA149 NITLPVYTLK159 ERCLQVVRSL 169 VKPENYRRLD179 IVRSLYEDLE189 DHPNVQKDLE199 RLTQERIAH
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: Pyrrolidine carboxamide derivative 1 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | pVHL54-213-EloB-EloC complex (4R)-4-HYDROXY-1-[(3-METHYLISOXAZOL-5-YL)ACETYL]-N-[4-(1,3-OXAZOL-5-YL)BENZYL]-L-PROLINAMIDE bound | PDB:3ZRC | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.90 Å | Mutation | No | [3] |
| PDB Sequence |
LRSVNSREPS
72 QVIFCNRSPR82 VVLPVWLNFD92 GEPQPYPTLP102 PGTGRRIHSY112 RGHLWLFRDA 122 GTHDGLLVNQ132 TELFVPSLNV142 DGQPIFANIT152 LPVYTLKERC162 LQVVRSLVKP 172 ENYRRLDIVR182 SLYEDLEDHP192 NVQKDLERLT202 QE
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
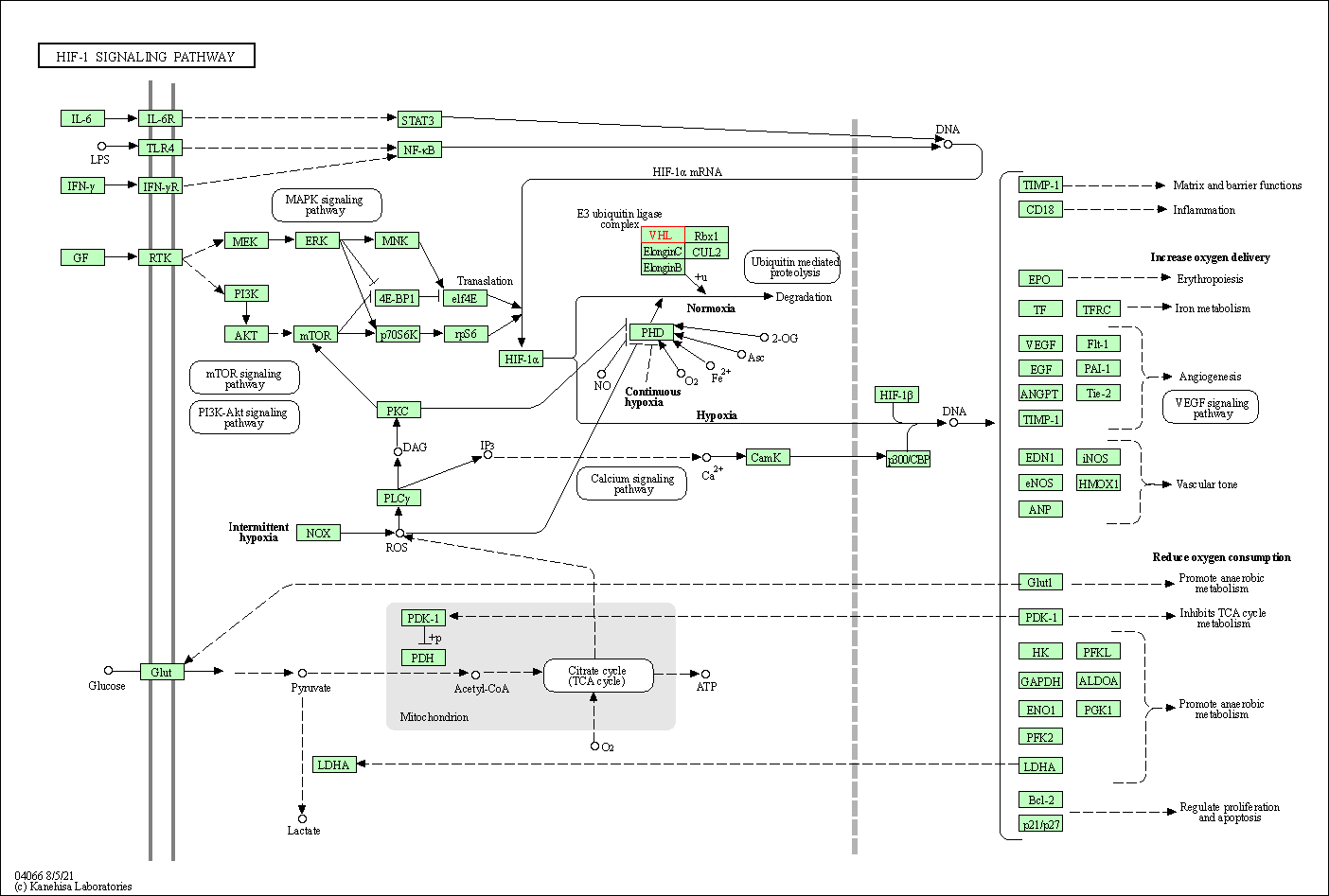
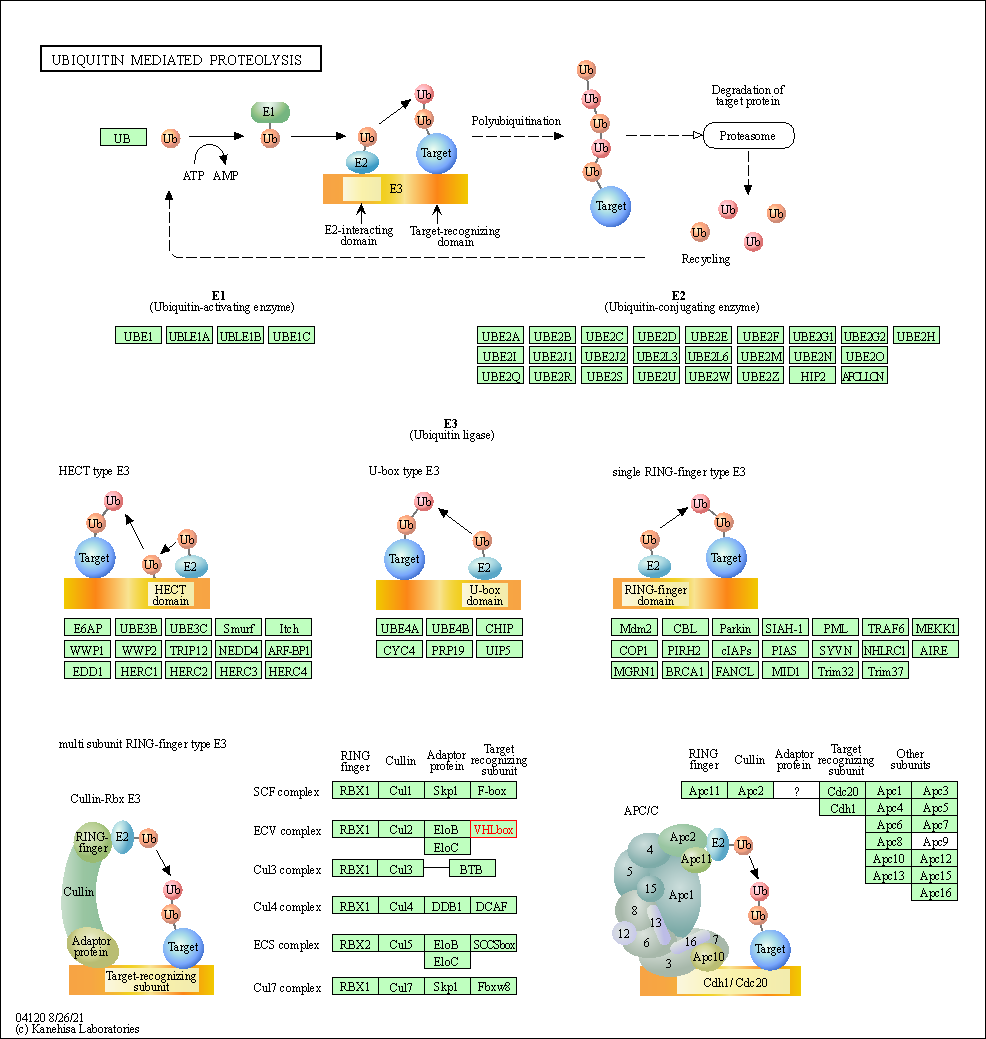
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| HIF-1 signaling pathway | hsa04066 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | hsa04120 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Genetic Information Processing => Folding, sorting and degradation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 14 | Degree centrality | 1.50E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 5.16E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.32E-01 | Radiality | 1.41E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.64E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.03E+01 | Topological coefficient | 1.10E-01 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) inhibitors: a patent survey (2011-2015).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2016;26(3):309-22. | |||||
| REF 2 | Surface Probing by Fragment-Based Screening and Computational Methods Identifies Ligandable Pockets on the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) E3 Ubiquitin Ligase. J Med Chem. 2018 Aug 23;61(16):7387-7393. | |||||
| REF 3 | Targeting the von Hippel-Lindau E3 ubiquitin ligase using small molecules to disrupt the VHL/HIF-1Alpha interaction. J Am Chem Soc. 2012 Mar 14;134(10):4465-8. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

