Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T98913
(Former ID: TTDS00411)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor (G-CSF-R)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
c-fms; GCSFR; GCSF receptor; G-CSF receptor; Fms proto-oncogene; CD114
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
CSF3R
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Neutropenia [ICD-11: 4B00] | |||||
| 2 | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||||
| Function |
Plays a crucial role in the proliferation, differientation and survival of cells along the neutrophilic lineage. In addition it may function in some adhesion or recognition events at the cell surface. Receptor for granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (CSF3), essential for granulocytic maturation.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Cytokine receptor
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MARLGNCSLTWAALIILLLPGSLEECGHISVSAPIVHLGDPITASCIIKQNCSHLDPEPQ
ILWRLGAELQPGGRQQRLSDGTQESIITLPHLNHTQAFLSCCLNWGNSLQILDQVELRAG YPPAIPHNLSCLMNLTTSSLICQWEPGPETHLPTSFTLKSFKSRGNCQTQGDSILDCVPK DGQSHCCIPRKHLLLYQNMGIWVQAENALGTSMSPQLCLDPMDVVKLEPPMLRTMDPSPE AAPPQAGCLQLCWEPWQPGLHINQKCELRHKPQRGEASWALVGPLPLEALQYELCGLLPA TAYTLQIRCIRWPLPGHWSDWSPSLELRTTERAPTVRLDTWWRQRQLDPRTVQLFWKPVP LEEDSGRIQGYVVSWRPSGQAGAILPLCNTTELSCTFHLPSEAQEVALVAYNSAGTSRPT PVVFSESRGPALTRLHAMARDPHSLWVGWEPPNPWPQGYVIEWGLGPPSASNSNKTWRME QNGRATGFLLKENIRPFQLYEIIVTPLYQDTMGPSQHVYAYSQEMAPSHAPELHLKHIGK TWAQLEWVPEPPELGKSPLTHYTIFWTNAQNQSFSAILNASSRGFVLHGLEPASLYHIHL MAASQAGATNSTVLTLMTLTPEGSELHIILGLFGLLLLLTCLCGTAWLCCSPNRKNPLWP SVPDPAHSSLGSWVPTIMEEDAFQLPGLGTPPITKLTVLEEDEKKPVPWESHNSSETCGL PTLVQTYVLQGDPRAVSTQPQSQSGTSDQVLYGQLLGSPTSPGPGHYLRCDSTQPLLAGL TPSPKSYENLWFQASPLGTLVTPAPSQEDDCVFGPLLNFPLLQGIRVHGMEALGSF Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| ADReCS ID | BADD_A06316 | |||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T04OY0 | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 2 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Pegfilgrastim | Drug Info | Approved | Malignant solid tumour | [2], [3] | |
| 2 | Tbo-Filgrastim | Drug Info | Approved | Neutropenia | [3], [4] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 9 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Peg-G-CSF | Drug Info | Phase 3 | Solid tumour/cancer | [5] | |
| 2 | AX-200 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Cardiovascular disease | [6] | |
| 3 | BLZ-945 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis | [7] | |
| 4 | MAXY-G34 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Neutropenia | [8] | |
| 5 | SBC-014 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Neutropenia | [9] | |
| 6 | AMG 820 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Solid tumour/cancer | [10] | |
| 7 | MK-6302 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Neutropenia | [11] | |
| 8 | PLX-5622 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Autoimmune diabetes | [12] | |
| 9 | PLX7486 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Pancreatic cancer | [13] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 1 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | ZD-6003 | Drug Info | Terminated | Solid tumour/cancer | [14] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 5 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Binder | [+] 1 Binder drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Pegfilgrastim | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 5 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Tbo-Filgrastim | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 2 | AX-200 | Drug Info | [17] | |||
| 3 | SBC-014 | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 4 | MK-6302 | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 5 | ZD-6003 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| Stimulator | [+] 3 Stimulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Peg-G-CSF | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 2 | G-CSF | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 3 | ZP-G-CSF | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| Inhibitor | [+] 7 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | BLZ-945 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 2 | AMG 820 | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| 3 | PLX-5622 | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 4 | PLX7486 | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 5 | AC-710 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 6 | AZD-7507 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 7 | N-(2-morpholinophenyl)-5-nitrofuran-2-carboxamide | Drug Info | [24] | |||
| Agonist | [+] 1 Agonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | MAXY-G34 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
| Protein Name | Pfam ID | Percentage of Identity (%) | E value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prolactin receptor (PRLR) | 25.701 (55/214) | 1.16E-11 | |
| Interleukin 23 receptor (IL23R) | 23.605 (55/233) | 2.45E-10 | |
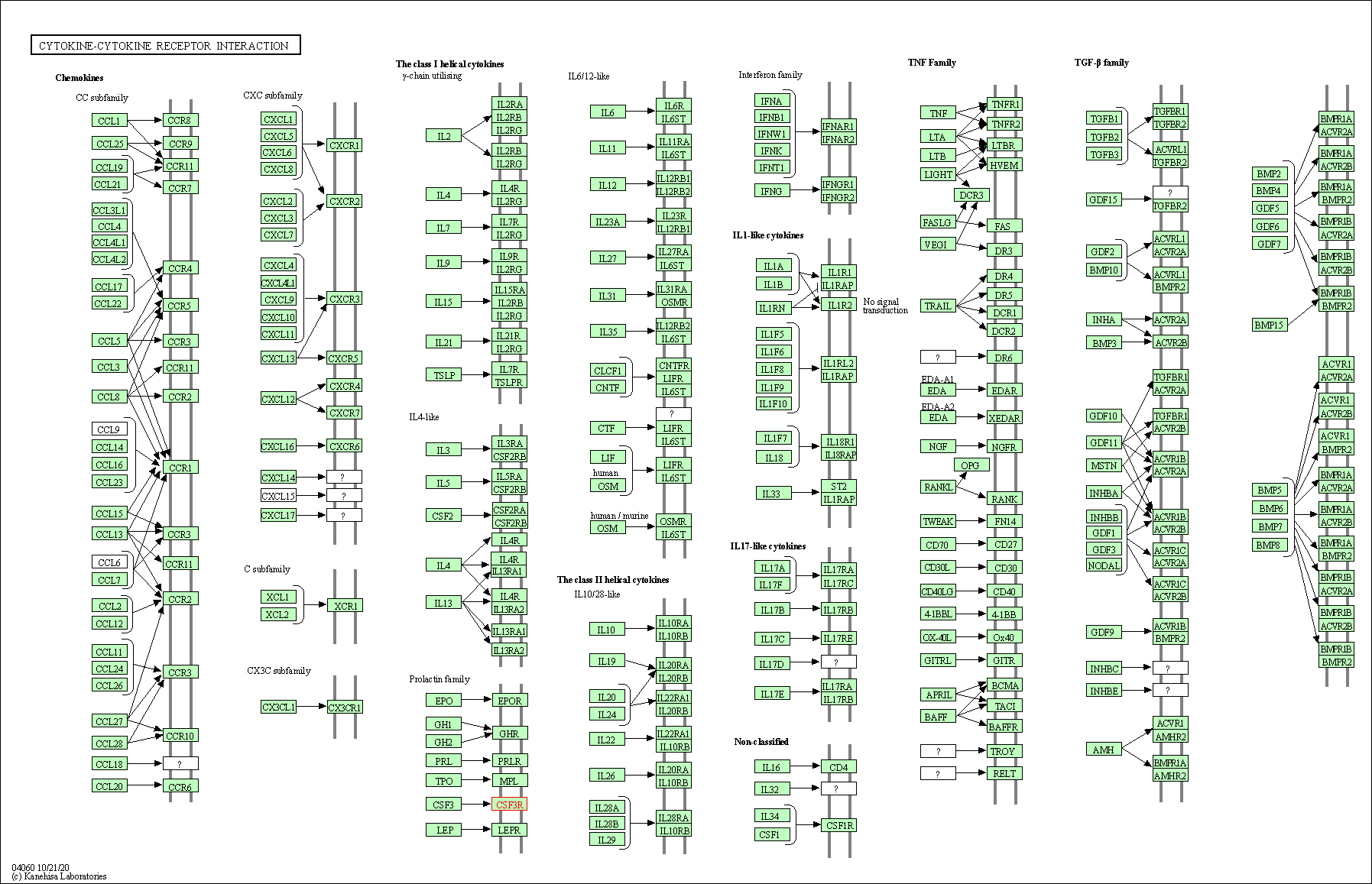
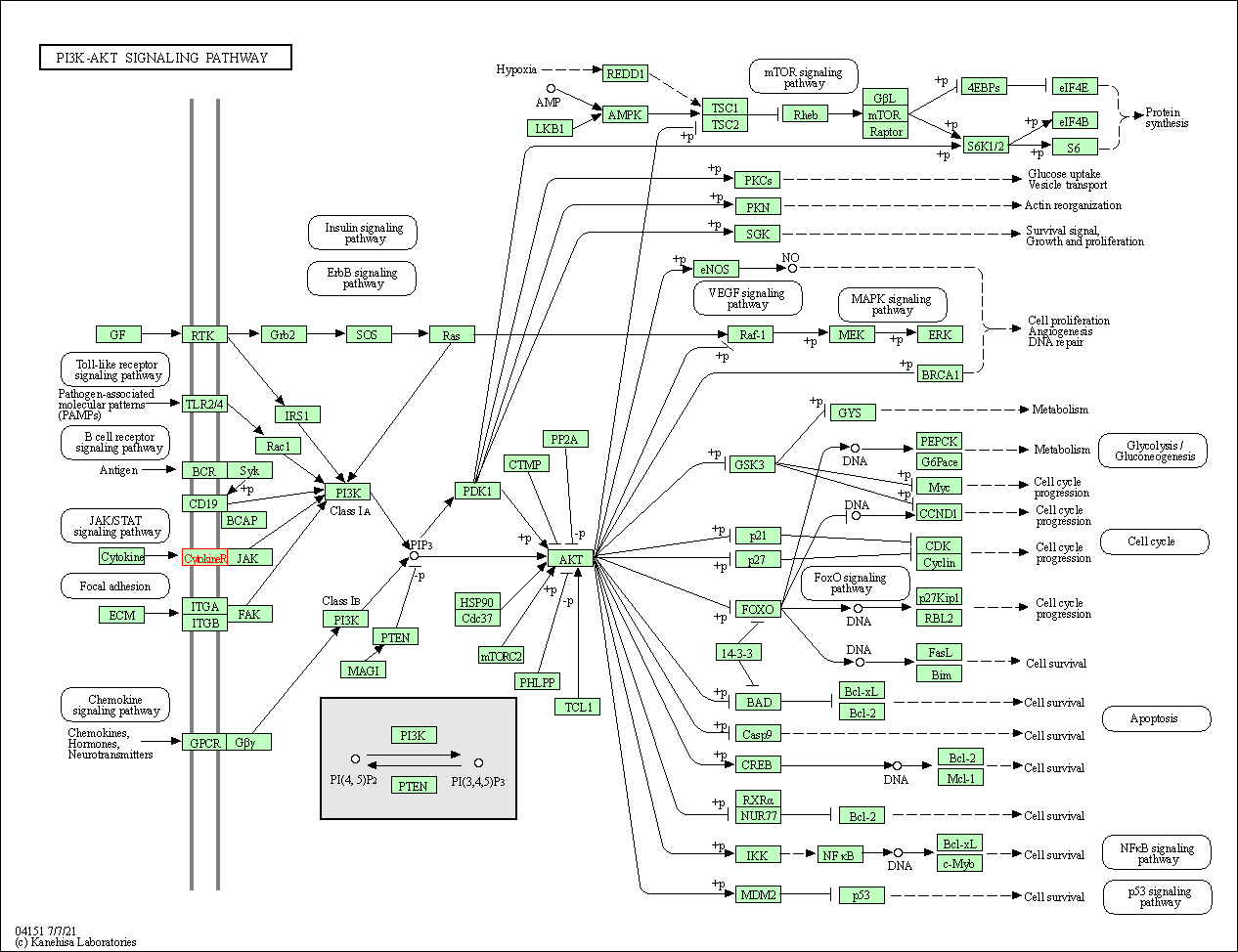
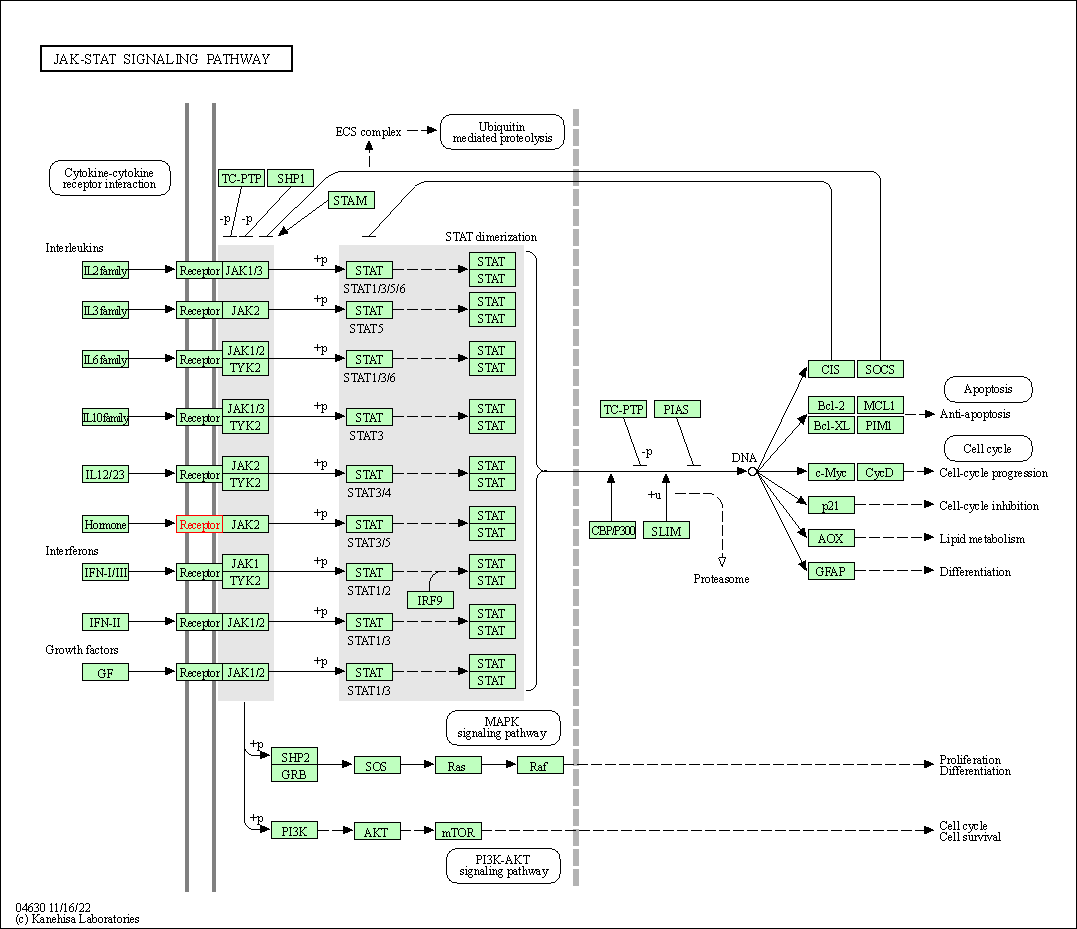
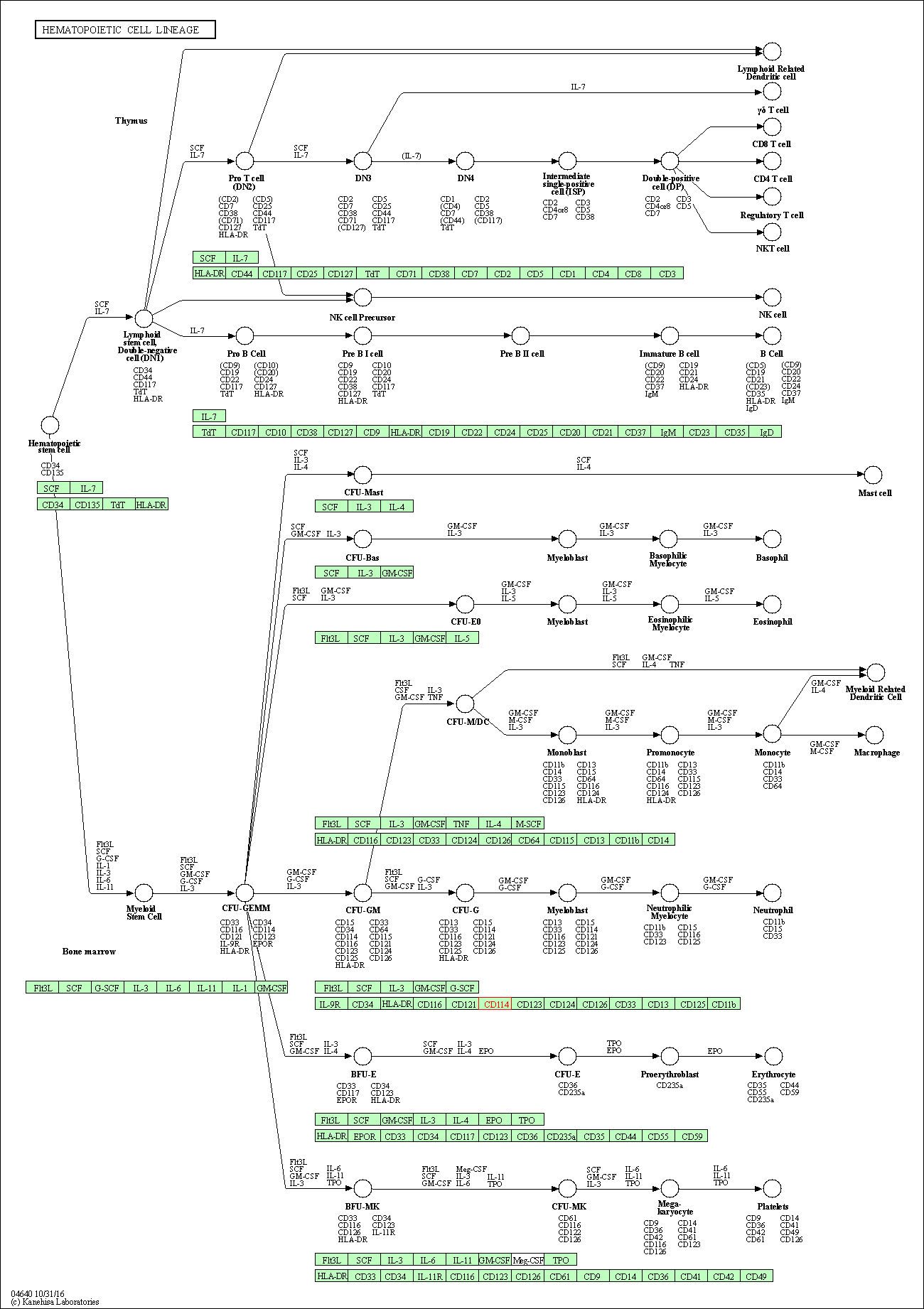
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | hsa04060 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| JAK-STAT signaling pathway | hsa04630 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Hematopoietic cell lineage | hsa04640 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Degree | 3 | Degree centrality | 3.22E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 1.05E-06 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.01E-01 | Radiality | 1.35E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 3.33E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 2.43E+01 | Topological coefficient | 3.69E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating Transcription Factors | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 5 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | |||||
| 2 | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | |||||
| 3 | Jak-STAT signaling pathway | |||||
| 4 | Hematopoietic cell lineage | |||||
| 5 | Pathways in cancer | |||||
| NetPath Pathway | [+] 2 NetPath Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Leptin Signaling Pathway | |||||
| 2 | RANKL Signaling Pathway | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Evidence that the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) receptor plays a role in the pharmacokinetics of G-CSF and PegG-CSF using a G-CSF-R KO model. Pharmacol Res. 2004 Jul;50(1):55-8. | |||||
| REF 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6969). | |||||
| REF 3 | Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod. 2007 Mar;70(3):461-77. | |||||
| REF 4 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 6968). | |||||
| REF 5 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01674855) Phase III Study of DA-3031(PEG-G-CSF) in Chemotherapy-induced Neutropenia. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 6 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00132470) Treatment With AX200 for Acute Ischemic Stroke. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 7 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04066244) Study of Safety and of the Mechanism of BLZ945 in ALS Patients. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 8 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00501332) Evaluation of Maxy-G34 in Breast Cancer Patients Treated With TAC (Docetaxel, Adriamycin, Cyclophosphamide) Chemotherapy. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 9 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00497809) Safety and Efficacy Study of GCSF Therapy to Treat Patients at High Risk for Chemotherapy Induced Severe Neutropenia. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 10 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800031593) | |||||
| REF 11 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Merck. | |||||
| REF 12 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01282684) Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of PLX5622 in Healthy Adult Volunteers. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 13 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800038879) | |||||
| REF 14 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800003738) | |||||
| REF 15 | Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013 Feb;12(2):87-90. | |||||
| REF 16 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Target id: 1719). | |||||
| REF 17 | Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in patients with acute ischemic stroke: results of the AX200 for Ischemic Stroke trial. Stroke. 2013 Oct;44(10):2681-7. | |||||
| REF 18 | Survival efficacy of the PEGylated G-CSFs Maxy-G34 and neulasta in a mouse model of lethal H-ARS, and residual bone marrow damage in treated survivors. Health Phys. 2014 Jan;106(1):21-38. | |||||
| REF 19 | A glycosylated recombinant human granulocyte colony stimulating factor produced in a novel protein production system (AVI-014) in healthy subjects: a first-in human, single dose, controlled study. BMC Clin Pharmacol. 2009; 9: 2. | |||||
| REF 20 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 21 | Merck ditches biogeneric. Nat Biotechnol. 2010 Jul;28(7):636. | |||||
| REF 22 | Microglial Stimulation of Glioblastoma Invasion Involves Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) and Colony Stimulating Factor 1 Receptor (CSF-1R) Signaling. Mol Med. 2012; 18(1): 519-527. | |||||
| REF 23 | National Cancer Institute Drug Dictionary (drug id 747694). | |||||
| REF 24 | Potent 2'-aminoanilide inhibitors of cFMS as potential anti-inflammatory agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 Nov 15;17(22):6070-4. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

