Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T78429
(Former ID: TTDR01206)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase beta (IKKB)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B inhibitor kinase beta; NFKBIKB; Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit beta; IkBKB; IKKB; IKK2; IKK-beta; IKK-B; I-kappa-B-kinase beta; I-kappa-B kinase 2
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
IKBKB
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 1 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Mature B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85] | |||||
| Function |
Serine kinase that plays an essential role in the NF-kappa-B signaling pathway which is activated by multiple stimuli such as inflammatory cytokines, bacterial or viral products, DNA damages or other cellular stresses. Acts as part of the canonical IKK complex in the conventional pathway of NF-kappa-B activation. Phosphorylates inhibitors of NF-kappa-B on 2 critical serine residues. These modifications allow polyubiquitination of the inhibitors and subsequent degradation by the proteasome. In turn, free NF-kappa-B is translocated into the nucleus and activates the transcription of hundreds of genes involved in immune response, growth control, or protection against apoptosis. In addition to the NF-kappa-B inhibitors, phosphorylates several other components of the signaling pathway including NEMO/IKBKG, NF-kappa-B subunits RELA and NFKB1, as well as IKK-related kinases TBK1 and IKBKE. IKK-related kinase phosphorylations may prevent the overproduction of inflammatory mediators since they exert a negative regulation on canonical IKKs. Phosphorylates FOXO3, mediating the TNF-dependent inactivation of this pro-apoptotic transcription factor. Also phosphorylates other substrates including NCOA3, BCL10 and IRS1. Within the nucleus, acts as an adapter protein for NFKBIA degradation in UV-induced NF-kappa-B activation.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Kinase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.7.11.10
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MSWSPSLTTQTCGAWEMKERLGTGGFGNVIRWHNQETGEQIAIKQCRQELSPRNRERWCL
EIQIMRRLTHPNVVAARDVPEGMQNLAPNDLPLLAMEYCQGGDLRKYLNQFENCCGLREG AILTLLSDIASALRYLHENRIIHRDLKPENIVLQQGEQRLIHKIIDLGYAKELDQGSLCT SFVGTLQYLAPELLEQQKYTVTVDYWSFGTLAFECITGFRPFLPNWQPVQWHSKVRQKSE VDIVVSEDLNGTVKFSSSLPYPNNLNSVLAERLEKWLQLMLMWHPRQRGTDPTYGPNGCF KALDDILNLKLVHILNMVTGTIHTYPVTEDESLQSLKARIQQDTGIPEEDQELLQEAGLA LIPDKPATQCISDGKLNEGHTLDMDLVFLFDNSKITYETQISPRPQPESVSCILQEPKRN LAFFQLRKVWGQVWHSIQTLKEDCNRLQQGQRAAMMNLLRNNSCLSKMKNSMASMSQQLK AKLDFFKTSIQIDLEKYSEQTEFGITSDKLLLAWREMEQAVELCGRENEVKLLVERMMAL QTDIVDLQRSPMGRKQGGTLDDLEEQARELYRRLREKPRDQRTEGDSQEMVRLLLQAIQS FEKKVRVIYTQLSKTVVCKQKALELLPKVEEVVSLMNEDEKTVVRLQEKRQKELWNLLKI ACSKVRGPVSGSPDSMNASRLSQPGQLMSQPSTASNSLPEPAKKSEELVAEAHNLCTLLE NAIQDTVREQDQSFTALDWSWLQTEEEEHSCLEQAS Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | PDB | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T83P5X | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 1 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Arsenic trioxide | Drug Info | Approved | Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia | [2], [3] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 3 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | IMD-1041 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Alzheimer disease | [4] | |
| 2 | SAR-113945 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Osteoarthritis | [5] | |
| 3 | IMD-0354 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Acne vulgaris | [6] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 1 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | MLN0415 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 1 | Arthritis | [7] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 17 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Arsenic trioxide | Drug Info | [8], [9] | |||
| 2 | IMD-1041 | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 3 | Parthenolide | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 4 | SAR-113945 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 5 | IMD-0354 | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 6 | 2-amino-5-phenylthiophene-3-carboxamide | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 7 | 2-amino-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid amide | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 8 | 3-amino-5-(4-chlorophenyl)thiophene-2-carboxamide | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 9 | 3-amino-benzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxylic acid amide | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 10 | 4-amino-biphenyl-3-carboxylic acid amide | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 11 | 5-amino-2-p-tolyl-oxazole-4-carboxylic acid amide | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 12 | 5-amino-2-phenyl-oxazole-4-carboxylic acid amide | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 13 | 5-Bromo-6-methoxy-9H-beta-carboline | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 14 | 6-phenyl-thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-4-ylamine | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 15 | PF-228 | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 16 | SC-514 | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 17 | Staurosporine | Drug Info | [17] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 1 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | MLN0415 | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: K252a | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Human IkB kinase beta | PDB:4KIK | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.83 Å | Mutation | No | [18] |
| PDB Sequence |
> Chain A
TQTCGAWEMK 18 ERLGTGNVIR31 WHNQETGEQI41 AIKQCRQELS51 PRNRERWCLE61 IQIMRRLTHP 71 NVVAARDVPE81 GMQNDLPLLA95 MEYCQGGDLR105 KYLNQFENCC115 GLREGAILTL 125 LSDIASALRY135 LHENRIIHRD145 LKPENIVLQQ155 GEQRLIHKII165 DLGYTSFVGT 185 LQYLAPELLE195 QQKYTVTVDY205 WSFGTLAFEC215 ITGFRPFLPN225 WQPVQWHSKV 235 RQKSEVDIVV245 SEDLNGTVKF255 SSLPYPNNLN266 SVLAERLEKW276 LQLMLMWHPR 286 QRGTDPTYGP296 NGCFKALDDI306 LNLKLVHILN316 MVTGTIHTYP326 VTEDESLQSL 336 KARIQQDTGI346 PEEDQELLQE356 AGLALIPDKP366 ATQCISLNEG379 HTLDMDLVFL 389 FDNSKITYET399 QRPQPESVSC412 ILQEPKRNLA422 FFQLRKVWGQ432 VWHSIQTLKE 442 DCNRLQQGQR452 AAMMNLLRNN462 SCLSKMKNSM472 ASMSQQLKAK482 LDFFKTSIQI 492 DLEKYSEQTD508 KLLLAWREME518 QAVELCGREN528 EVKLLVERMM538 ALQTDIVDLQ 548 RSGTLDDLEE565 QARELYRRLR575 EKPRDQRTEG585 DSQEMVRLLL595 QAIQSFEKKV 605 RVIYTQLSKT615 VVCKQKALEL625 LPKVEEVVSL635 MNEDEKTVVR645 LQEKRQKELW 655 NLLKIACS> Chain B HSWSPSLTTQ 10 TCGAWEMKER20 LGTGGFGNVI30 RWHNQETGEQ40 IAIKQCRQEL50 SPRNRERWCL 60 EIQIMRRLTH70 PNVVAARDVP80 EGMQNLAPND90 LPLLAMEYCQ100 GGDLRKYLNQ 110 FENCCGLREG120 AILTLLSDIA130 SALRYLHENR140 IIHRDLKPEN150 IVLQQGEQRL 160 IHKIIDLGYA170 KELLCTFVGT185 LQYLAPELLE195 QQKYTVTVDY205 WSFGTLAFEC 215 ITGFRPFLPN225 WQPVQWHSKV235 RQKSEVDIVV245 SEDLNGTVKF255 SSSLPYPNNL 265 NSVLAERLEK275 WLQLMLMWHP285 RQRGTDPTYG295 PNGCFKALDD305 ILNLKLVHIL 315 NMVTGTIHTY325 PVTEDESLQS335 LKARIQQDTG345 IPEEDQELLQ355 EAGLALIPDK 365 PATQCISLNE378 GHTLDMDLVF388 LFDNSKITYE398 TQISPRPQPE408 SVSCILQEPK 418 RNLAFFQLRK428 VWGQVWHSIQ438 TLKEDCNRLQ448 QGQRAAMMNL458 LRNNSCLSKM 468 KNSMASMSQQ478 LKAKLDFFKT488 SIQIDLEKYS498 EQTEFGITSD508 KLLLAWREME 518 QAVELCGREN528 EVKLLVERMM538 ALQTDIVDLQ548 RSGTLDDLEE565 QARELYRRLR 575 EKPRDQRTEG585 DSQEMVRLLL595 QAIQSFEKKV605 RVIYTQLSKT615 VVCKQKALEL 625 LPKVEEVVSL635 MNEDEKTVVR645 LQEKRQKELW655 NLLKIACS
|
|||||
|
|
LEU21[A]
3.402
GLY22[A]
3.403
THR23[A]
3.698
VAL29[A]
3.675
ALA42[A]
3.397
LYS44[A]
3.755
GLU61[A]
4.544
VAL74[A]
4.124
MET96[A]
3.699
GLU97[A]
2.956
TYR98[A]
3.646
CYS99[A]
2.929
GLY102[A]
3.484
ASP103[A]
3.761
GLU149[A]
2.713
ASN150[A]
3.777
VAL152[A]
3.812
ILE165[A]
3.437
ASP166[A]
3.726
LEU21[B]
3.153
GLY22[B]
3.318
THR23[B]
3.884
ASN28[B]
4.430
VAL29[B]
3.677
ALA42[B]
3.515
LYS44[B]
3.682
VAL74[B]
4.272
MET96[B]
3.590
GLU97[B]
2.718
TYR98[B]
3.242
CYS99[B]
2.698
GLY102[B]
3.527
ASP103[B]
3.890
LYS147[B]
4.930
GLU149[B]
2.566
ASN150[B]
3.544
VAL152[B]
3.822
ILE165[B]
3.264
ASP166[B]
3.217
|
|||||
| Ligand Name: L-serine-O-phosphate | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Human IkB kinase beta | PDB:4KIK | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.83 Å | Mutation | No | [18] |
| PDB Sequence |
> Chain A
TQTCGAWEMK 18 ERLGTGNVIR31 WHNQETGEQI41 AIKQCRQELS51 PRNRERWCLE61 IQIMRRLTHP 71 NVVAARDVPE81 GMQNDLPLLA95 MEYCQGGDLR105 KYLNQFENCC115 GLREGAILTL 125 LSDIASALRY135 LHENRIIHRD145 LKPENIVLQQ155 GEQRLIHKII165 DLGYTSFVGT 185 LQYLAPELLE195 QQKYTVTVDY205 WSFGTLAFEC215 ITGFRPFLPN225 WQPVQWHSKV 235 RQKSEVDIVV245 SEDLNGTVKF255 SSLPYPNNLN266 SVLAERLEKW276 LQLMLMWHPR 286 QRGTDPTYGP296 NGCFKALDDI306 LNLKLVHILN316 MVTGTIHTYP326 VTEDESLQSL 336 KARIQQDTGI346 PEEDQELLQE356 AGLALIPDKP366 ATQCISLNEG379 HTLDMDLVFL 389 FDNSKITYET399 QRPQPESVSC412 ILQEPKRNLA422 FFQLRKVWGQ432 VWHSIQTLKE 442 DCNRLQQGQR452 AAMMNLLRNN462 SCLSKMKNSM472 ASMSQQLKAK482 LDFFKTSIQI 492 DLEKYSEQTD508 KLLLAWREME518 QAVELCGREN528 EVKLLVERMM538 ALQTDIVDLQ 548 RSGTLDDLEE565 QARELYRRLR575 EKPRDQRTEG585 DSQEMVRLLL595 QAIQSFEKKV 605 RVIYTQLSKT615 VVCKQKALEL625 LPKVEEVVSL635 MNEDEKTVVR645 LQEKRQKELW 655 NLLKIACS> Chain B HSWSPSLTTQ 10 TCGAWEMKER20 LGTGGFGNVI30 RWHNQETGEQ40 IAIKQCRQEL50 SPRNRERWCL 60 EIQIMRRLTH70 PNVVAARDVP80 EGMQNLAPND90 LPLLAMEYCQ100 GGDLRKYLNQ 110 FENCCGLREG120 AILTLLSDIA130 SALRYLHENR140 IIHRDLKPEN150 IVLQQGEQRL 160 IHKIIDLGYA170 KELLCTFVGT185 LQYLAPELLE195 QQKYTVTVDY205 WSFGTLAFEC 215 ITGFRPFLPN225 WQPVQWHSKV235 RQKSEVDIVV245 SEDLNGTVKF255 SSSLPYPNNL 265 NSVLAERLEK275 WLQLMLMWHP285 RQRGTDPTYG295 PNGCFKALDD305 ILNLKLVHIL 315 NMVTGTIHTY325 PVTEDESLQS335 LKARIQQDTG345 IPEEDQELLQ355 EAGLALIPDK 365 PATQCISLNE378 GHTLDMDLVF388 LFDNSKITYE398 TQISPRPQPE408 SVSCILQEPK 418 RNLAFFQLRK428 VWGQVWHSIQ438 TLKEDCNRLQ448 QGQRAAMMNL458 LRNNSCLSKM 468 KNSMASMSQQ478 LKAKLDFFKT488 SIQIDLEKYS498 EQTEFGITSD508 KLLLAWREME 518 QAVELCGREN528 EVKLLVERMM538 ALQTDIVDLQ548 RSGTLDDLEE565 QARELYRRLR 575 EKPRDQRTEG585 DSQEMVRLLL595 QAIQSFEKKV605 RVIYTQLSKT615 VVCKQKALEL 625 LPKVEEVVSL635 MNEDEKTVVR645 LQEKRQKELW655 NLLKIACS
|
|||||
|
|
VAL241[A]
3.120
ASP242[A]
3.622
ILE243[A]
3.733
PHE255[A]
4.224
SER256[A]
1.329
SER258[A]
1.351
LEU259[A]
4.306
GLU274[A]
3.610
GLN278[A]
3.470
ARG53[B]
4.707
ARG57[B]
4.871
ARG144[B]
2.733
|
|||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
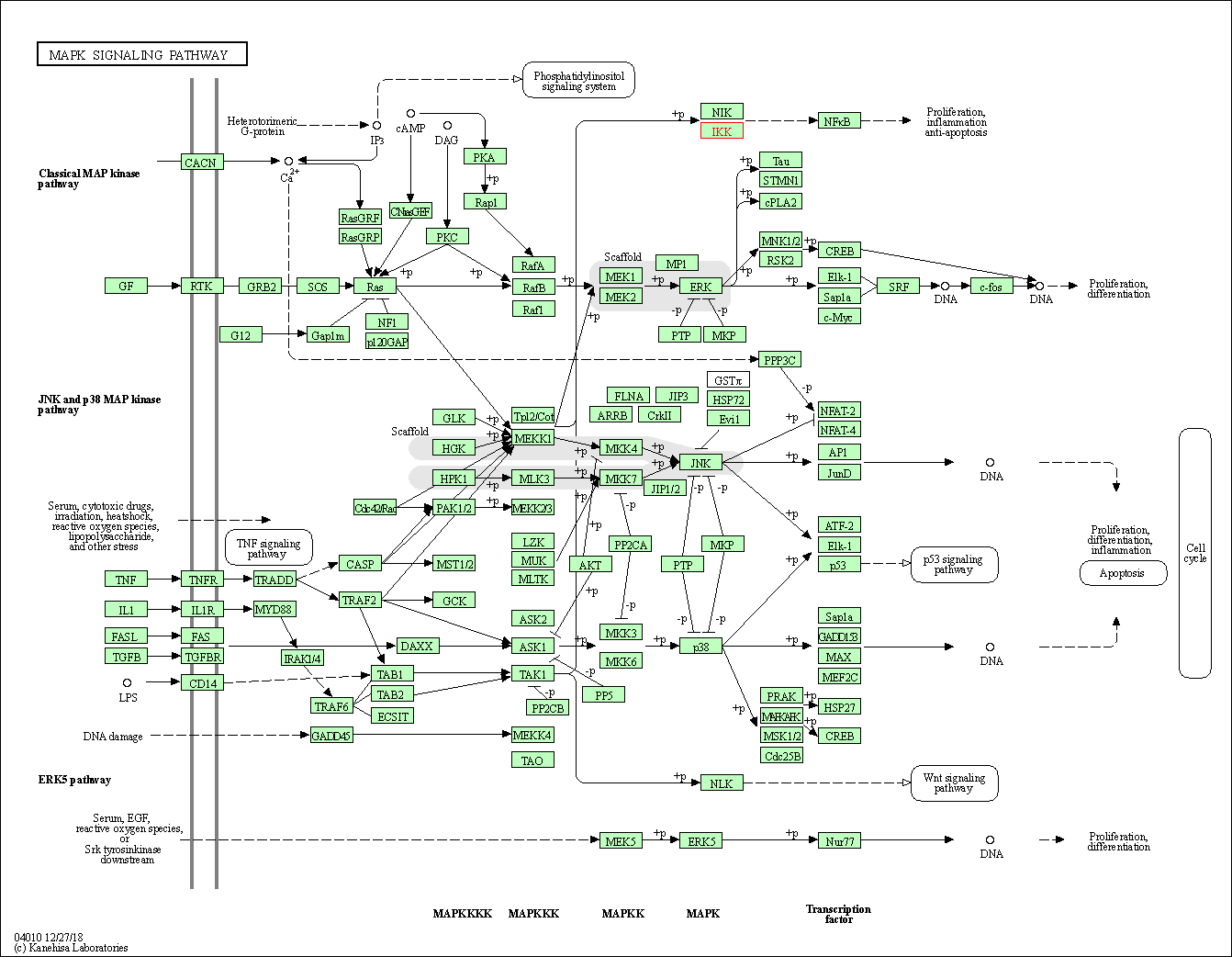
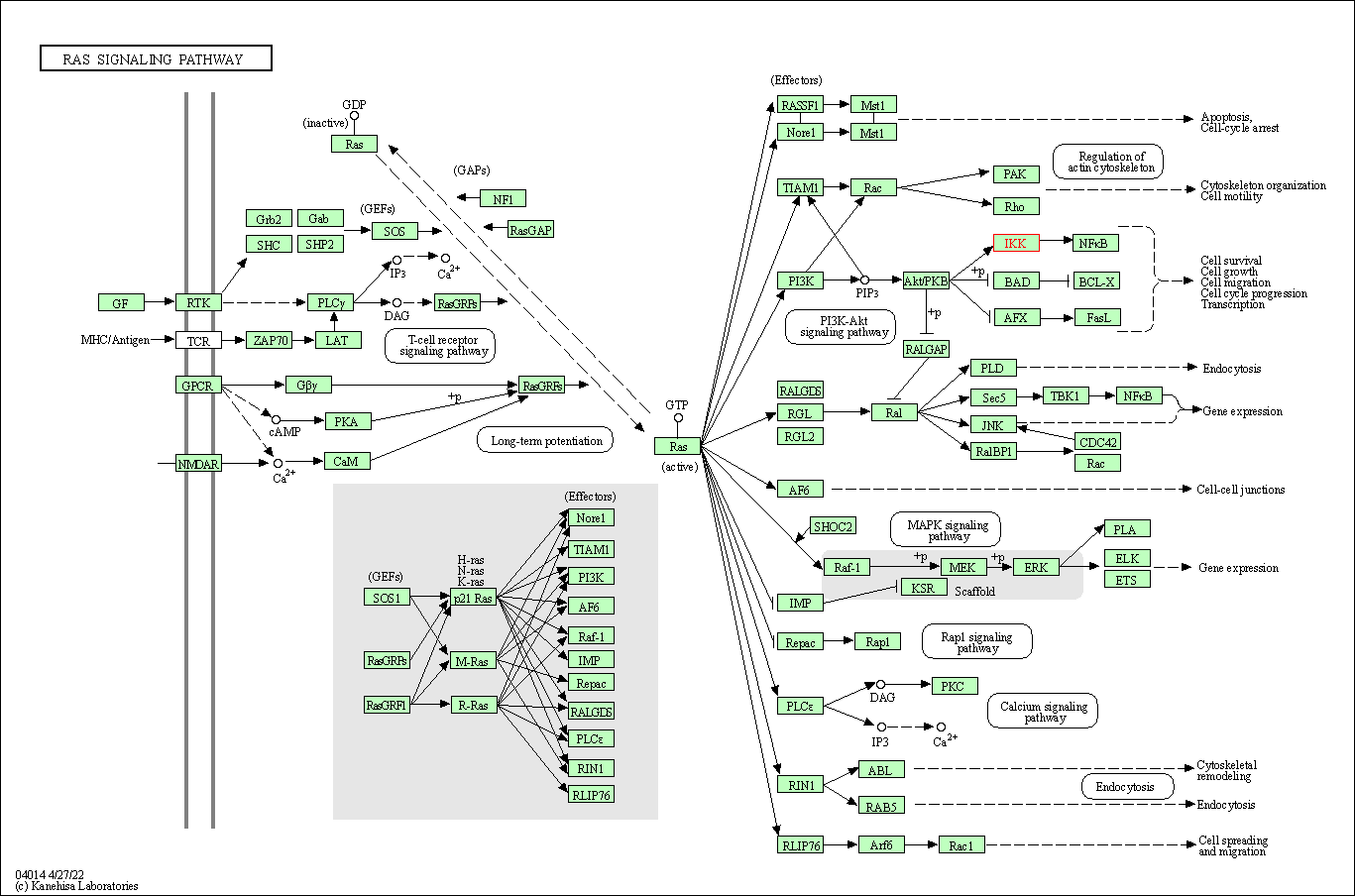

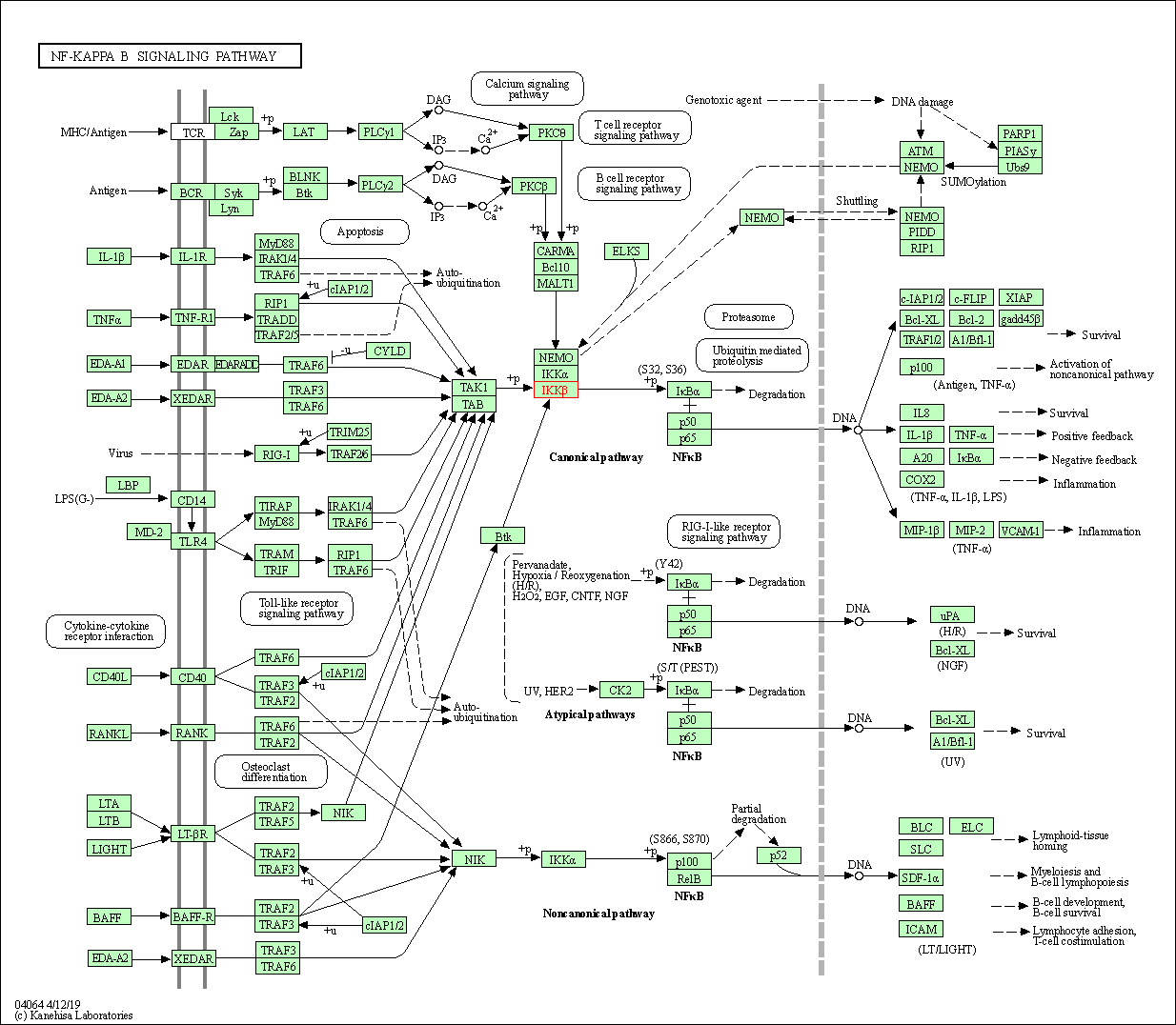
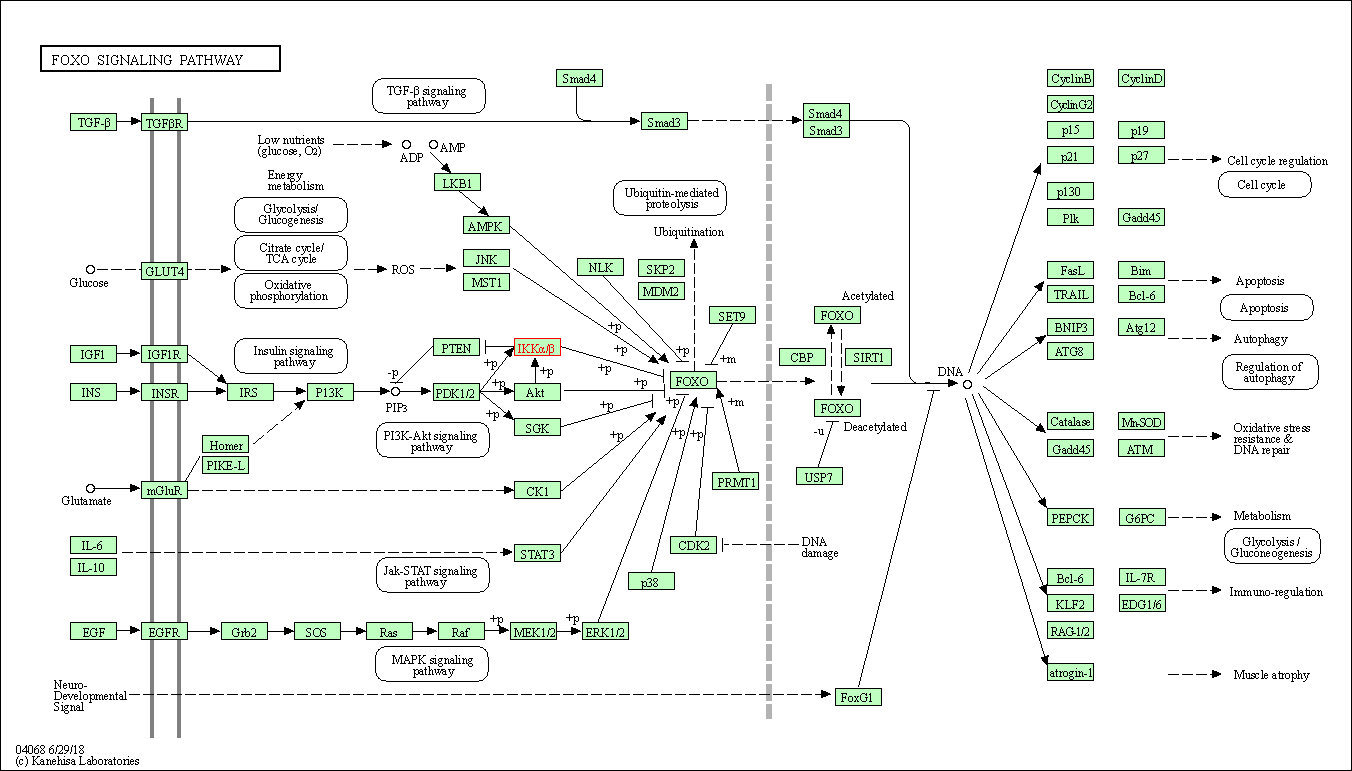









| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAPK signaling pathway | hsa04010 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Ras signaling pathway | hsa04014 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Chemokine signaling pathway | hsa04062 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | hsa04064 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| FoxO signaling pathway | hsa04068 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| mTOR signaling pathway | hsa04150 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | hsa04151 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
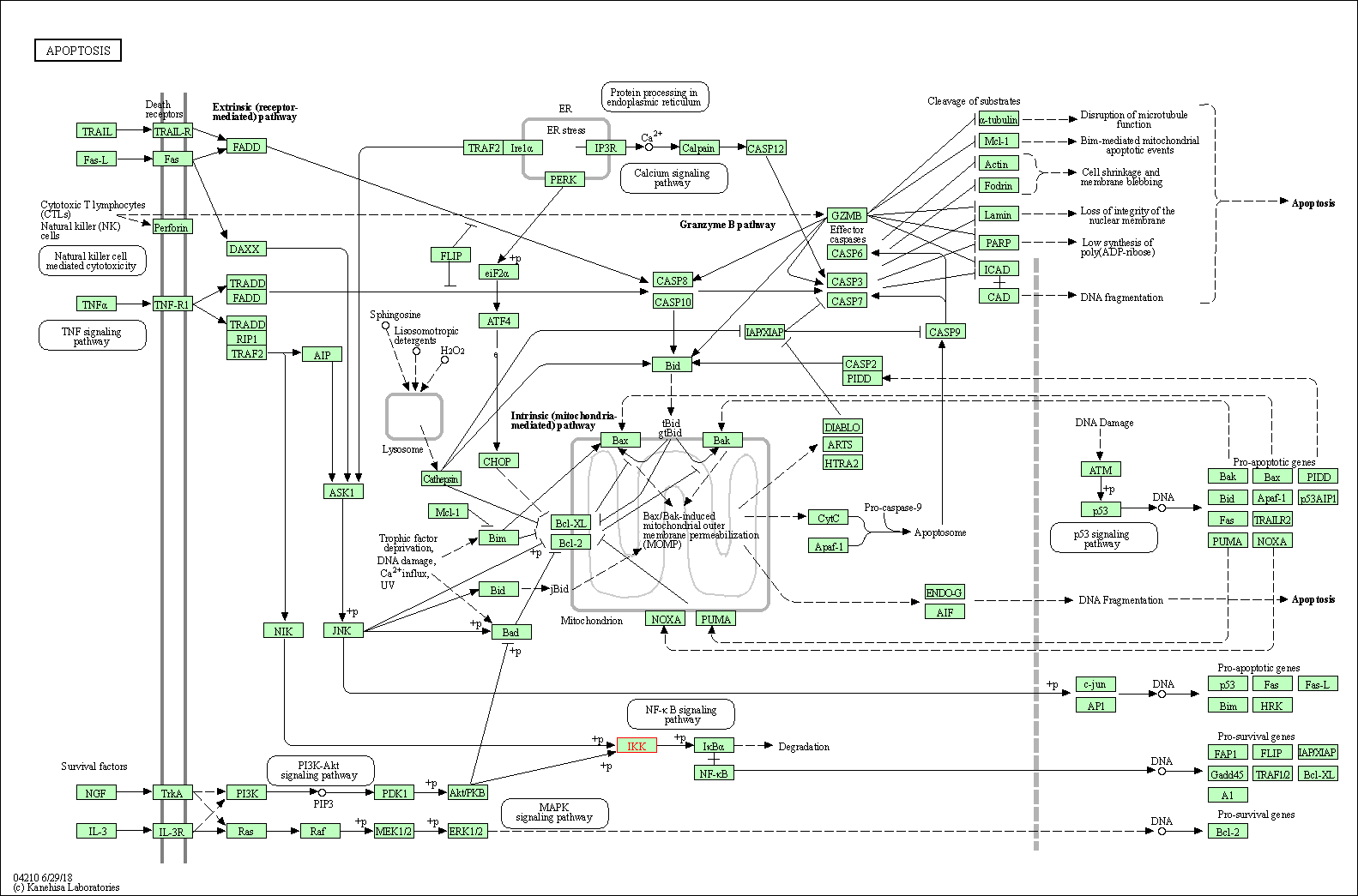
| Apoptosis | hsa04210 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Cell growth and death | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Osteoclast differentiation | hsa04380 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Development and regeneration | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04620 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
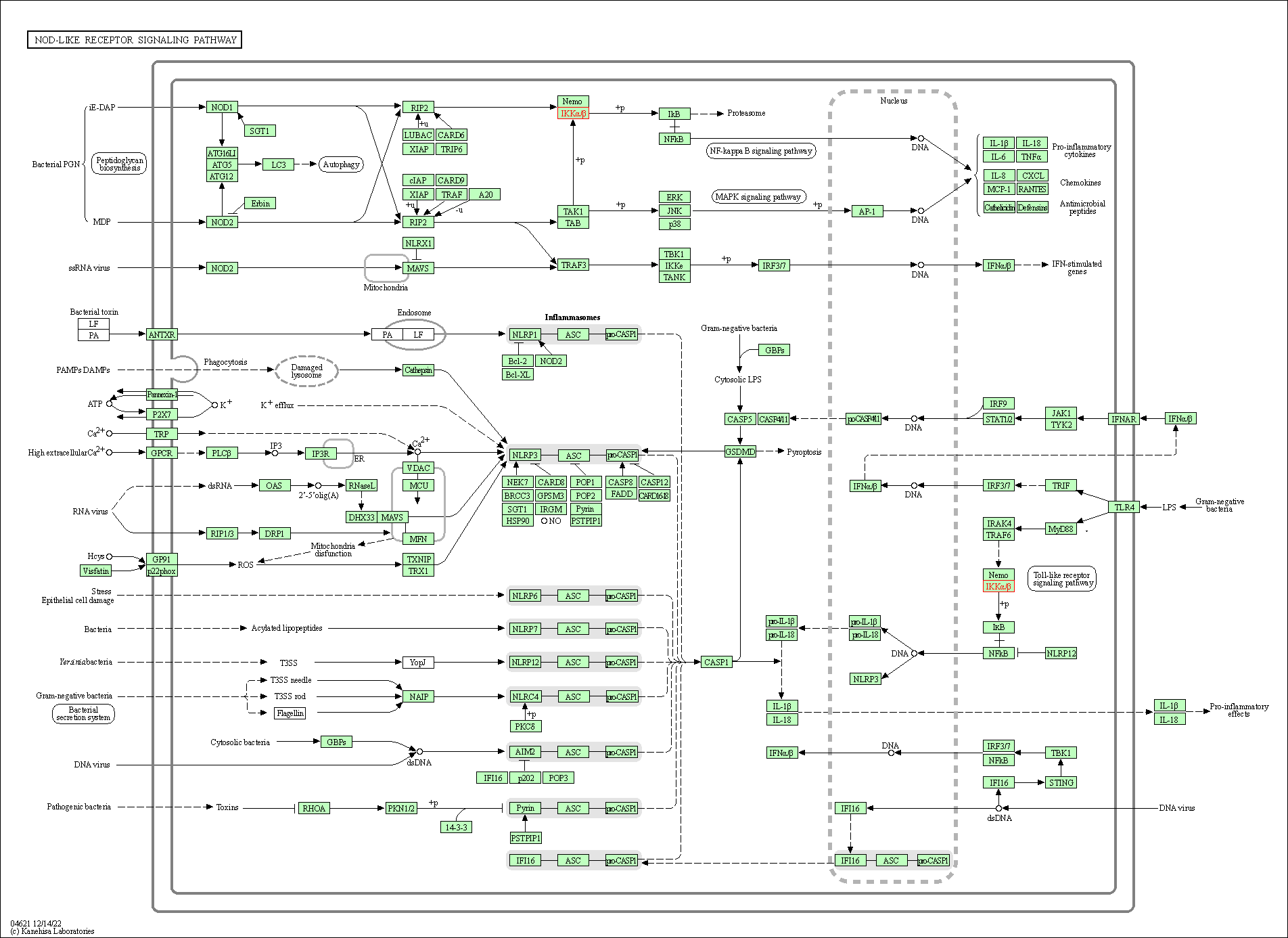
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04621 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | hsa04622 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway | hsa04623 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway | hsa04625 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
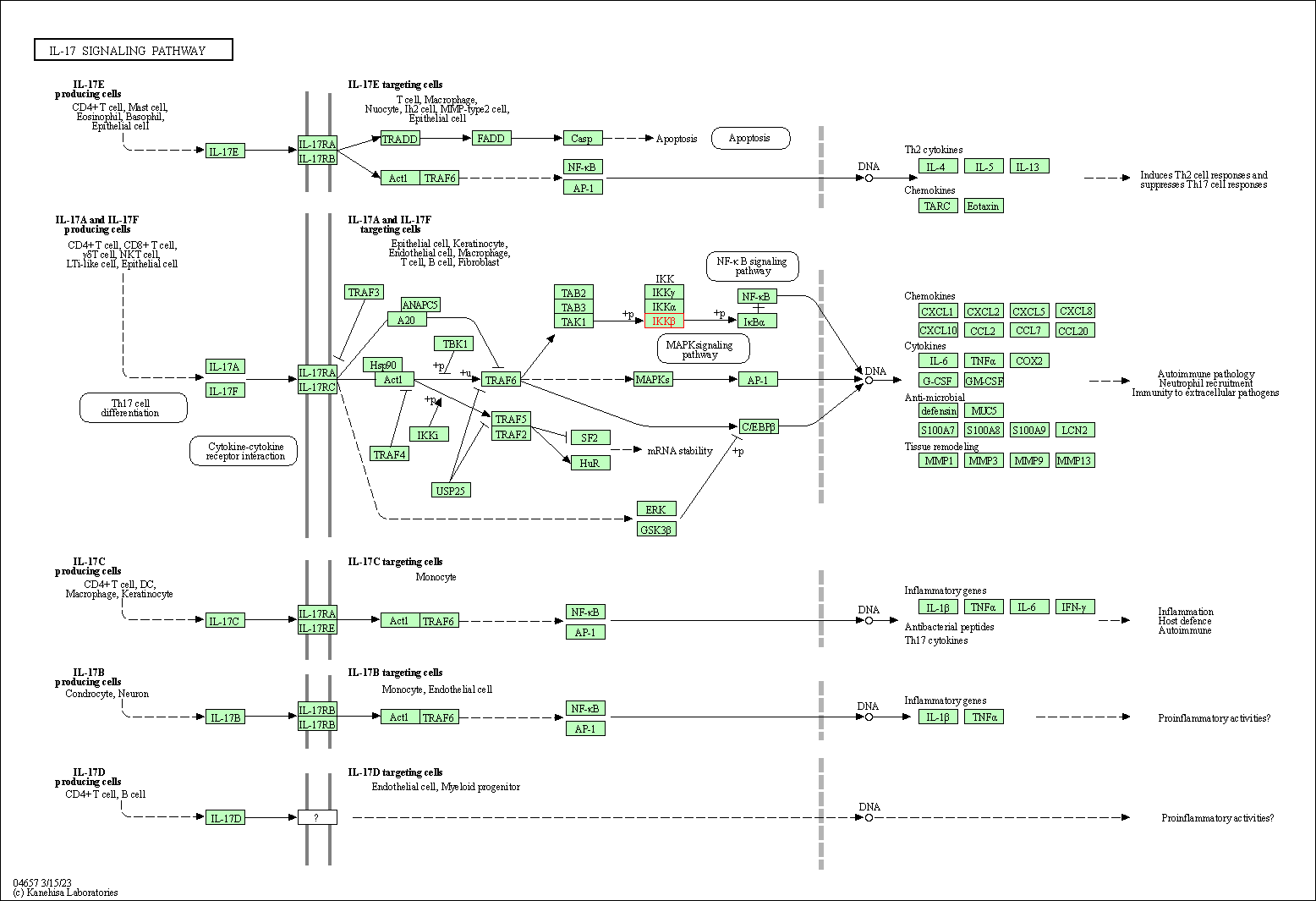
| IL-17 signaling pathway | hsa04657 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation | hsa04658 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Th17 cell differentiation | hsa04659 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
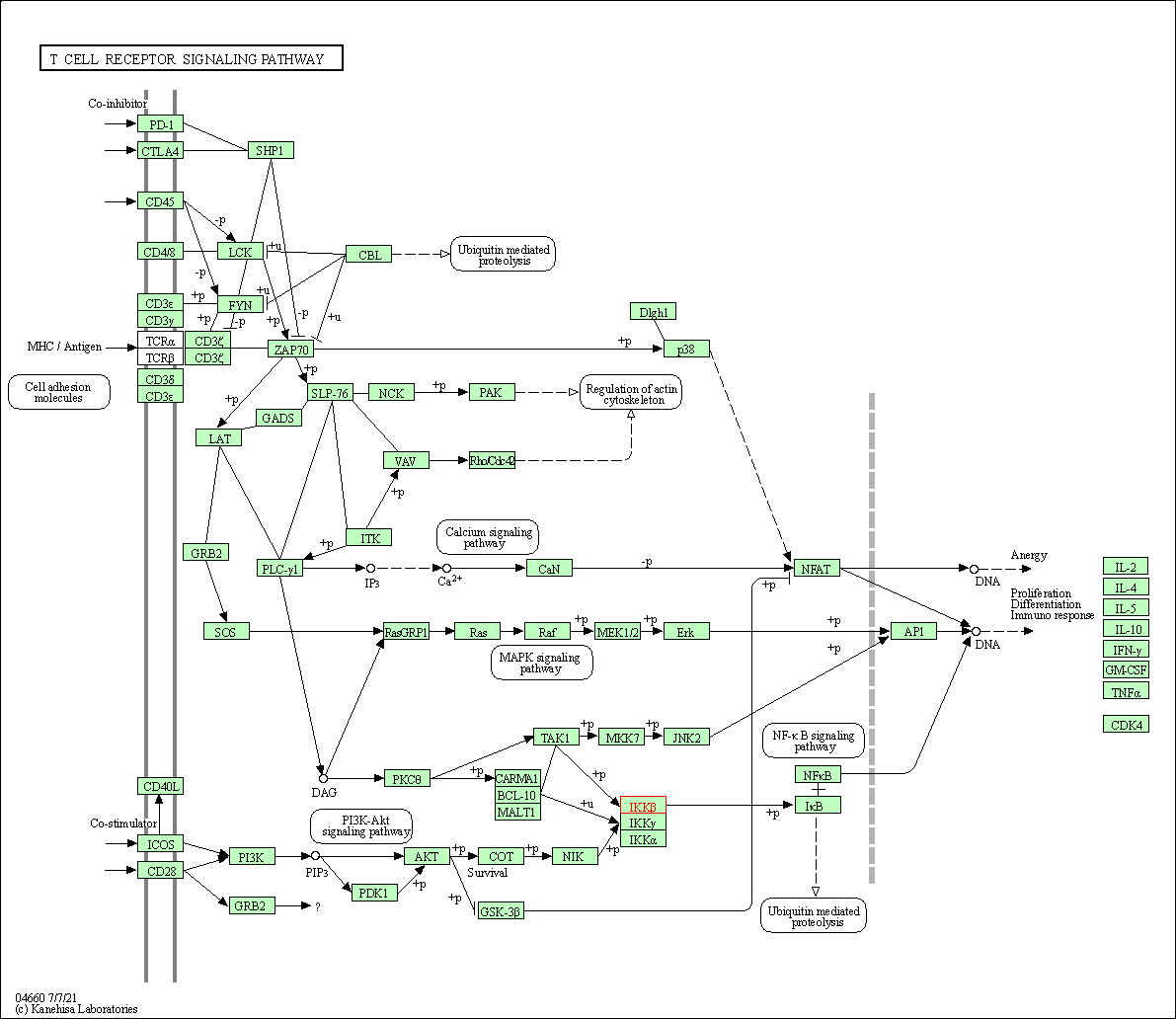
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04660 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| B cell receptor signaling pathway | hsa04662 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Immune system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| TNF signaling pathway | hsa04668 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | hsa04722 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Insulin signaling pathway | hsa04910 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Adipocytokine signaling pathway | hsa04920 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 48 | Degree centrality | 5.16E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 2.77E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.54E-01 | Radiality | 1.44E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 2.26E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.71E+01 | Topological coefficient | 5.17E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | The NF B pathway: a therapeutic target in glioblastoma. Oncotarget. 2011 August; 2(8): 646-653. | |||||
| REF 2 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (ANDA) 078729. | |||||
| REF 3 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 4 | Inhibition of I B phosphorylation prevents load-induced cardiac dysfunction in mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012 Dec 15;303(12):H1435-45. | |||||
| REF 5 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01598415) Safety of Single Doses of SAR113945 and Efficacy and Safety of a New Formulation Given Into the Knee in Osteoarthritis Patients / Part II. U.S. National Institutes ofHealth. | |||||
| REF 6 | Activation of histamine H4 receptor inhibits TNFalpha/IMD-0354-induced apoptosis in human salivary NS-SV-AC cells. Apoptosis. 2014 Dec;19(12):1702-11. | |||||
| REF 7 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800025030) | |||||
| REF 8 | How acute promyelocytic leukaemia revived arsenic. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002 Sep;2(9):705-13. | |||||
| REF 9 | Arsenic trioxide in multiple myeloma: rationale and future directions. Cancer J. 2002 Jan-Feb;8(1):12-25. | |||||
| REF 10 | The anti-inflammatory natural product parthenolide from the medicinal herb Feverfew directly binds to and inhibits IkappaB kinase. Chem Biol. 2001 Aug;8(8):759-66. | |||||
| REF 11 | I B kinase beta inhibitor IMD-0354 suppresses airway remodelling in a Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus-sensitized mouse model of chronic asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2011 Jan;41(1):104-15. | |||||
| REF 12 | Company report (Millennium) | |||||
| REF 13 | Evolution of the thienopyridine class of inhibitors of IkappaB kinase-beta: part I: hit-to-lead strategies. J Med Chem. 2006 May 18;49(10):2898-908. | |||||
| REF 14 | Novel IKK inhibitors: beta-carbolines. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2003 Jul 21;13(14):2419-22. | |||||
| REF 15 | Cellular characterization of a novel focal adhesion kinase inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 2007 May 18;282(20):14845-52. | |||||
| REF 16 | The selectivity of protein kinase inhibitors: a further update. Biochem J. 2007 Dec 15;408(3):297-315. | |||||
| REF 17 | UCN-01: a potent abrogator of G2 checkpoint function in cancer cells with disrupted p53. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996 Jul 17;88(14):956-65. | |||||
| REF 18 | Crystal structure of a human IB kinase asymmetric dimer. J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 2;288(31):22758-67. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

