Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T59045
(Former ID: TTDS00024)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
GABA transaminase (ABAT)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
L-AIBAT; Gamma-amino-N-butyrate transaminase; GABA-T; GABA-AT; GABA aminotransferase; ABAT; (S)-3-amino-2-methylpropionate transaminase
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
ABAT
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 5 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||||
| 2 | Epilepsy/seizure [ICD-11: 8A61-8A6Z] | |||||
| 3 | Epileptic encephalopathy [ICD-11: 8A62] | |||||
| 4 | Mineral deficiency [ICD-11: 5B5K] | |||||
| 5 | Nutritional deficiency [ICD-11: 5B50-5B71] | |||||
| Function |
Catalyzes the conversion of gamma-aminobutyrate and L- beta-aminoisobutyrate to succinate semialdehyde and methylmalonate semialdehyde, respectively. Can also convert delta-aminovalerate andbeta-alanine.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Transaminase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 2.6.1.19
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MASMLLAQRLACSFQHSYRLLVPGSRHISQAAAKVDVEFDYDGPLMKTEVPGPRSQELMK
QLNIIQNAEAVHFFCNYEESRGNYLVDVDGNRMLDLYSQISSVPIGYSHPALLKLIQQPQ NASMFVNRPALGILPPENFVEKLRQSLLSVAPKGMSQLITMACGSCSNENALKTIFMWYR SKERGQRGFSQEELETCMINQAPGCPDYSILSFMGAFHGRTMGCLATTHSKAIHKIDIPS FDWPIAPFPRLKYPLEEFVKENQQEEARCLEEVEDLIVKYRKKKKTVAGIIVEPIQSEGG DNHASDDFFRKLRDIARKHGCAFLVDEVQTGGGCTGKFWAHEHWGLDDPADVMTFSKKMM TGGFFHKEEFRPNAPYRIFNTWLGDPSKNLLLAEVINIIKREDLLNNAAHAGKALLTGLL DLQARYPQFISRVRGRGTFCSFDTPDDSIRNKLILIARNKGVVLGGCGDKSIRFRPTLVF RDHHAHLFLNIFSDILADFK Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T68XXK | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 5 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Divalproex sodium | Drug Info | Approved | Seizure disorder | [2] | |
| 2 | L-Alanine | Drug Info | Approved | Glioma | [3], [4], [5] | |
| 3 | Pyridoxal Phosphate | Drug Info | Approved | Malnutrition | [6], [7] | |
| 4 | Pyruvic acid | Drug Info | Approved | Malnutrition | [8], [9] | |
| 5 | Vigabatrin | Drug Info | Approved | Complex partial seizure | [10], [11] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 3 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | CPP-115 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Tourette syndrome | [12] | |
| 2 | K-828-AB | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Dementia | [13] | |
| 3 | CPP -15 | Drug Info | Phase 1 | Infantile spasm | [14] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 2 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 20 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Divalproex sodium | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 2 | L-Alanine | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 3 | Pyridoxal Phosphate | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 4 | Pyruvic acid | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 5 | Vigabatrin | Drug Info | [11], [15], [16], [17] | |||
| 6 | CPP-115 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 7 | K-828-AB | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 8 | 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| 9 | T83193 | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 10 | (4e)-4-Aminohex-4-Enoic Acid | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 11 | 1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 12 | 3-chloro-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propan-1-one | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| 13 | 4-Amino Hexanoic Acid | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 14 | 4-hydroxy-3-nitrobenzaldehyde | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 15 | 4-hydroxybenzylamine | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 16 | Acetate Ion | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 17 | Gamma-acetylenic GABA | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 18 | NIPECOTIC ACID | Drug Info | [24] | |||
| 19 | OXAMATE | Drug Info | [24] | |||
| 20 | Sodium valproate | Drug Info | [25] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 1 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | CPP -15 | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
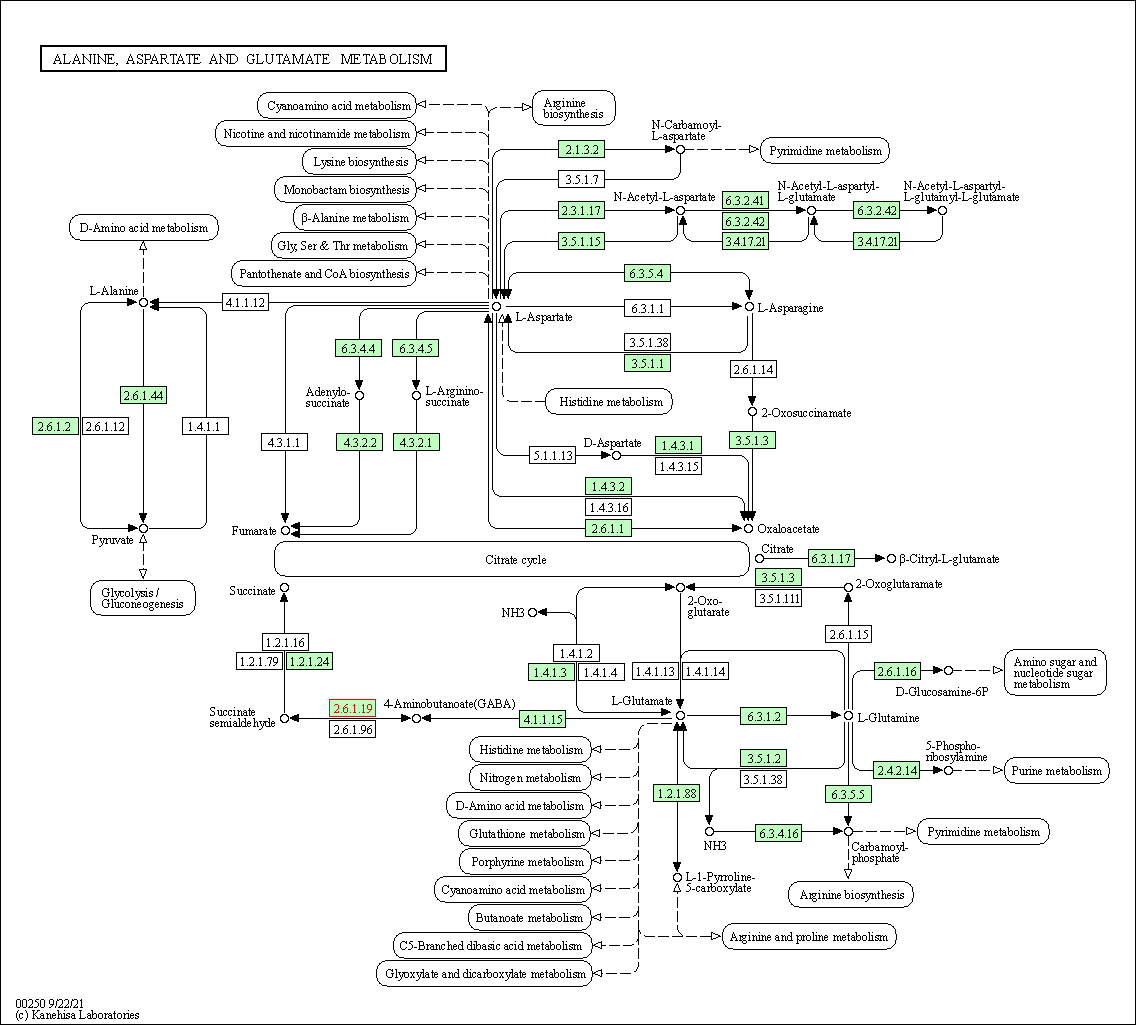
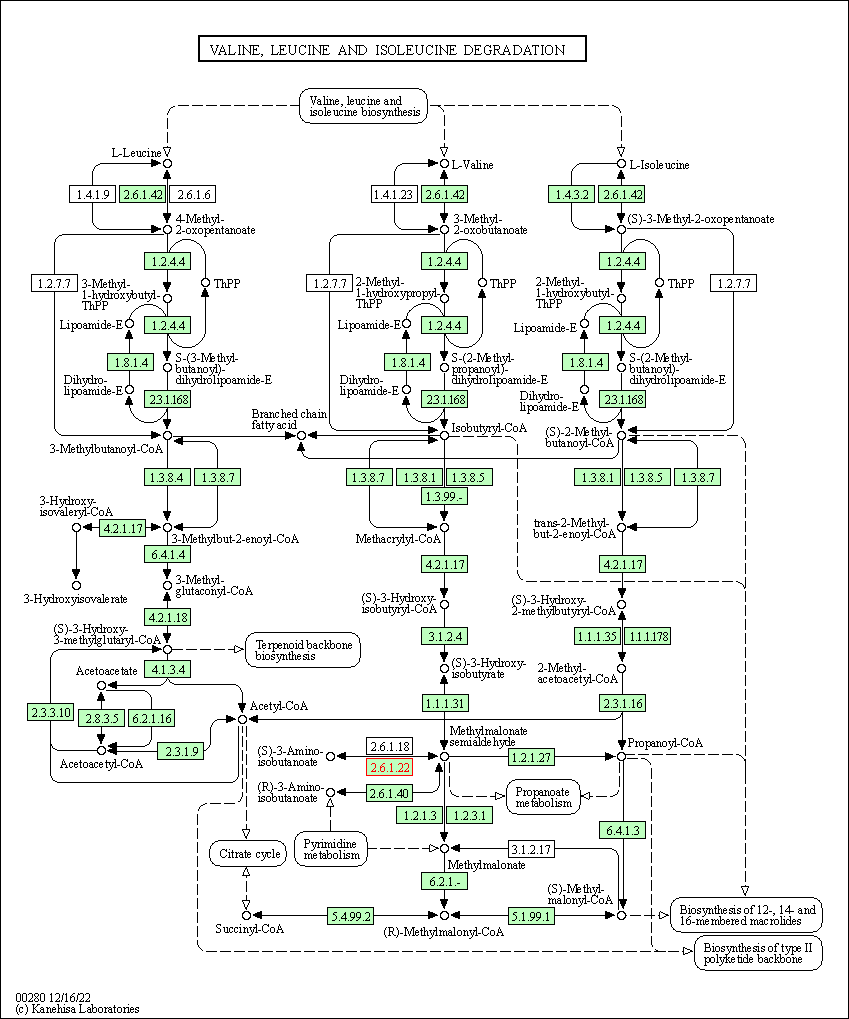
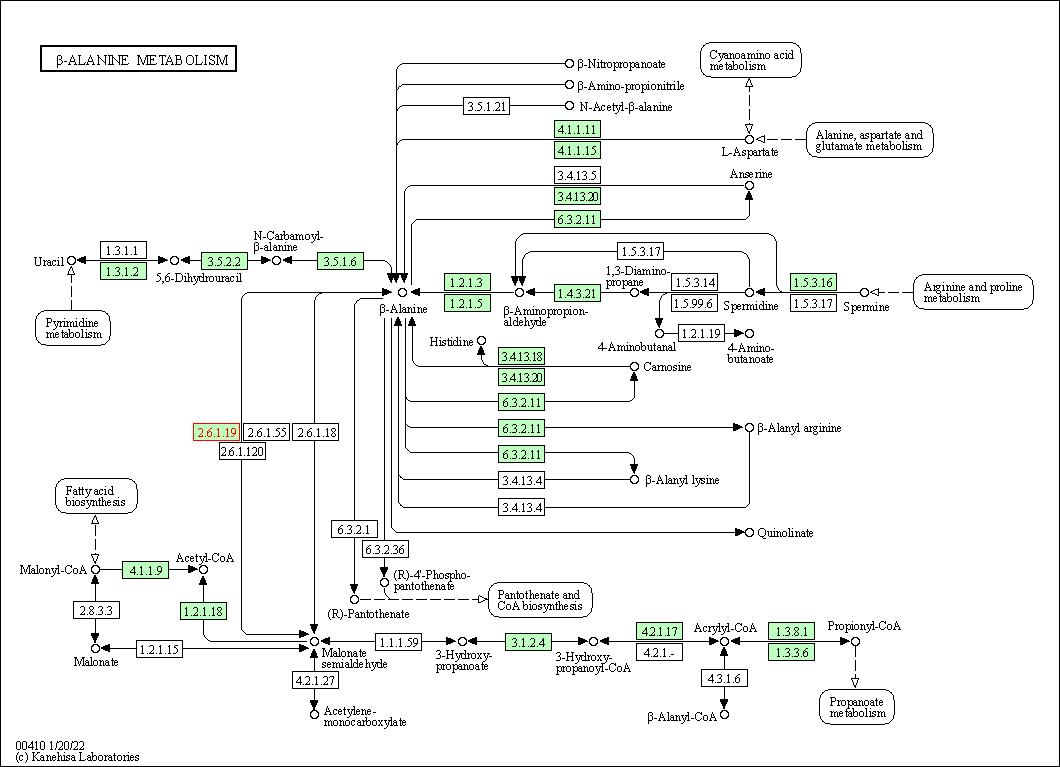
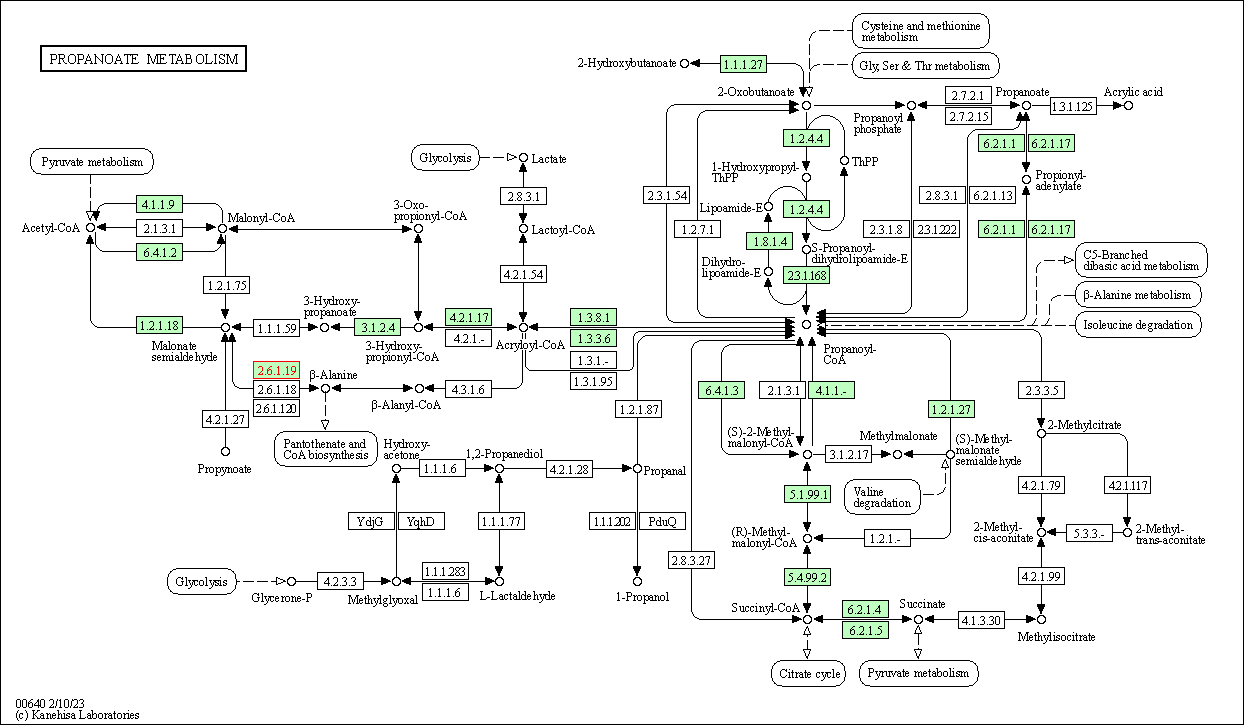
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism | hsa00250 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Amino acid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation | hsa00280 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Amino acid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| beta-Alanine metabolism | hsa00410 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Metabolism of other amino acids | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Propanoate metabolism | hsa00640 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Carbohydrate metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Butanoate metabolism | hsa00650 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Carbohydrate metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| GABAergic synapse | hsa04727 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 8 | Degree centrality | 8.59E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 4.11E-04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 1.68E-01 | Radiality | 1.26E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 1.79E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 5.38E+00 | Topological coefficient | 1.92E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BioCyc | [+] 4 BioCyc Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | GABA shunt | |||||
| 2 | Valine degradation | |||||
| 3 | Beta-alanine degradation | |||||
| 4 | 4-aminobutyrate degradation | |||||
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 7 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism | |||||
| 2 | Valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation | |||||
| 3 | beta-Alanine metabolism | |||||
| 4 | Propanoate metabolism | |||||
| 5 | Butanoate metabolism | |||||
| 6 | Metabolic pathways | |||||
| 7 | GABAergic synapse | |||||
| Panther Pathway | [+] 3 Panther Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Aminobutyrate degradation | |||||
| 2 | Pyrimidine Metabolism | |||||
| 3 | Gamma-aminobutyric acid synthesis | |||||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | [+] 5 Pathwhiz Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Aspartate Metabolism | |||||
| 2 | Glutamate Metabolism | |||||
| 3 | Beta-Alanine Metabolism | |||||
| 4 | Valine, Leucine and Isoleucine Degradation | |||||
| 5 | Propanoate Metabolism | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 2 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | GABA synthesis, release, reuptake and degradation | |||||
| 2 | Alanine and aspartate metabolism | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | DrugBank: a knowledgebase for drugs, drug actions and drug targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan;36(Database issue):D901-6. | |||||
| REF 2 | FDA approved drugs (1996) in CenterWatch | |||||
| REF 3 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 720). | |||||
| REF 4 | Drug information of L-Alanine, Health Canada, 2008. (drugid: 7638) | |||||
| REF 5 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 6 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 5249). | |||||
| REF 7 | Drug information of Pyridoxal Phosphate, 2008. eduDrugs. | |||||
| REF 8 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 4809). | |||||
| REF 9 | FDA Approved Drug Products from FDA Official Website. 2009. Application Number: (ANDA) 065200. | |||||
| REF 10 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 4821). | |||||
| REF 11 | Hughes B: 2009 FDA drug approvals. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010 Feb;9(2):89-92. | |||||
| REF 12 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 13 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Kowa Co Ltd. | |||||
| REF 14 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Catalyst Pharma. | |||||
| REF 15 | Glutamate- and GABA-based CNS therapeutics. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2006 Feb;6(1):7-17. | |||||
| REF 16 | Gamma-vinyl GABA, an irreversible inhibitor of GABA transaminase, alters the acquisition and expression of cocaine-induced sensitization in male rats. Synapse. 2002 Dec 15;46(4):240-50. | |||||
| REF 17 | Vigabatrin for refractory complex partial seizures: multicenter single-blind study with long-term follow-up. Neurology. 1987 Feb;37(2):184-9. | |||||
| REF 18 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of Catalyst Pharma. | |||||
| REF 19 | Phase II clinical trial of K-828-AB for treating behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia. Kowa Co. Ltd. | |||||
| REF 20 | Inactivation of GABA transaminase by 3-chloro-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propan-1-one. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Feb 1;19(3):731-4. | |||||
| REF 21 | Inhibition of GABA shunt enzymes' activity by 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006 Feb;16(3):592-5. | |||||
| REF 22 | How many drug targets are there Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. | |||||
| REF 23 | Treatment of Huntington disease with gamma-acetylenic GABA an irreversible inhibitor of GABA-transaminase: increased CSF GABA and homocarnosine without clinical amelioration. Neurology. 1981 Feb;31(2):207-11. | |||||
| REF 24 | Aminomethyl-1,2,4-benzothiadiazines as potential analogues of gamma-aminobutyric acid. Unexpected discovery of a taurine antagonist. J Med Chem. 1982 Feb;25(2):113-6. | |||||
| REF 25 | Influence of a GABA transaminase inhibitor on central nervous system oxygen toxicity. Aviat Space Environ Med. 1978 Jul;49(7):877-9. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

