Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T29500
(Former ID: TTDS00029)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Adrenergic receptor alpha-1B (ADRA1B)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Alpha-1B adrenoreceptor; Alpha-1B adrenoceptor; Alpha-1B adrenergic receptor; Alpha 1B-adrenoreceptor; Alpha 1B-adrenoceptor
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
ADRA1B
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Successful target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 5 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder [ICD-11: 6A05] | |||||
| 2 | Hypertension [ICD-11: BA00-BA04] | |||||
| 3 | Mental/behavioural/neurodevelopmental disorder [ICD-11: 6E20-6E8Z] | |||||
| 4 | Obesity [ICD-11: 5B80-5B81] | |||||
| 5 | Pain [ICD-11: MG30-MG3Z] | |||||
| Function |
Its effect is mediated by G(q) and G(11) proteins. Nuclear ADRA1A-ADRA1B heterooligomers regulate phenylephrine (PE)-stimulated ERK signaling in cardiac myocytes. This alpha-adrenergic receptor mediates its action by association with G proteins that activate a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
GPCR rhodopsin
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| Sequence |
MNPDLDTGHNTSAPAHWGELKNANFTGPNQTSSNSTLPQLDITRAISVGLVLGAFILFAI
VGNILVILSVACNRHLRTPTNYFIVNLAMADLLLSFTVLPFSAALEVLGYWVLGRIFCDI WAAVDVLCCTASILSLCAISIDRYIGVRYSLQYPTLVTRRKAILALLSVWVLSTVISIGP LLGWKEPAPNDDKECGVTEEPFYALFSSLGSFYIPLAVILVMYCRVYIVAKRTTKNLEAG VMKEMSNSKELTLRIHSKNFHEDTLSSTKAKGHNPRSSIAVKLFKFSREKKAAKTLGIVV GMFILCWLPFFIALPLGSLFSTLKPPDAVFKVVFWLGYFNSCLNPIIYPCSSKEFKRAFV RILGCQCRGRGRRRRRRRRRLGGCAYTYRPWTRGGSLERSQSRKDSLDDSGSCLSGSQRT LPSASPSPGYLGRGAPPPVELCAFPEWKAPGALLSLPAPEPPGRRGRHDSGPLFTFKLLT EPESPGTDGGASNGGCEAAADVANGQPGFKSNMPLAPGQF Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T82C7M | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approved Drug(s) | [+] 4 Approved Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Methamphetamine | Drug Info | Approved | Pain | [2] | |
| 2 | Methoxamine | Drug Info | Approved | Hypertension | [3], [4] | |
| 3 | Phendimetrazine | Drug Info | Approved | Obesity | [5] | |
| 4 | Propericiazine | Drug Info | Approved | Psychiatric disorder | [1], [6], [7] | |
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 1 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | MEDETOMIDINE | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Pain | [8] | |
| Discontinued Drug(s) | [+] 2 Discontinued Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | SOU-001 | Drug Info | Discontinued in Phase 2 | Urinary incontinence | [9] | |
| 2 | SNAP-5089 | Drug Info | Terminated | Heart arrhythmia | [10], [11] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 6 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Antagonist | [+] 8 Antagonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Methamphetamine | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| 2 | Phendimetrazine | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 3 | 5-methylurapidil | Drug Info | [33] | |||
| 4 | AH 11110 | Drug Info | [36] | |||
| 5 | Cyclazosin | Drug Info | [37] | |||
| 6 | Rec 15/2615 | Drug Info | [41] | |||
| 7 | spiroxatrine | Drug Info | [33] | |||
| 8 | [125I]BE-2254 | Drug Info | [44] | |||
| Stimulator | [+] 1 Stimulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Methoxamine | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| Binder | [+] 1 Binder drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | Propericiazine | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| Inhibitor | [+] 50 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | MEDETOMIDINE | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 2 | Sunepitron | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 3 | TIOSPIRONE | Drug Info | [17] | |||
| 4 | MAZAPERTINE | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 5 | ABANOQUIL | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| 6 | AGN-193080 | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 7 | BMY-7378 | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 8 | NIGULDIPINE | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 9 | Siramesine | Drug Info | [24] | |||
| 10 | SK&F-104078 | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 11 | SK&F-104856 | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 12 | SNAP-5089 | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 13 | WB-4101 | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| 14 | (+/-)-nantenine | Drug Info | [25] | |||
| 15 | (2,6-Dichloro-phenyl)-(1H-imidazol-2-yl)-amine | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 16 | (2-Bromo-phenyl)-(1H-imidazol-2-yl)-amine | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 17 | 2-Pyridin-4-yl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-isoquinoline | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 18 | 4-((E)-1-Naphthalen-1-yl-propenyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| 19 | 4-((Z)-1-Naphthalen-1-yl-propenyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| 20 | 4-(1-Naphthalen-1-yl-ethyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 21 | 4-(1-Naphthalen-1-yl-propyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| 22 | 4-(1-Naphthalen-1-yl-vinyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| 23 | 4-(2,3-Dihydro-1H-phenalen-1-yl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| 24 | 4-(3,4-Dihydro-1H-isoquinolin-2-yl)-quinoline | Drug Info | [27] | |||
| 25 | 4-(3-Hydroxy-piperidin-3-yl)-benzene-1,2-diol | Drug Info | [29] | |||
| 26 | 4-(4-butylpiperidin-1-yl)-1-o-tolylbutan-1-one | Drug Info | [30] | |||
| 27 | 4-(4-Isopropyl-morpholin-2-yl)-benzene-1,2-diol | Drug Info | [29] | |||
| 28 | 4-(4-Methyl-indan-1-yl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [31] | |||
| 29 | 4-Benzo[b]thiophen-4-yl-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [32] | |||
| 30 | 4-Morpholin-2-yl-benzene-1,2-diol | Drug Info | [29] | |||
| 31 | 6-fluoronorepinehprine | Drug Info | [34] | |||
| 32 | A-119637 | Drug Info | [35] | |||
| 33 | A-123189 | Drug Info | [35] | |||
| 34 | AGN-192172 | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 35 | CORYNANTHEINE | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 36 | FLUANISONE | Drug Info | [38] | |||
| 37 | Imidazolidin-2-ylidene-o-tolyl-amine | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 38 | Imidazolidin-2-ylidene-quinoxalin-6-yl-amine | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 39 | ISOCLOZAPINE | Drug Info | [39] | |||
| 40 | LEVONORDEFRIN | Drug Info | [28] | |||
| 41 | N-(5-Bromo-quinoxalin-6-yl)-guanidine | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 42 | OCTOCLOTHEPIN | Drug Info | [40] | |||
| 43 | RWJ-68157 | Drug Info | [42] | |||
| 44 | RWJ-69736 | Drug Info | [42] | |||
| 45 | SK&F-105854 | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 46 | SK&F-106686 | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 47 | SK&F-86466 | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 48 | SNAP-8719 | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 49 | UH-301 | Drug Info | [43] | |||
| 50 | [3H]RX821002 | Drug Info | [46] | |||
| Modulator | [+] 1 Modulator drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | SOU-001 | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| Agonist | [+] 1 Agonist drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | [125I]HEAT | Drug Info | [45] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium signaling pathway | hsa04020 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | hsa04022 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | hsa04080 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signaling molecules and interaction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes | hsa04261 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Circulatory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
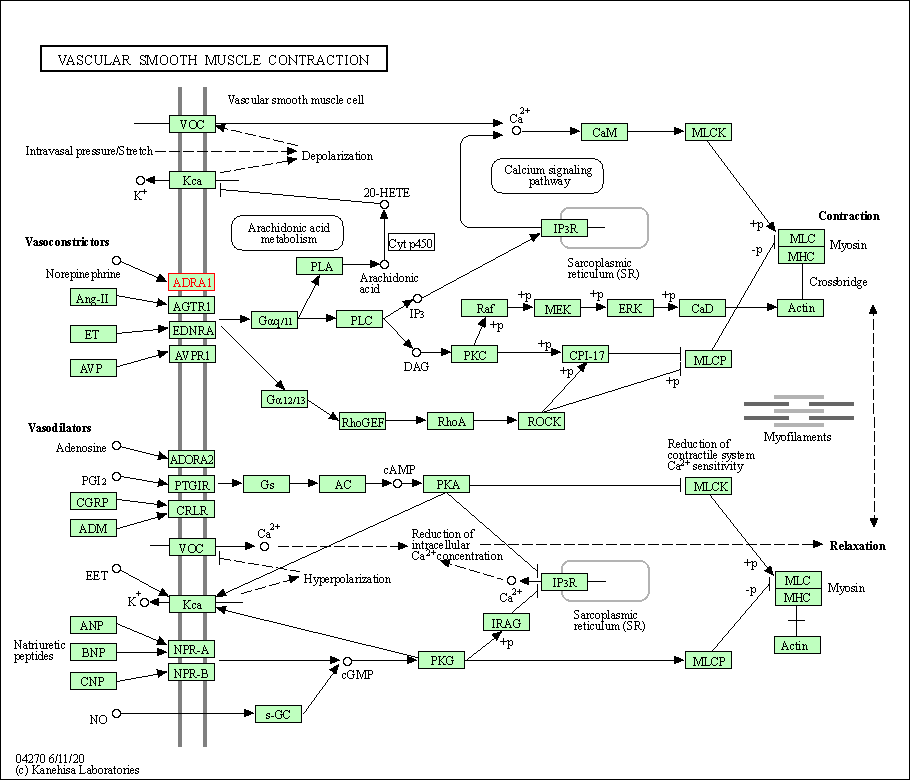
| Vascular smooth muscle contraction | hsa04270 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Circulatory system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
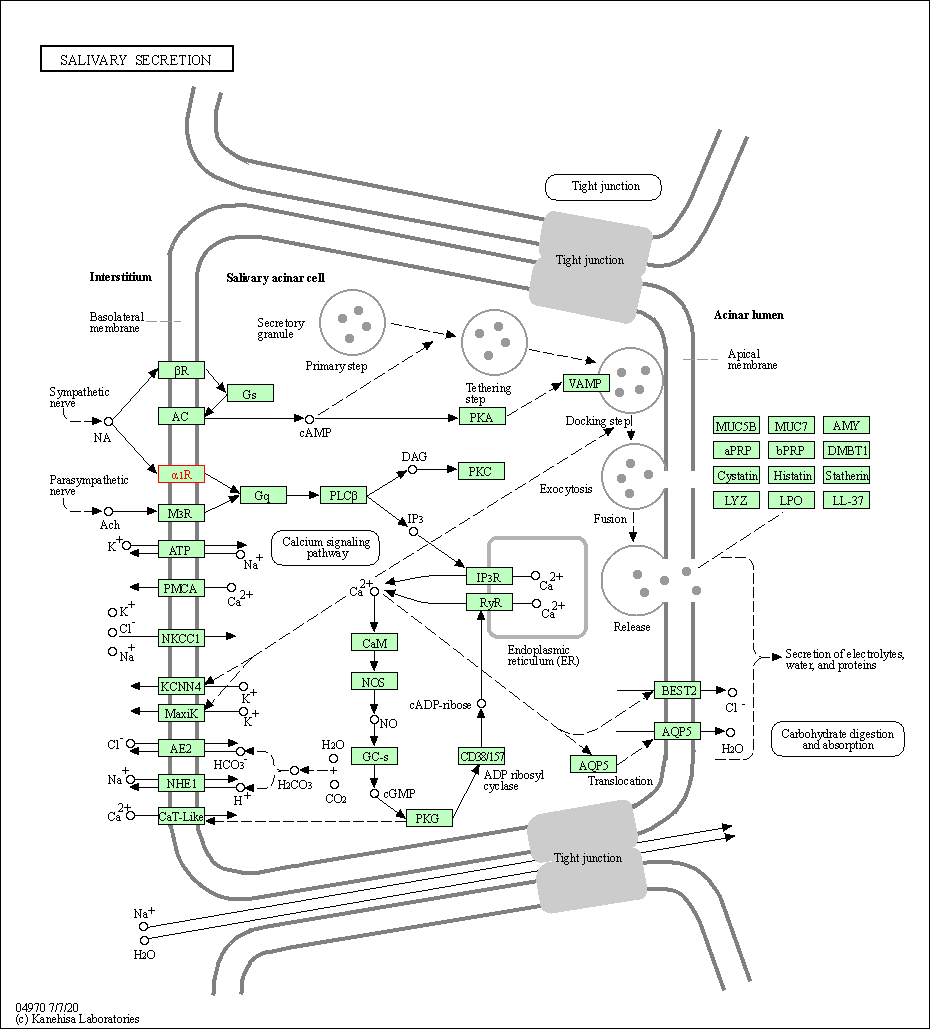
| Salivary secretion | hsa04970 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 3 | Degree centrality | 3.22E-04 | Betweenness centrality | 1.32E-05 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.00E-01 | Radiality | 1.35E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 3.33E-01 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 3.20E+01 | Topological coefficient | 3.52E-01 | Eccentricity | 12 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Co-Targets | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-Targets | ||||||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 6 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Calcium signaling pathway | |||||
| 2 | cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | |||||
| 3 | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | |||||
| 4 | Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes | |||||
| 5 | Vascular smooth muscle contraction | |||||
| 6 | Salivary secretion | |||||
| NetPath Pathway | [+] 1 NetPath Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | IL2 Signaling Pathway | |||||
| Panther Pathway | [+] 1 Panther Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Alpha adrenergic receptor signaling pathway | |||||
| PID Pathway | [+] 1 PID Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | LPA receptor mediated events | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 3 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Adrenoceptors | |||||
| 2 | G alpha (q) signalling events | |||||
| 3 | G alpha (12/13) signalling events | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 8 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Monoamine GPCRs | |||||
| 2 | Calcium Regulation in the Cardiac Cell | |||||
| 3 | GPCRs, Class A Rhodopsin-like | |||||
| 4 | Vitamin D Receptor Pathway | |||||
| 5 | Gastrin-CREB signalling pathway via PKC and MAPK | |||||
| 6 | GPCR ligand binding | |||||
| 7 | GPCR downstream signaling | |||||
| 8 | AMPK Signaling | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | Interaction of neuroleptics and antidepressants with rat brain alpha 2-receptors: a possible relationship between alpha 2-receptor antagonism and antidepressant action. Biol Psychiatry. 1984 Sep;19(9):1283-91. | |||||
| REF 2 | Pharmacotherapy for obesity. Drugs. 2005;65(10):1391-418. | |||||
| REF 3 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 483). | |||||
| REF 4 | Drug information of Methoxamine, 2008. eduDrugs. | |||||
| REF 5 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. 2015 | |||||
| REF 6 | Drug Information of Troleandomycin from nextbio research in illumina. 2015. | |||||
| REF 7 | Affinity of neuroleptics for D1 receptor of human brain striatum. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 1994 Jul;19(4):265-9. | |||||
| REF 8 | Sedative and cardiopulmonary effects of medetomidine hydrochloride and xylazine hydrochloride and their reversal with atipamezole hydrochloride in calves. Am J Vet Res. 2008 Mar;69(3):319-29. | |||||
| REF 9 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800014478) | |||||
| REF 10 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 498). | |||||
| REF 11 | Trusted, scientifically sound profiles of drug programs, clinical trials, safety reports, and company deals, written by scientists. Springer. 2015. Adis Insight (drug id 800006771) | |||||
| REF 12 | Mirtazapine treatment after conditioning with methamphetamine alters subsequent expression of place preference. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2009 Jan 1;99(1-3):231-9. | |||||
| REF 13 | Activation of alpha1-adrenoceptors inhibits growth hormone secretion in humans. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2009 Oct;117(9):460-2. | |||||
| REF 14 | Drugs, their targets and the nature and number of drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Oct;5(10):821-34. | |||||
| REF 15 | A structure-activity relationship study of benzylic modifications of 4-[1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl]-1H-imidazoles on alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenergic recep... J Med Chem. 1994 Jul 22;37(15):2328-33. | |||||
| REF 16 | An integrated in silico 3D model-driven discovery of a novel, potent, and selective amidosulfonamide 5-HT1A agonist (PRX-00023) for the treatment o... J Med Chem. 2006 Jun 1;49(11):3116-35. | |||||
| REF 17 | 3-Benzisothiazolylpiperazine derivatives as potential atypical antipsychotic agents. J Med Chem. 1996 Jan 5;39(1):143-8. | |||||
| REF 18 | A new arylpiperazine antipsychotic with high D2/D3/5-HT1A/alpha 1A-adrenergic affinity and a low potential for extrapyramidal effects. J Med Chem. 1994 Apr 15;37(8):1060-2. | |||||
| REF 19 | Drug repositioning: identifying and developing new uses for existing drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004 Aug;3(8):673-83. | |||||
| REF 20 | Alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors: from the gene to the clinic. 1. Molecular biology and adrenoceptor subclassification. J Med Chem. 1995 Sep 1;38(18):3415-44. | |||||
| REF 21 | Analogs of UK 14,304: Structural features responsible for alpha2 adrenoceptor activity, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 5(15):1745-1750 (1995). | |||||
| REF 22 | Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of fluoro analogues of 8-{2-[4-(4-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1yl]ethyl}-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione ... J Med Chem. 2005 Apr 21;48(8):3076-9. | |||||
| REF 23 | Alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors: from the gene to the clinic. 2. Structure-activity relationships and therapeutic applications. J Med Chem. 1995 Sep 15;38(19):3681-716. | |||||
| REF 24 | Sigma ligands with subnanomolar affinity and preference for the sigma 2 binding site. 1. 3-(omega-aminoalkyl)-1H-indoles. J Med Chem. 1995 May 26;38(11):1998-2008. | |||||
| REF 25 | Synthetic studies and pharmacological evaluations on the MDMA ('Ecstasy') antagonist nantenine. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Jan 15;20(2):628-31. | |||||
| REF 26 | Synthesis and evaluation of 2-(arylamino)imidazoles as alpha 2-adrenergic agonists. J Med Chem. 1997 Jan 3;40(1):18-23. | |||||
| REF 27 | 4-(3,4-dihydro-1H-isoquinolin-2yl)-pyridines and 4-(3,4-dihydro-1H-isoquinolin-2-yl)-quinolines as potent NR1/2B subtype selective NMDA receptor an... Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2003 May 19;13(10):1759-62. | |||||
| REF 28 | Medetomidine analogs as alpha 2-adrenergic ligands. 2. Design, synthesis, and biological activity of conformationally restricted naphthalene deriva... J Med Chem. 1996 Jul 19;39(15):3001-13. | |||||
| REF 29 | Conformational effects on the activity of drugs. 13. A revision of previously proposed models for the activation of alpha- and beta-adrenergic rece... J Med Chem. 1992 Mar 20;35(6):1009-18. | |||||
| REF 30 | Discovery of N-{1-[3-(3-oxo-2,3-dihydrobenzo[1,4]oxazin-4-yl)propyl]piperidin-4-yl}-2-phenylacetamide (Lu AE51090): an allosteric muscarinic M1 rec... J Med Chem. 2010 Sep 9;53(17):6386-97. | |||||
| REF 31 | Medetomidine analogs as alpha 2-adrenergic ligands. 3. Synthesis and biological evaluation of a new series of medetomidine analogs and their potent... J Med Chem. 1997 Sep 12;40(19):3014-24. | |||||
| REF 32 | alpha(2) Adrenoceptor agonists as potential analgesic agents. 2. Discovery of 4-(4-Imidazo)-1,3-dimethyl-6,7-dihydrothianaphthene [corrected] as a ... J Med Chem. 2000 Mar 9;43(5):765-8. | |||||
| REF 33 | Affinity of serotonin receptor antagonists and agonists to recombinant and native alpha1-adrenoceptor subtypes. Jpn J Pharmacol. 2001 Jun;86(2):189-95. | |||||
| REF 34 | Structural basis of the selectivity of the beta(2)-adrenergic receptor for fluorinated catecholamines. Bioorg Med Chem. 2009 Dec 1;17(23):7987-92. | |||||
| REF 35 | Two novel and potent 3-[(o-methoxyphenyl)piperazinylethyl]-5-phenylthien. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2001 May 7;11(9):1119-21. | |||||
| REF 36 | Structure activity relationships of a series of buspirone analogs at alpha-1 adrenoceptors: further evidence that rat aorta alpha-1 adrenoceptors are of the alpha-1D-subtype. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996 Jul;278(1):136-44. | |||||
| REF 37 | Identification of alpha1-adrenoceptor subtypes involved in contraction of young CD rat epididymal vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 2009 Jan 14;602(2-3):388-94. | |||||
| REF 38 | 2-Phenylpyrroles as conformationally restricted benzamide analogues. A new class of potential antipsychotics. 1. J Med Chem. 1987 Nov;30(11):2099-104. | |||||
| REF 39 | Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of triflate-substituted analogues of clozapine: identification of a novel atypical neuroleptic. J Med Chem. 1997 Dec 5;40(25):4146-53. | |||||
| REF 40 | Exploring the neuroleptic substituent in octoclothepin: potential ligands for positron emission tomography with subnanomolar affinity for (1)-adre... J Med Chem. 2010 Oct 14;53(19):7021-34. | |||||
| REF 41 | Pharmacological characterization of the uroselective alpha-1 antagonist Rec 15/2739 (SB 216469): role of the alpha-1L adrenoceptor in tissue selectivity, part II. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997 Jun;281(3):1284-93. | |||||
| REF 42 | Novel arylpiperazines as selective alpha1-adrenergic receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2000 May 15;10(10):1093-6. | |||||
| REF 43 | N-[2-[(substituted chroman-8-yl)oxy]ethyl]-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)butylamines: synthesis and wide range of antagonism at the human 5-HT1A receptor. J Med Chem. 1997 Apr 11;40(8):1252-7. | |||||
| REF 44 | Cloning and pharmacological characterization of human alpha-1 adrenergic receptors: sequence corrections and direct comparison with other species homologues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Jan;272(1):134-42. | |||||
| REF 45 | KMD-3213, a novel, potent, alpha 1a-adrenoceptor-selective antagonist: characterization using recombinant human alpha 1-adrenoceptors and native tissues. Mol Pharmacol. 1995 Aug;48(2):250-8. | |||||
| REF 46 | Alpha-adrenoreceptor reagents. 4. Resolution of some potent selective prejunctional alpha 2-adrenoreceptor antagonists. J Med Chem. 1986 Oct;29(10):2000-3. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

