Target Information
| Target General Information | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target ID |
T16117
(Former ID: TTDC00063)
|
|||||
| Target Name |
Nitric-oxide synthase brain (NOS1)
|
|||||
| Synonyms |
Peptidyl-cysteine S-nitrosylase NOS1; Nitric oxide synthase, brain; Neuronal NOS; NOS, type I; NOS type I; NNOS; NC-NOS; N-NOS; BNOS
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| Gene Name |
NOS1
|
|||||
| Target Type |
Clinical trial target
|
[1] | ||||
| Disease | [+] 2 Target-related Diseases | + | ||||
| 1 | Headache [ICD-11: 8A80-8A84] | |||||
| 2 | Migraine [ICD-11: 8A80] | |||||
| Function |
In the brain and peripheral nervous system, NO displays many properties of a neurotransmitter. Probably has nitrosylase activity and mediates cysteine S-nitrosylation of cytoplasmic target proteins such SRR. Produces nitric oxide (NO) which is a messenger molecule with diverse functions throughout the body.
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| BioChemical Class |
Paired donor oxygen oxidoreductase
|
|||||
| UniProt ID | ||||||
| EC Number |
EC 1.14.13.39
|
|||||
| Sequence |
MEDHMFGVQQIQPNVISVRLFKRKVGGLGFLVKERVSKPPVIISDLIRGGAAEQSGLIQA
GDIILAVNGRPLVDLSYDSALEVLRGIASETHVVLILRGPEGFTTHLETTFTGDGTPKTI RVTQPLGPPTKAVDLSHQPPAGKEQPLAVDGASGPGNGPQHAYDDGQEAGSLPHANGLAP RPPGQDPAKKATRVSLQGRGENNELLKEIEPVLSLLTSGSRGVKGGAPAKAEMKDMGIQV DRDLDGKSHKPLPLGVENDRVFNDLWGKGNVPVVLNNPYSEKEQPPTSGKQSPTKNGSPS KCPRFLKVKNWETEVVLTDTLHLKSTLETGCTEYICMGSIMHPSQHARRPEDVRTKGQLF PLAKEFIDQYYSSIKRFGSKAHMERLEEVNKEIDTTSTYQLKDTELIYGAKHAWRNASRC VGRIQWSKLQVFDARDCTTAHGMFNYICNHVKYATNKGNLRSAITIFPQRTDGKHDFRVW NSQLIRYAGYKQPDGSTLGDPANVQFTEICIQQGWKPPRGRFDVLPLLLQANGNDPELFQ IPPELVLEVPIRHPKFEWFKDLGLKWYGLPAVSNMLLEIGGLEFSACPFSGWYMGTEIGV RDYCDNSRYNILEEVAKKMNLDMRKTSSLWKDQALVEINIAVLYSFQSDKVTIVDHHSAT ESFIKHMENEYRCRGGCPADWVWIVPPMSGSITPVFHQEMLNYRLTPSFEYQPDPWNTHV WKGTNGTPTKRRAIGFKKLAEAVKFSAKLMGQAMAKRVKATILYATETGKSQAYAKTLCE IFKHAFDAKVMSMEEYDIVHLEHETLVLVVTSTFGNGDPPENGEKFGCALMEMRHPNSVQ EERKSYKVRFNSVSSYSDSQKSSGDGPDLRDNFESAGPLANVRFSVFGLGSRAYPHFCAF GHAVDTLLEELGGERILKMREGDELCGQEEAFRTWAKKVFKAACDVFCVGDDVNIEKANN SLISNDRSWKRNKFRLTFVAEAPELTQGLSNVHKKRVSAARLLSRQNLQSPKSSRSTIFV RLHTNGSQELQYQPGDHLGVFPGNHEDLVNALIERLEDAPPVNQMVKVELLEERNTALGV ISNWTDELRLPPCTIFQAFKYYLDITTPPTPLQLQQFASLATSEKEKQRLLVLSKGLQEY EEWKWGKNPTIVEVLEEFPSIQMPATLLLTQLSLLQPRYYSISSSPDMYPDEVHLTVAIV SYRTRDGEGPIHHGVCSSWLNRIQADELVPCFVRGAPSFHLPRNPQVPCILVGPGTGIAP FRSFWQQRQFDIQHKGMNPCPMVLVFGCRQSKIDHIYREETLQAKNKGVFRELYTAYSRE PDKPKKYVQDILQEQLAESVYRALKEQGGHIYVCGDVTMAADVLKAIQRIMTQQGKLSAE DAGVFISRMRDDNRYHEDIFGVTLRTYEVTNRLRSESIAFIEESKKDTDEVFSS Click to Show/Hide
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | Click to Show 3D Structure of This Target | AlphaFold | ||||
| ADReCS ID | BADD_A05675 | |||||
| HIT2.0 ID | T70VMI | |||||
| Drugs and Modes of Action | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Trial Drug(s) | [+] 2 Clinical Trial Drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | NXN-188 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Migraine | [2] | |
| 2 | NXN-462 | Drug Info | Phase 2 | Headache | [1] | |
| Mode of Action | [+] 1 Modes of Action | + | ||||
| Inhibitor | [+] 125 Inhibitor drugs | + | ||||
| 1 | NXN-188 | Drug Info | [3] | |||
| 2 | NXN-462 | Drug Info | [1] | |||
| 3 | L-NIL | Drug Info | [4] | |||
| 4 | ((E)-7-But-2-enyl)-azepan-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 5 | (+/-)-2-Methyl-1-(1-phenylethyl)-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 6 | (4S,5R)-4,5-Diethyl-oxazolidin-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 7 | (4S,5R)-4,5-Dimethyl-oxazolidin-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 8 | (4S,5S)-4,5-Diethyl-oxazolidin-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 9 | (5-Imino-[1,4]thiazepan-3-yl)-methanol | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 10 | (5S,6R)-[Octahydro-quinolin-(2E)-ylidene]amine | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 11 | (5S,6S)-[Octahydro-quinolin-(2E)-ylidene]amine | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 12 | (6r,1'r,2's)-5,6,7,8 Tetrahydrobiopterin | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 13 | (R)-3-Propyl-[1,4]thiazepan-(5E)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 14 | (S)-2-Amino-5-(N-methyl-guanidino)-pentanoic acid | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 15 | (S)-3-Propyl-[1,4]thiazepan-(5E)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 16 | (S)-6-Amino-2-(2-imino-ethylamino)-hexanoic acid | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 17 | 1-(2-amino-benzothiazol-5-yl)-2-ethyl-isothiourea | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| 18 | 1-(2-amino-benzothiazol-6-yl)-2-ethyl-isothiourea | Drug Info | [12] | |||
| 19 | 1-(Benzhydrylamino)ethaniminium bromide | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 20 | 1-Benzyl-2-methyl-1H-imidazole | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 21 | 1-[(3-Methoxybenzyl)amino]ethaniminium chloride | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 22 | 1400W | Drug Info | [6], [13] | |||
| 23 | 2'-Monophosphoadenosine 5'-Diphosphoribose | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 24 | 2-(2-Amino-ethyl)-7-imino-azepane | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 25 | 2-amino-4,6-dimethylpyridine | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 26 | 2-amino-4-methylpyridine | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 27 | 2-Amino-5-(N-nitro-guanidino)-pentanoic acid | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 28 | 2-aminopyridine | Drug Info | [14] | |||
| 29 | 2-Aminothiazoline | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 30 | 2-Methyl-[1,4]thiazepan-(5E)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 31 | 3,4-Dihydro-1H-quinolin-(2E)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 32 | 3,4-Dimethyl-pyrrolidin-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 33 | 3-(2-Amino-ethyl)-5-imino-[1,4]oxazepane | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 34 | 3-(2-Nitro-ethyl)-[1,4]oxazepan-(5Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 35 | 3-Bromo-1H-indazole-7-carbonitrile | Drug Info | [17] | |||
| 36 | 3-bromo-7-nitro-1H-indazole | Drug Info | [10], [18] | |||
| 37 | 3-Butyl-[1,4]thiazepan-(5E)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 38 | 3-Ethyl-[1,4]thiazepan-(5E)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 39 | 3-Isobutyl-[1,4]thiazepan-(5E)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 40 | 3-Methyl-pyrrolidin-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 41 | 3-Methyl-[1,4]thiazepan-(5E)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 42 | 3-Propyl-[1,4]thiazepan-(5E)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 43 | 4,5,6,7-tetrafluoro-3-methyl-1H-indazole | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 44 | 4,5-Dimethyl-pyrrolidin-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 45 | 4-bromo-1H-indazole | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 46 | 4-Butyl-thiazolidin-(2E)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 47 | 4-chloro-1H-indazole | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 48 | 4-Ethyl-3-methyl-pyrrolidin-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 49 | 4-Ethyl-5-methyl-pyrrolidin-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 50 | 4-Ethyl-oxazolidin-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 51 | 4-Ethyl-pyrrolidin-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 52 | 4-iodo-1H-indazole | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 53 | 4-Isopropyl-pyrrolidin-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 54 | 4-Methyl-5-propyl-pyrrolidin-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 55 | 4-methyl-6-propylpyridin-2-amine | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 56 | 4-Methyl-oxazolidin-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 57 | 4-Methyl-piperidin-(2E)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 58 | 4-Methyl-pyrrolidin-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 59 | 4-[(2-Methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]pyridine | Drug Info | [6] | |||
| 60 | 5-bromo-1H-indazole | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 61 | 5-Bromomethyl-oxazolidin-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 62 | 5-chloro-1H-indazole | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 63 | 5-Ethyl-3-methyl-pyrrolidin-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 64 | 5-Ethyl-4-methyl-pyrrolidin-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 65 | 5-Ethyl-4-propyl-pyrrolidin-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 66 | 5-Ethyl-oxazolidin-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 67 | 5-iodo-1H-indazole | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 68 | 5-Methyl-oxazolidin-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [7] | |||
| 69 | 5-Methyl-pyrrolidin-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 70 | 5-N-Allyl-Arginine | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 71 | 6-(2-Fluoropropyl)-4-methylpyridin-2-amine | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| 72 | 6-(3-Fluoropropyl)-4-methylpyridin-2-amine | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| 73 | 6-bromo-1H-indazole | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 74 | 6-chloro-1H-indazole | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 75 | 6-isobutyl-4-methylpyridin-2-amine | Drug Info | [20] | |||
| 76 | 7-(2-Nitro-ethyl)-azepan-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 77 | 7-bromo-1H-indazole | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 78 | 7-Butyl-azepan-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 79 | 7-chloro-1H-indazole | Drug Info | [19] | |||
| 80 | 7-Methoxy-1H-indazole | Drug Info | [21] | |||
| 81 | 7-Methyl-[1,4]thiazepan-(5E)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 82 | 7-nitro-1H-indazole | Drug Info | [18] | |||
| 83 | Acetate Ion | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 84 | Alpha-D-Mannose | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 85 | AR-C102222 | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 86 | AR-C133057XX | Drug Info | [15] | |||
| 87 | Azepan-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 88 | Azocan-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [5] | |||
| 89 | Azonan-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 90 | EUSYNSTYELAMIDE B | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 91 | Eusynstyelamide C | Drug Info | [22] | |||
| 92 | Flavin-Adenine Dinucleotide | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 93 | Formic Acid | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 94 | Heme | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 95 | Hexahydro-cyclopenta[b]pyrrol-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 96 | Hexahydro-cyclopenta[c]pyrrol-(1Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 97 | Hexahydro-pyrrolizin-(3E)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 98 | L-NIO | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 99 | N*1*-(5-Methyl-2-nitro-phenyl)-butane-1,4-diamine | Drug Info | [24] | |||
| 100 | N-(5-Amino-6-oxo-heptyl)-acetamidine | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 101 | N-Butyl-N'-Hydroxyguanidine | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 102 | N-Isopropyl-N'-Hydroxyguanidine | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 103 | N-omega-allyl-L-arginine | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 104 | N-Omega-Hydroxy-L-Arginine | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 105 | N-omega-propargyl-L-arginine | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 106 | N-Omega-Propyl-L-Arginine | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 107 | N5-(1-Imino-3-Butenyl)-L-Ornithine | Drug Info | [10] | |||
| 108 | N5-(1-iminobut-3-enyl)-L-ornithine | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 109 | N5-(1-iminobutyl)-L-ornithine | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 110 | N5-(1-iminopent-3-enyl)-L-ornithine | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 111 | N5-(1-iminopropyl)-L-ornithine | Drug Info | [23] | |||
| 112 | Nitroarginine | Drug Info | [25] | |||
| 113 | Octahydro-isoindol-(1Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 114 | Piperidin-(2E)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [9] | |||
| 115 | Pyrrolidin-(2Z)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [16] | |||
| 116 | S-Ethyl-N-Phenyl-Isothiourea | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 117 | S-Ethyl-N-[4-(Trifluoromethyl)Phenyl]Isothiourea | Drug Info | [13] | |||
| 118 | Tetrahydro-pyrimidin-2-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 119 | THIOCITRULLINE | Drug Info | [26] | |||
| 120 | [1,3]Oxazinan-(2E)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 121 | [1,3]Thiazinan-(2E)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [11] | |||
| 122 | [1,4]Oxazepan-(3E)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 123 | [1,4]Oxazepan-(5E)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 124 | [1,4]Thiazepan-(3E)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| 125 | [1,4]Thiazepan-(5E)-ylideneamine | Drug Info | [8] | |||
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-based Target Expression Variations | ||||||
| Drug Binding Sites of Target | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ligand Name: Arginine | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Structure of human nNOS heme domain with L-Arg bound | PDB:4D1N | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 2.03 Å | Mutation | Yes | [27] |
| PDB Sequence |
CPRFLKVKNW
311 ETEVVLTDTL321 HLKSTLETGC331 TEYICMGSIM341 HPSQHARRPE351 DVATKDQLFP 361 LAKEFIDQYY371 SSIKRFGSKA381 HMERLEEVNK391 EIDTTSTYQL401 KDTELIYGAK 411 HAWRNASRCV421 GRIQWSKLQV431 FDARDCTTAH441 GMFNYICNHV451 KYATNKGNLR 461 SAITIFPQRT471 DGKHDFRVWN481 SQLIRYAGYK491 QPDGSTLGDP501 ANVQFTEICI 511 QQGWKPPRGR521 FDVLPLLLQA531 NGNDPELFQI541 PPELVLEVPI551 RHPKFEWFKD 561 LGLKWYGLPA571 VSNMLLEIGG581 LEFSACPFSG591 WYMGTEIGVR601 DYCDNSRYNI 611 LEEVAKKMNL621 DMRKTSSLWK631 DQALVEINIA641 VLYSFQSDKV651 TIVDHHSATE 661 SFIKHMENEY671 RCRGGCPADW681 VWIVPPMSGS691 ITPVFHQEML701 NYRLTPSFEY 711 QPDPWNTHVW721
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Ligand Name: BH4 | Ligand Info | |||||
| Structure Description | Structure of the human nitric oxide synthase R354A/G357D mutant heme domain in complex with N-(1-(2-(Ethyl(methyl)amino)ethyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquino-lin-6-yl)thiophene-2-carboximidamide | PDB:6CIC | ||||
| Method | X-ray diffraction | Resolution | 1.75 Å | Mutation | Yes | [28] |
| PDB Sequence |
CPRFLKVKNW
311 ETEVVLTDTL321 HLKSTLETGC331 TEYICMGSIM341 HPSQHARRPE351 DVATKDQLFP 361 LAKEFIDQYY371 SSIKRFGSKA381 HMERLEEVNK391 EIDTTSTYQL401 KDTELIYGAK 411 HAWRNASRCV421 GRIQWSKLQV431 FDARDCTTAH441 GMFNYICNHV451 KYATNKGNLR 461 SAITIFPQRT471 DGKHDFRVWN481 SQLIRYAGYK491 QPDGSTLGDP501 ANVQFTEICI 511 QQGWKPPRGR521 FDVLPLLLQA531 NGNDPELFQI541 PPELVLEVPI551 RHPKFEWFKD 561 LGLKWYGLPA571 VSNMLLEIGG581 LEFSACPFSG591 WYMGTEIGVR601 DYCDNSRYNI 611 LEEVAKKMNL621 DMRKTSSLWK631 DQALVEINIA641 VLYSFQSDKV651 TIVDHHSATE 661 SFIKHMENEY671 RCRGGCPADW681 VWIVPPMSGS691 ITPVFHQEML701 NYRLTPSFEY 711 QPDPWNTHVW721 K
|
|||||
|
|
||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target and Ligand Pair | ||||||
| Click to View More Binding Site Information of This Target with Different Ligands | ||||||
| Different Human System Profiles of Target | Top |
|---|---|
|
Human Similarity Proteins
of target is determined by comparing the sequence similarity of all human proteins with the target based on BLAST. The similarity proteins for a target are defined as the proteins with E-value < 0.005 and outside the protein families of the target.
A target that has fewer human similarity proteins outside its family is commonly regarded to possess a greater capacity to avoid undesired interactions and thus increase the possibility of finding successful drugs
(Brief Bioinform, 21: 649-662, 2020).
Human Tissue Distribution
of target is determined from a proteomics study that quantified more than 12,000 genes across 32 normal human tissues. Tissue Specificity (TS) score was used to define the enrichment of target across tissues.
The distribution of targets among different tissues or organs need to be taken into consideration when assessing the target druggability, as it is generally accepted that the wider the target distribution, the greater the concern over potential adverse effects
(Nat Rev Drug Discov, 20: 64-81, 2021).
Human Pathway Affiliation
of target is determined by the life-essential pathways provided on KEGG database. The target-affiliated pathways were defined based on the following two criteria (a) the pathways of the studied target should be life-essential for both healthy individuals and patients, and (b) the studied target should occupy an upstream position in the pathways and therefore had the ability to regulate biological function.
Targets involved in a fewer pathways have greater likelihood to be successfully developed, while those associated with more human pathways increase the chance of undesirable interferences with other human processes
(Pharmacol Rev, 58: 259-279, 2006).
Biological Network Descriptors
of target is determined based on a human protein-protein interactions (PPI) network consisting of 9,309 proteins and 52,713 PPIs, which were with a high confidence score of ≥ 0.95 collected from STRING database.
The network properties of targets based on protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have been widely adopted for the assessment of target’s druggability. Proteins with high node degree tend to have a high impact on network function through multiple interactions, while proteins with high betweenness centrality are regarded to be central for communication in interaction networks and regulate the flow of signaling information
(Front Pharmacol, 9, 1245, 2018;
Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:134-142, 2017).
Human Similarity Proteins
Human Tissue Distribution
Human Pathway Affiliation
Biological Network Descriptors
|
|
|
There is no similarity protein (E value < 0.005) for this target
|
|
Note:
If a protein has TS (tissue specficity) scores at least in one tissue >= 2.5, this protein is called tissue-enriched (including tissue-enriched-but-not-specific and tissue-specific). In the plots, the vertical lines are at thresholds 2.5 and 4.
|
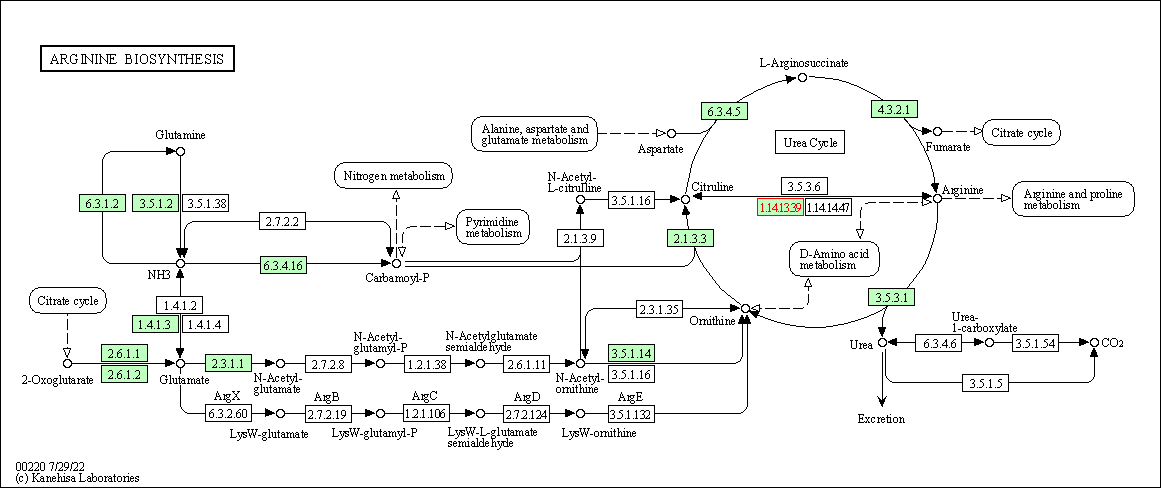

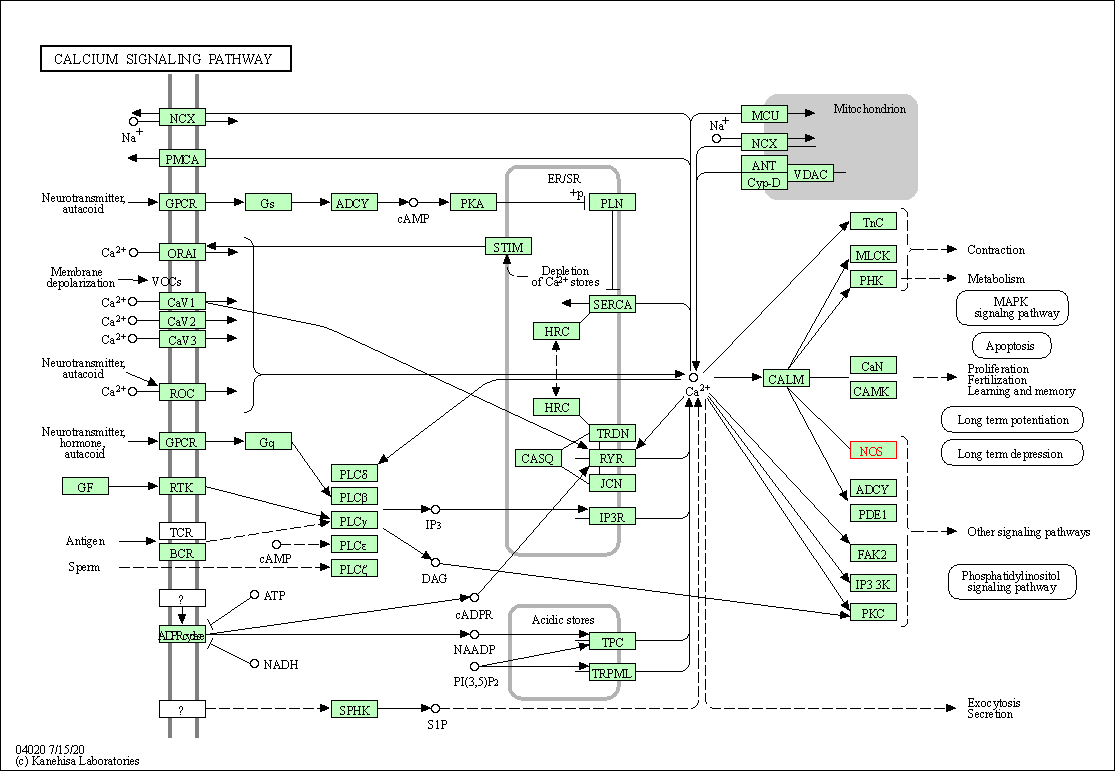
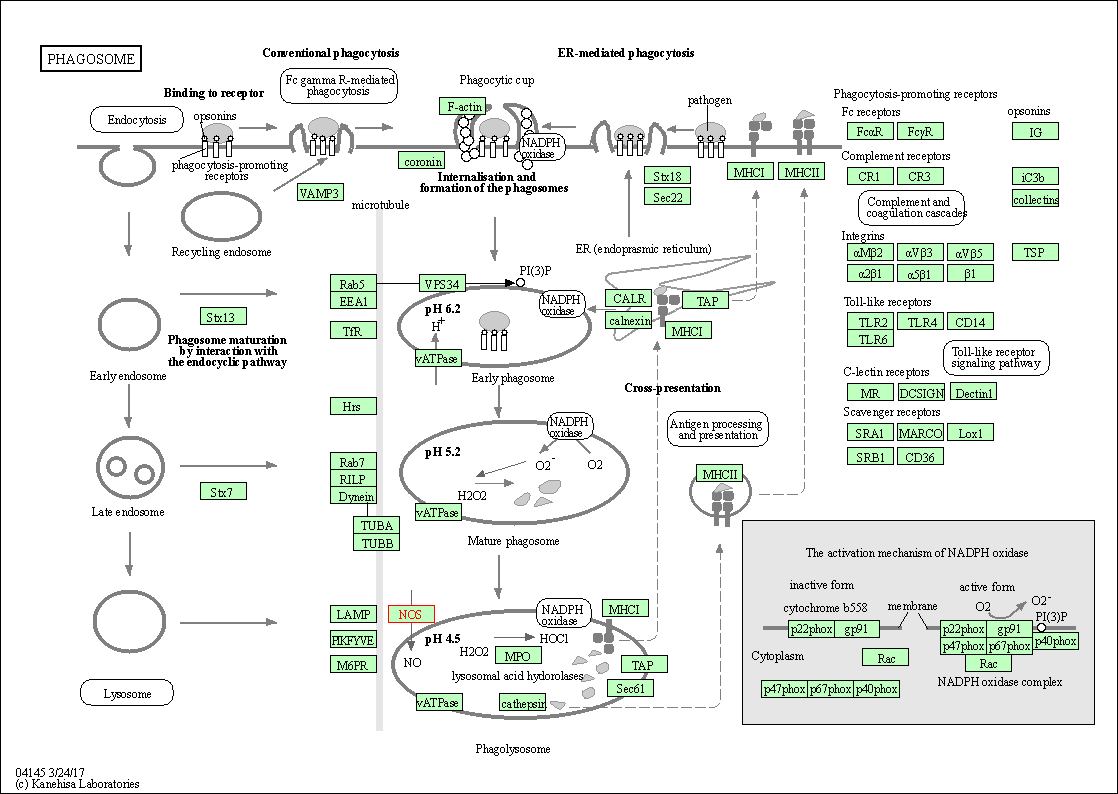
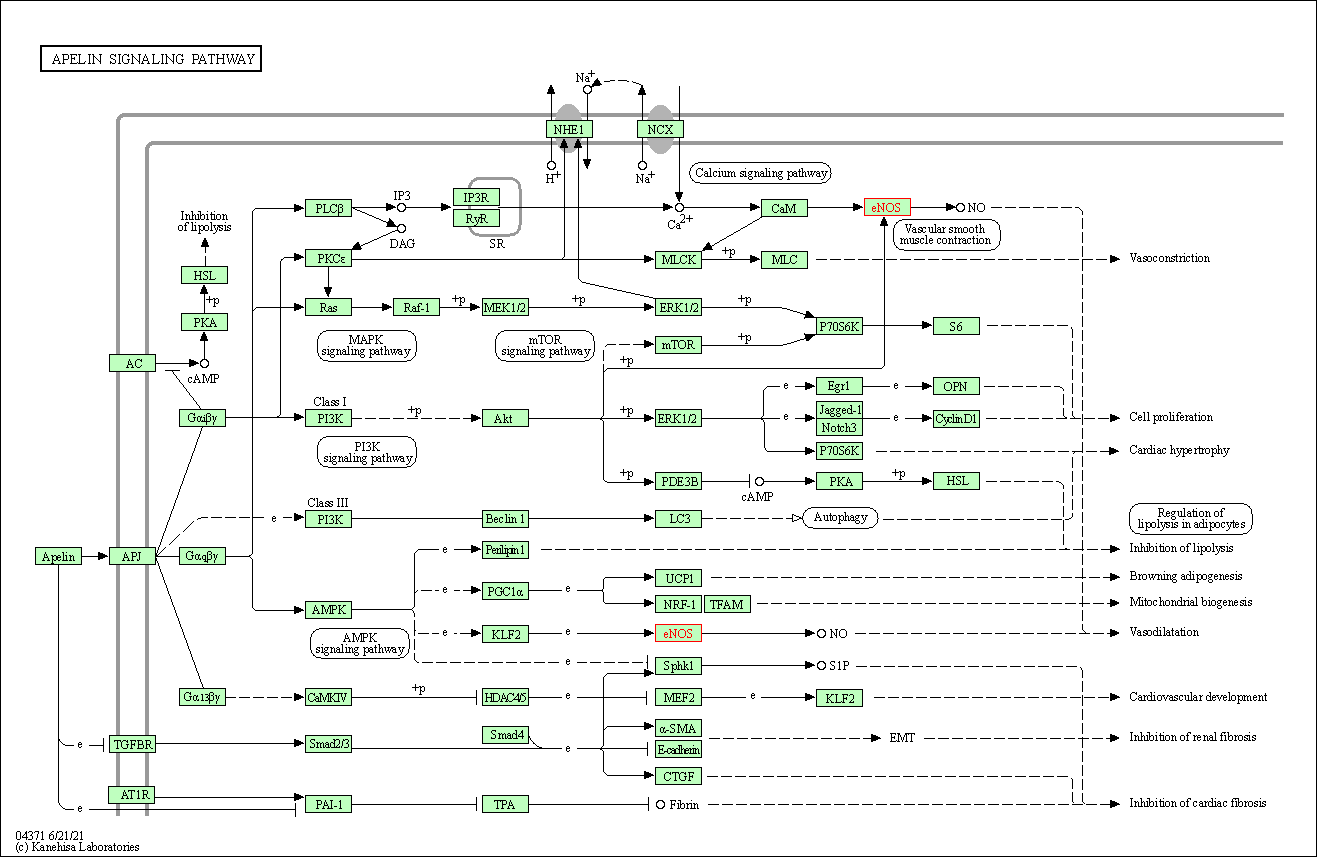
| KEGG Pathway | Pathway ID | Affiliated Target | Pathway Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arginine biosynthesis | hsa00220 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Amino acid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Arginine and proline metabolism | hsa00330 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Metabolism => Amino acid metabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Calcium signaling pathway | hsa04020 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Phagosome | hsa04145 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Cellular Processes => Transport and catabolism | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Apelin signaling pathway | hsa04371 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Environmental Information Processing => Signal transduction | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
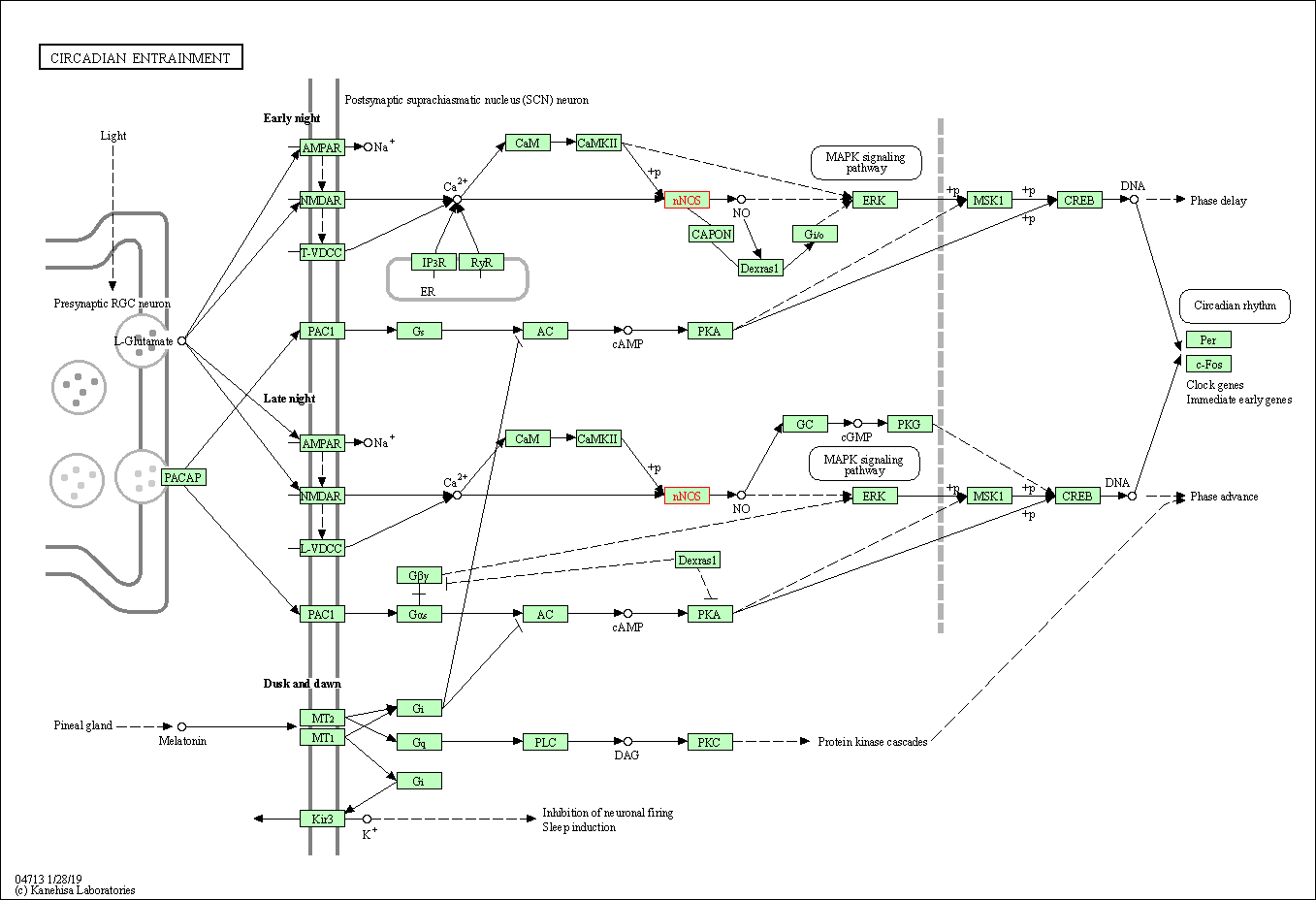
| Circadian entrainment | hsa04713 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Environmental adaptation | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
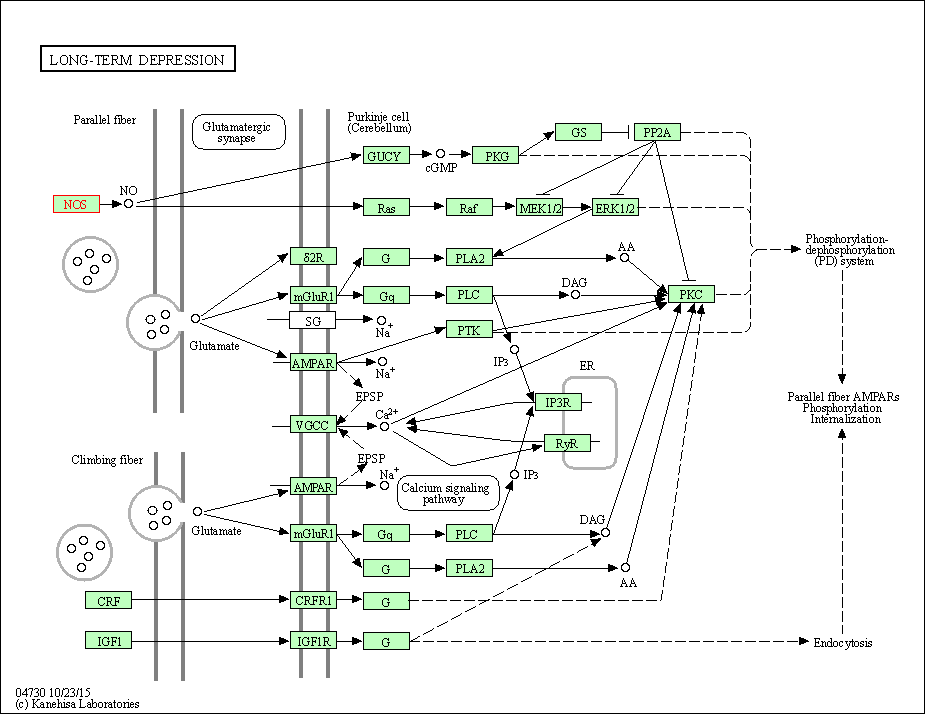
| Long-term depression | hsa04730 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Nervous system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
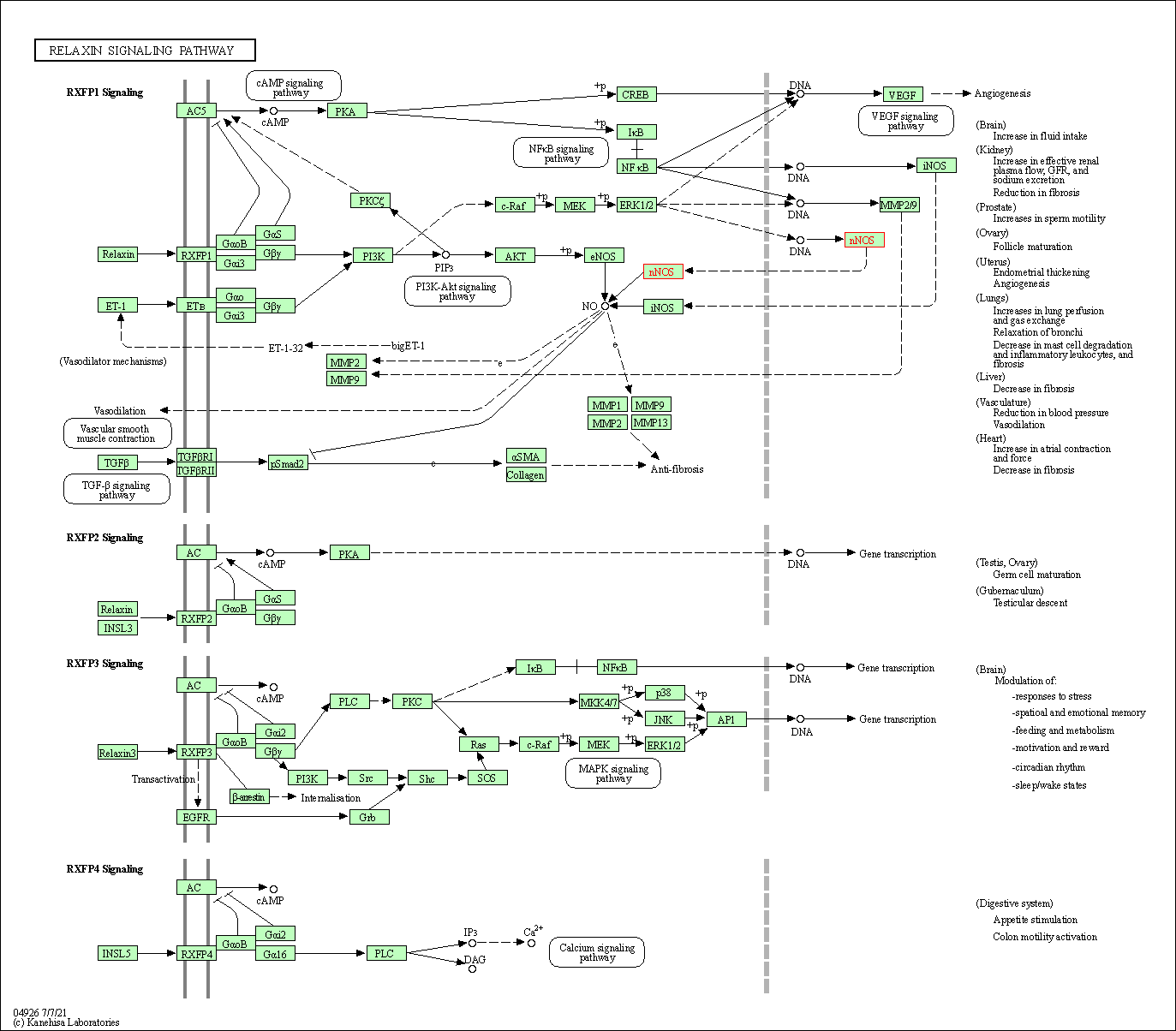
| Relaxin signaling pathway | hsa04926 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Endocrine system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
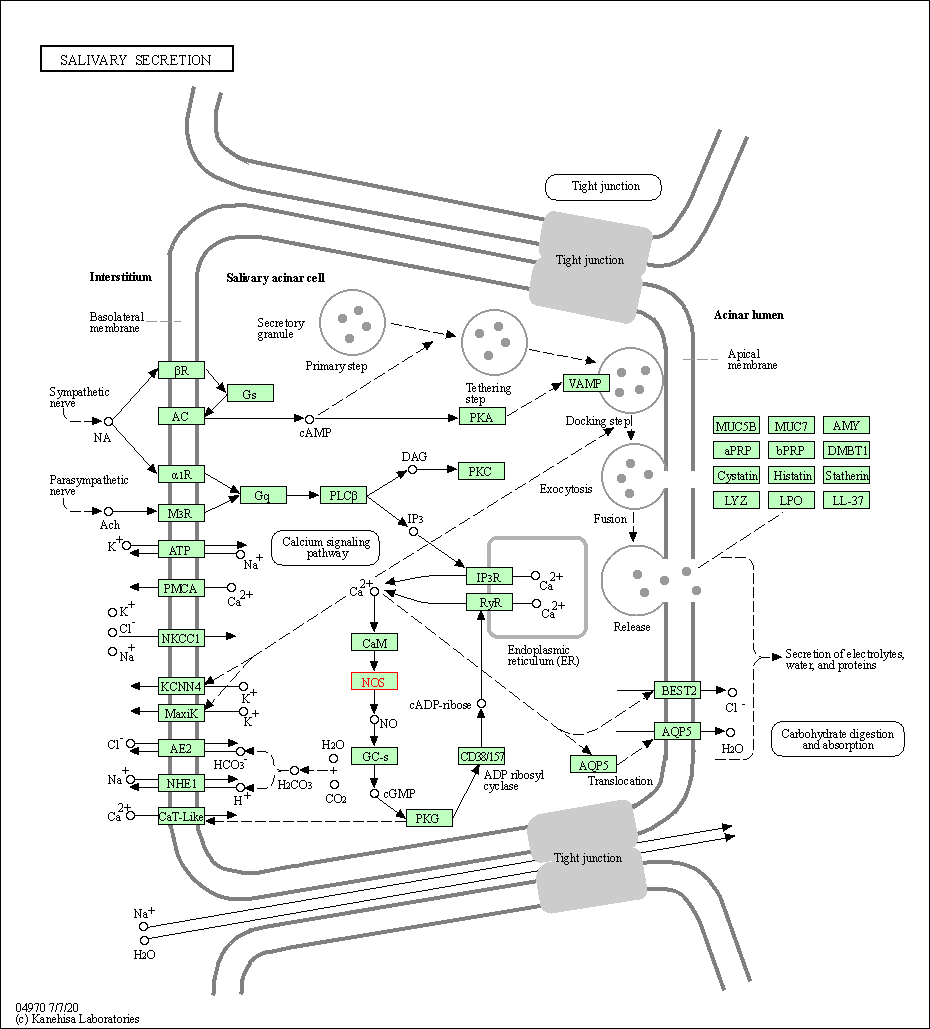
| Salivary secretion | hsa04970 | Affiliated Target |

|
| Class: Organismal Systems => Digestive system | Pathway Hierarchy | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Information of Affiliated Human Pathways | |||
| Degree | 15 | Degree centrality | 1.61E-03 | Betweenness centrality | 2.44E-03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness centrality | 2.31E-01 | Radiality | 1.41E+01 | Clustering coefficient | 9.52E-02 |
| Neighborhood connectivity | 2.31E+01 | Topological coefficient | 8.56E-02 | Eccentricity | 11 |
| Download | Click to Download the Full PPI Network of This Target | ||||
| Chemical Structure based Activity Landscape of Target | Top |
|---|---|
| Drug Property Profile of Target | Top | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Molecular Weight (mw) based Drug Clustering | (2) Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient (xlogp) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (3) Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) based Drug Clustering | (4) Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| (5) Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) based Drug Clustering | (6) Topological Polar Surface Area (polararea) based Drug Clustering | |
|
|
||
| "RO5" indicates the cutoff set by lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in GREEN denotes the no violation of any cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in PURPLE refers to the violation of only one cutoff in lipinski's rule of five; "D123AB" colored in BLACK represents the violation of more than one cutoffs in lipinski's rule of five | ||
| Target Poor or Non Binders | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Poor or Non Binders | ||||||
| Target Regulators | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target-regulating microRNAs | ||||||
| Target-interacting Proteins | ||||||
| Target Profiles in Patients | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Expression Profile (TEP) |
||||||
| Target Affiliated Biological Pathways | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BioCyc | [+] 1 BioCyc Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Citrulline-nitric oxide cycle | |||||
| KEGG Pathway | [+] 9 KEGG Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Arginine and proline metabolism | |||||
| 2 | Metabolic pathways | |||||
| 3 | Calcium signaling pathway | |||||
| 4 | Phagosome | |||||
| 5 | Circadian entrainment | |||||
| 6 | Long-term depression | |||||
| 7 | Salivary secretion | |||||
| 8 | Alzheimer's disease | |||||
| 9 | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) | |||||
| NetPath Pathway | [+] 1 NetPath Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | EGFR1 Signaling Pathway | |||||
| Panther Pathway | [+] 1 Panther Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | CCKR signaling map ST | |||||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | [+] 1 Pathwhiz Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Arginine and Proline Metabolism | |||||
| Reactome | [+] 2 Reactome Pathways | + | ||||
| 1 | ROS production in response to bacteria | |||||
| 2 | Nitric oxide stimulates guanylate cyclase | |||||
| WikiPathways | [+] 8 WikiPathways | + | ||||
| 1 | Monoamine Transport | |||||
| 2 | Myometrial Relaxation and Contraction Pathways | |||||
| 3 | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) | |||||
| 4 | Quercetin and Nf-kB/ AP-1 Induced Cell Apoptosis | |||||
| 5 | Spinal Cord Injury | |||||
| 6 | Alzheimers Disease | |||||
| 7 | Effects of Nitric Oxide | |||||
| 8 | Serotonin Transporter Activity | |||||
| Target-Related Models and Studies | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Validation | ||||||
| References | Top | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF 1 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01748877) Efficacy, Tolerability, and Safety of NXN-462 in Patients With Post-Herpetic Neuralgia. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 2 | ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00920686) Study of NXN 188 for the Treatment of Migraine With Aura. U.S. National Institutes of Health. | |||||
| REF 3 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | |||||
| REF 4 | Discovery of a series of aminopiperidines as novel iNOS inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008 Jan 1;18(1):336-43. | |||||
| REF 5 | Selective heterocyclic amidine inhibitors of human inducible nitric oxide synthase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2001 Oct 8;11(19):2651-3. | |||||
| REF 6 | N-Substituted acetamidines and 2-methylimidazole derivatives as selective inhibitors of neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Nov 15;20(22):6495-9. | |||||
| REF 7 | 4,5-Disubstituted-1,3-oxazolidin-2-imine derivatives: a new class of orally bioavailable nitric oxide synthase inhibitor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004 Jan 19;14(2):313-6. | |||||
| REF 8 | Synthesis of analogs of (1,4)-3- and 5-imino oxazepane, thiazepane, and diazepane as inhibitors of nitric oxide synthases. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004 Dec 6;14(23):5907-11. | |||||
| REF 9 | Bicyclic amidine inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase: discovery of perhydro-iminopyrindine and perhydro-iminoquinoline as potent, orally active inh... Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005 Apr 15;15(8):1997-2001. | |||||
| REF 10 | How many drug targets are there Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. | |||||
| REF 11 | 2-Iminopiperidine and other 2-iminoazaheterocycles as potent inhibitors of human nitric oxide synthase isoforms. J Med Chem. 1996 Feb 2;39(3):669-72. | |||||
| REF 12 | Novel 2-aminobenzothiazoles as selective neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 May 1;17(9):2540-4. | |||||
| REF 13 | The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1;28(1):235-42. | |||||
| REF 14 | L337H mutant of rat neuronal nitric oxide synthase resembles human neuronal nitric oxide synthase toward inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2009 Jul 23;52(14):4533-7. | |||||
| REF 15 | Anchored plasticity opens doors for selective inhibitor design in nitric oxide synthase. Nat Chem Biol. 2008 Nov;4(11):700-7. | |||||
| REF 16 | Evaluation of pyrrolidin-2-imines and 1,3-thiazolidin-2-imines as inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004 Sep 6;14(17):4539-44. | |||||
| REF 17 | Inhibitory effects of a series of 7-substituted-indazoles toward nitric oxide synthases: particular potency of 1H-indazole-7-carbonitrile. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Jun 1;16(11):5962-73. | |||||
| REF 18 | Fluorinated indazoles as novel selective inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase (NOS): synthesis and biological evaluation. Bioorg Med Chem. 2009 Sep 1;17(17):6180-7. | |||||
| REF 19 | 4-substituted indazoles as new inhibitors of neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 Jun 1;17(11):3177-80. | |||||
| REF 20 | Design and synthesis of 2-amino-4-methylpyridine analogues as inhibitors for inducible nitric oxide synthase and in vivo evaluation of [18F]6-(2-fl... J Med Chem. 2009 Apr 23;52(8):2443-53. | |||||
| REF 21 | Inhibition of neuronal nitric oxide synthase by 7-methoxyindazole and related substituted indazoles. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2001 May 7;11(9):1153-6. | |||||
| REF 22 | Eusynstyelamides A, B, and C, nNOS inhibitors, from the ascidian Eusynstyela latericius. J Nat Prod. 2009 Jun;72(6):1115-20. | |||||
| REF 23 | Structure-activity relationship of novel and known inhibitors of human dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase-1: alkenyl-amidines as new leads. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Dec 15;16(24):10205-9. | |||||
| REF 24 | Nitroaromatic amino acids as inhibitors of neuronal nitric oxide synthase. J Med Chem. 1998 Jul 2;41(14):2636-42. | |||||
| REF 25 | Crystal structure of nitric oxide synthase bound to nitro indazole reveals a novel inactivation mechanism. Biochemistry. 2001 Nov 13;40(45):13448-55. | |||||
| REF 26 | Evaluation of 3-substituted arginine analogs as selective inhibitors of human nitric oxide synthase isozymes. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005 Jun 2;15(11):2881-5. | |||||
| REF 27 | Structures of human constitutive nitric oxide synthases. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014 Oct;70(Pt 10):2667-74. | |||||
| REF 28 | Structural Basis for Isoform Selective Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibition by Thiophene-2-carboximidamides. Biochemistry. 2018 Nov 6;57(44):6319-6325. | |||||
If You Find Any Error in Data or Bug in Web Service, Please Kindly Report It to Dr. Zhou and Dr. Zhang.

